- Grissom Joint Air Reserve Base
Infobox Airport
name = Grissom Joint Air Reserve Base
nativename =Part of Air Force Reserve Command (AFRC)
Formerly Part of Strategic Air Command (SAC)
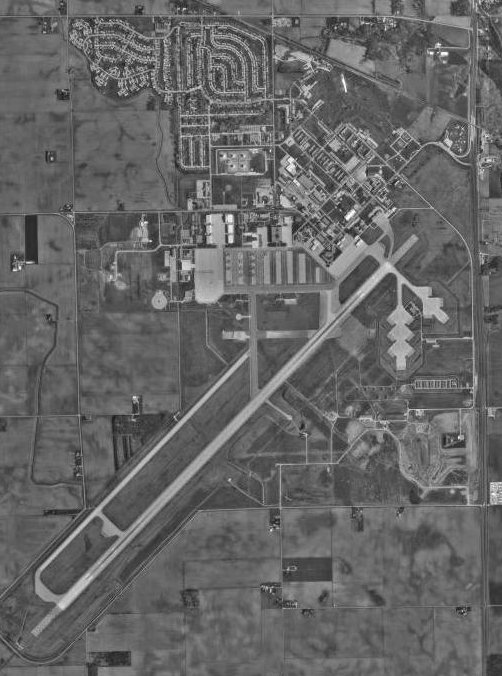

image-width = 300
caption = 24 March 1998
image2-width = 150
caption2 = Location of Grissom Air Reserve Base
IATA = GUS
ICAO = KGUS
FAA = GUS
type = Military
owner =United States Air Force
operator =
city-served =
location =Peru, Indiana
elevation-f = 812
elevation-m = 247
coordinates = coord|40|38|53|N|086|09|08|W|type:airport|display=inline
website = [http://www.grissom.afrc.af.mil/ www.grissom.afrc.af.mil]
r1-number = 5/23
r1-length-f = 12,501
r1-length-m = 3,810
r1-surface =Asphalt
footnotes = Source:Federal Aviation Administration FAA-airport|ID=GUS|use=PR|own=MA|site=05575.*A]Grissom Joint Air Reserve Base Airport codes|GUS|KGUS|GUS, formerly known as Grissom Air Force Base, is a military
airport located five miles (8 km) south of thecentral business district of Peru, a city in Miami County,Indiana ,United States . It is about sixty miles north ofIndianapolis and other nearby cities include Kokomo (15 miles south) andLogansport (13 miles west). [ [http://www.afreserve.com/bases.asp?id=55 Grissom Air Reserve Base] (page as US Air Force Reserve site)] The base is acensus-designated place (CDP), which had a population of 1,652 at the 2000 census.Geography
Grissom JARB is located at coor dms|40|40|15|N|86|9|17|W|city (40.670699, -86.154670).GR|1
According to the
United States Census Bureau , the CDP has a total area of 10.9km² (4.2 mi²), all land.Demographics
As of the
census GR|2 of 2000, there were 1,652 people, 581 households, and 431 families residing in the CDP. Thepopulation density was 151.9/km² (393.6/mi²). There were 1,091 housing units at an average density of 100.3/km² (259.9/mi²). The racial makeup of the CDP was 86.68% White, 7.63% African American, 0.48% Native American, 0.67% Asian, 0.06% Pacific Islander, 1.45% from other races, and 3.03% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 3.15% of the population.There were 581 households out of which 51.3% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 54.7% were married couples living together, 12.6% had a female householder with no husband present, and 25.8% were non-families. 19.1% of all households were made up of individuals and 1.4% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.84 and the average family size was 3.27.
In the CDP the population was spread out with 36.4% under the age of 18, 9.1% from 18 to 24, 39.6% from 25 to 44, 12.8% from 45 to 64, and 2.1% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 27 years. For every 100 females there were 100.7 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 100.8 males.
The median income for a household in the CDP was $45,000, and the median income for a family was $44,939. Males had a median income of $34,286 versus $21,447 for females. The
per capita income for the CDP was $15,869. About 8.6% of families and 8.9% of the population were below thepoverty line , including 13.5% of those under age 18 and none of those age 65 or over.History
Formerly called Bunker Hill Air Force Base, it was renamed after the
astronaut , Indiana native, and Purdue University graduate, Lieutenant ColonelVirgil I. “Gus” Grissom , USAF, who was killed in a spacecraft fire on Pad 34 atCape Canaveral AFS, Florida in January 1967 during a pre-launch prep for the Apollo I mission he was slated to command. The base was officially renamed on May 12, 1968. TheAir Force Reserve began being a part of the Grissom personnel complement in the early 1970s with the relocation of the434th Special Operations Wing and theirA-37 Dragonfly aircraft to the base.The 931st Air Refueling Group arrived on the base in 1978 and were the second group of Air Force Reservists that would be stationed on the base. The base also served as the home of one active duty wing and two reserve wings, utilizing 60
KC-135 Stratotanker s and 18A-10 Thunderbolt II fighter planes.Grissom Joint Air Reserve Base accounts for one-fourth of the Air Force Reserve Command bases in the
United States of America . The base started up onJuly 1 ,1942 , as Naval Air Station Bunker Hill for the United States Navy and it was used to train Navy, Marine and Coast Guard pilots for four years. Few people actually know thatTed Williams of baseball fame was an alumnus of the institution.The base was closed and allowed the area to be used for farming again after
World War II . TheKorean War saw the reopening of the base by the Air Force onJune 22 ,1954 , as Bunker Hill Air Force Base. The base served as the home to the4433d Air Base Squadron , the323d Fighter-Bomber Wing and saw the addition of the319th Fighter-Interceptor Squadron in 1955 while under the orders of theTactical Air Command . Between 1955 and 1960, the 319th FIS operated theF-89 Scorpion andF-94 Starfire . Starting in 1960, the 319th was equiped with theF-106 Delta Dart .Strategic Air Command (SAC) assumed operational control of Bunker Hill onSeptember 1 ,1957 , which led to the 305th Bomb Wing to be stationed on the base, flying theB-47 Stratojet .KC-135 Stratotanker s began to be stationed on the base in the same year, and two years later saw the arrival of theB-58 Hustler as they began replacing the B-47s.Changes in the U.S. Air Force led to the deactivation of one reserve unit, and one active unit in 1994. Because of this, the base was reassigned as an
Air Force Reserve Command (AFRC) facility. The principal AFRC unit that is still based at Grissom is the434th Air Refueling Wing (434 ARW), anAir Mobility Command (AMC)-gained AFRC unit operating theKC-135R Stratotanker air refueling aircraft. Units from other branches of the U.S. armed forces are also based at Grissom. Since the 1970s, theArmy Reserve has had a presence on Grissom and the Marines and Navy both addedMarine Corps Reserve andNavy Reserve units to the base in 2001 and 2002, respectively.The base also serves its duty to the local community, not only its military duty. It has a combined workforce consisting of both military personnel and civilians and is currently the largest employer in Miami County and third largest employer in north central Indiana. It has an economic impact of 75 million dollars per year and is also involved heavily in community activities. One such program is the Marine Corps Reserve's "
Toys for Tots " conducted annually in November and December. The base has also been designated as a "Tree City" by theNational Arbor Day Foundation .In 2003, the
Air Force Reserve Command changed the name of Grissom Air Reserve Base to that of Grissom Joint Air Reserve Base.In 2005, in another effort to downsize the base, Navy Reserve units stationed there were transferred to the Navy Operational Support Center/
Heslar Naval Armory in Indianapolis.In 1975, the main active duty USAF wing stationed at Grissom AFB was the 305th Air Refueling Wing operating the
KC-135 Stratotanker . This unit was later deactivated and then reactivated in 1994 as the305th Air Mobility Wing atMcGuire AFB , New Jersey, where it currently operates theKC-10 A Extender and the C-17A Globemaster III.In March 2008, Grissom Air Reserve Base will open to civil operations. Montgomery Aviation of Zionsville, IN, will manage the day-to-day civil operations at Grissom JARB. Under a five year contract with the Miami County Economic Development Authority, Montgomery Aviation will provide maintenance, fuel, and other services. Apparently this is the first step in making Grissom a joint civil-military regional airport.
ee also
*
Grissom Air Museum [ [http://www.grissomairmuseum.com/home.html Grissom Air Museum] Home Site]
*Central Air Defense Force (Air Defense Command)References
External links
* [http://www.grissom.afrc.af.mil/ Grissom Air Reserve Base] (official site)
*FAA-diagram|00470
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
