- Cyanophycin
-
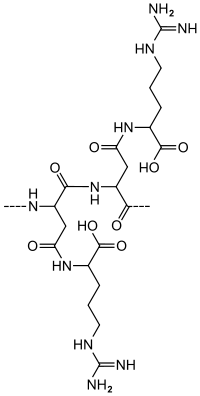
Cyanophycin, or multi-L-arginyl-poly (L-aspartic acid), is a non-protein, non-ribosomally produced amino acid polymer composed of an aspartic acid backbone and arginine side groups.
Cyanophycin was first detected in 1887 by an Italian scientist (Borzi, 1887) and can be found in most cyanobacteria and a few heterotrophic bacteria such as Acinetobacter sp.[1]. Cyanophycin is largely insoluble under physiological conditions and is accumulated in the form of granules in the cytoplasm during phosphate or sulfur starvation, generally in the early and mid-stationary phase. It is used as a nitrogen- and possibly carbon-storage compound and also serves as a dynamic buffer for fixed nitrogen in cyanobacterial heterocysts. Nitrogen and carbon are mobilized from cyanophycin by intracellular cyanophycinase in the form of aspartate-arginine dipeptides.
Cyanophycin is synthesized from arginine and aspartate in an ATP-dependent reaction catalyzed by a single enzyme, cyanophycin synthetase [2]. Cyanophycin is of potential interest to biotechnology as a source of polyaspartic acid. Due to its unusual polyamphoteric character, cyanophycin is soluble in water under acidic (0.1 M HCl) and alkali conditions. Heterologous expression of cyanophycin synthetase allows production of cyanophycin in a number of biotechnologically relevant bacteria such as Escherichia coli and Corynebacterium glutamicum [3].
References
- ^ Krehenbrink, M.; Oppermann-Sanio, FB; Steinbüchel, A (2002). "Evaluation of non-cyanobacterial genome sequences for occurrence of genes encoding proteins homologous to cyanophycin synthetase and cloning of an active cyanophycin synthetase from Acinetobacter sp. strain DSM 587". Arch Microbiol 177 (5): 371–380. doi:10.1007/s00203-001-0396-9. PMID 11976746.
- ^ Ziegler, K.; Diener, A; Herpin, C; Richter, R; Deutzmann, R; Lockau, W (1998). "Molecular characterization of cyanophycin synthetase, the enzyme catalyzing the biosynthesis of the cyanobacterial reserve material multi-L-arginyl-poly-L-aspartate (cyanophycin)". Eur J Biochem 254 (1): 154–159. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1327.1998.2540154.x. PMID 9652408.
- ^ Oppermann-Sanio, F.; Steinbüchel, A. (2002). "Occurrence, functions and biosynthesis of polyamides in microorganisms and biotechnological production". Naturwissenschaften 89 (1): 11–22. doi:10.1007/s00114-001-0280-0. PMID 12008968.
Categories:- Peptides
- Biochemistry stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.