- James McCune Smith
-
James McCune Smith 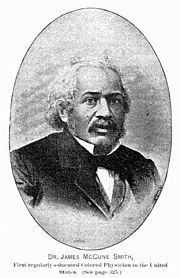
Inscription: "First regularly-educated Colored Physician in the United States."Born 28 April 1813
New York City, New York, United StatesDied 17 November 1865 (aged 52)
Long Island, New York, United StatesFields Internal medicine Institutions Free Negro Orphan Asylum
Wilberforce CollegeAlma mater African Free School
Glasgow UniversityJames McCune Smith (April 18, 1813 – November 17, 1865) was an American physician, apothecary, abolitionist, and author. He is the first African-American to earn a medical degree, and the first to run a pharmacy in the United States. Smith wrote forcefully in refutation of the common misconceptions about race, intelligence, medicine, and society in general. His friends and colleagues in this movement were often famous and consisted of many noted abolitionists, including Frederick Douglass.
Contents
Biography
Early years
Smith was born to a self-emancipated mother and father in New York City, New York.[1] He attended the African Free School, where he is described as an "exceptionally bright student".[2] In the course of his studies, he was tutored by Rev. Peter Williams, Jr., an Episcopalian minister at St. Joseph's Church in New York City, and who was also a graduate of the African Free School. Upon graduation, Smith tried to attend several American colleges, but he was denied admission by each of them due to racial discrimination.
Williams suggested that Smith attend the University of Glasgow in Scotland.[3] Williams helped Smith raise money for his trip to Scotland and his subsequent education there. Smith was accepted to the university, where he later graduated at the top of his class. He obtained a bachelor's degree in 1835, a master's degree in 1836, and a medical degree in 1837. He then traveled from Glasgow to Paris to complete a brief internship.[4]Career
Medicine
Upon his return to New York City in 1837, Smith became the United States' first professionally trained African-American physician. His practice spanned 25 years. In 1846, he was appointed the only doctor of the Free Negro Orphan Asylum, where he worked for more than twenty years.[4] He opened what has been called the first black pharmacy in the United States, which was located on West Broadway.[5]
Abolitionist Movement
While in Scotland, Smith was a member of the Glasgow Emancipation Society.[3] When he returned to New York, he became a member of the American Anti-Slavery Society. In 1850, he was one of the key organizers of New York's resistance to the Fugitive Slave Act as a member of the Committee of Thirteen. During the mid 1850s, he helped Frederick Douglass to establish the National Council of Colored People.[2]
Essays and writings
Smith was a prolific writer and essayist. Among other works, he wrote the introduction to Fredrick Douglass' second autobiography, My Bondage and My Freedom (1855), which constituted an important move away from seeking approval and authentication from white abolitionists in African-American accounts of slavery. In this introduction, he writes:
"...the worst of our institutions, in its worst aspect, cannot keep down energy, truthfulness, and earnest struggle for the right."[5]
Smith also wrote from the view of a trained doctor. The physician and abolitionist wrote an essay that refuted the theories of race in Thomas Jefferson's "Notes on the State of Virginia".[6] He also wrote essays that rejected phrenology and homeopathy.
At Glasgow, Smith was trained in the then-new science of statistics. He used this training to refute the arguments of slave owners, who claimed that blacks were inferior and that slaves were better off than free blacks.[7] He wrote an essay critiquing the U.S. Census of 1840 on racial and statistical grounds.
Personal life & Death
Smith was appointed professor of anthropology at Wilberforce College, Ohio, the oldest African-American college in the United States, but Smith was too ill to take the position.[8] Smith died November 17, 1865 of congestive heart failure in Long Island, New York two years later at the age of 52, just nineteen days before the adoption of the Thirteenth Amendment to the Constitution of the United States, abolishing slavery throughout the country.[9] Smith was survived by his widow, Malvina, and five children.[10]
After Smith's death, his descendants passed for white, and later generations didn't know he was their ancestor until Greta Blau, Smith's great-great-great-granddaughter, took a course on the history of blacks in New York and realized he was her ancestor. Smith would lie buried in an unmarked grave at Cypress Hills Cemetery, in Brooklyn, New York for 145 years, until his descendants ceremoniously dedicated a tombstone in September, 2010.[11]
Publications
- Smith, James McCune (1841). A Lecture on the Haytien Revolutions. New-York: D. Fanshaw. OCLC 16788188.
- Smith, James McCune (1843). The Destiny of the People of Color. New York: s.n.. OCLC 27872624.
- Smith, James McCune (1846). A Dissertation on the Influence of Climate on Longevity. New York: Office of Merchants' Magazine. OCLC 34227767.
- Smith, James McCune (1860). Ira Aldridge. New York: Arno Press; The New York Times. OCLC 35129946.
- Smith, James McCune; Stauffer, John ed. (2006). The Works of James McCune Smith: Black Intellectual and Abolitionist. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0195309618.
References
- ^ "James McCune Smith". New York Divided. http://www.nydivided.org/popup/People/JamesMcCuneSmith.php. Retrieved 2008-11-18.
- ^ a b "African Free School Bios: James McCune Smith". NewYorkHistory.org. https://www.nyhistory.org/web/afs/bios/james-mccune-smith.html. Retrieved 2006-12-21.
- ^ a b Douglas Blane. "Created Equal". University of Glasgow. http://www.gla.ac.uk:443/avenue/32/na2.html. Retrieved 2006-12-10.[dead link]
- ^ a b work=Biography.com "James McCune Smith Biography (1813–65)". 2006. Archived from the original on 2007-09-30. http://web.archive.org/web/20070930030442/http://www.biography.com/search/article.do?id=9486894 work=Biography.com. Retrieved 2008-11-18.
- ^ a b "African American Medical Pioneers: James McCune Smith". PBS.org. http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/amex/partners/early/e_pioneers_smith.html. Retrieved 2006-12-10.
- ^ T.M. Morgan (Jul 2003). "The education and medical practice of Dr. James McCune Smith (1813-1865), first black American to hold a medical degree.". J Natl Med Assoc. 95 (7): 603–14. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&list_uids=12911258&dopt=Abstract. Free full text
- ^ New York Divided, Slavery and the Civil War. Exhibit at the New York Historical Society.
- ^ "James McCune Smith.". Biographies. Answers.com. n.d.. http://www.answers.com/topic/james-mccune-smith. Retrieved 2008-11-18.
- ^ "James McCune Smith". American Abolitionst Biographies. http://americanabolitionist.liberalarts.iupui.edu/smithjm.htm. Retrieved 2006-12-10.
- ^ "James McCune Smith - His Life and Times". http://www.jamesmccunesmith.com/. Retrieved 2009-07-28.
- ^ Descendants of 1st black US doctor mark NYC grave By KAREN MATTHEWS, Washington Post, September 26, 2010
External links
- James McCune Smith at the African American Registry
- "James M. Smith Community School". http://schools.nyc.gov/SchoolPortals/05/M200/default.htm.
- "The African Free School Collection". at the New-York Historical Society. https://www.nyhistory.org/web/afs/.
- Louverture Project: "Toussaint Louverture and the Haitian Revolutions". http://thelouvertureproject.org/index.php?title=Toussaint_L%27Ouverture_and_the_Haytian_Revolutions. - 1841 Speech by James McCune Smith
- The education and medical practice of Dr. James McCune Smith (1813-1865), first black American to hold a medical degree. J Natl Med Assoc. 2003 Jul;95(7):603-14. Smith's medical education and influence.
Categories:- 1813 births
- 1865 deaths
- Alumni of the University of Glasgow
- American abolitionists
- American physicians
- People from New York
- Wilberforce University
- African-American physicians
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
