- Acyloin
-
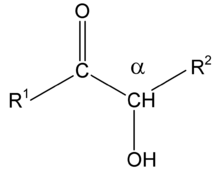
Acyloins (also referred to as ketols) are a class of organic compounds in organic chemistry sharing a common functional group consisting of a hydroxyl group placed on the α-position of a carbonyl group.
Contents
Nomenclature
Common types of ketols include: Alpha-ketols have the hydroxyl group adjacent to the keto group. Beta-ketols have the hydroxyl group at the second carbon from the keto group. Gamma-ketols have the hydroxyl group at the third carbon from the keto group.
Synthesis of acyloins
Classic organic reactions exist for the synthesis of acyloins.
- The acyloin condensation is a reductive coupling of esters
- The benzoin condensation is condensation reaction between aldehydes catalyzed by a nucleophile
- Oxidation of carbonyls is possible with molecular oxygen but not selective
- Better alternative is oxidation of corresponding silyl enol ethers with mCPBA in the Rubottom oxidation
- MoOPH oxidation of carbonyls is a system with molybdenum peroxide, pyridine and hexamethylphosphoramide.
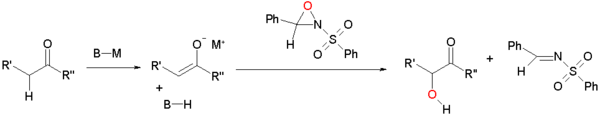
Enolate oxidation by sulfonyloxaziridines
Enolates can be oxidized by sulfonyloxaziridines [1][2]. The enolate reacts by nucleophilic displacement at the electron deficient oxygen of the oxaziridine ring.
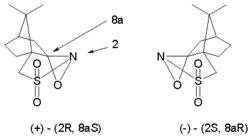
This reaction type is extended to asymmetric synthesis by the use of chiral oxaziridines derived from camphor (camphorsulfonyl oxaziridine). Each isomer gives exclusive access to one of the two possible enantiomers. This modification is applied in the Holton Taxol total synthesis.
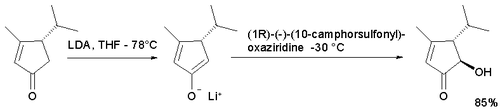
In the enolate oxidation of the cyclopentaenone below [3] with either camphor enantiomer the trans isomer is obtained because access for the hydroxyl group in the cis position is limited. The use of the standard oxaziridine did not result in an acyloin.
Reactions of acyloins
- Reduction of acyloins give diols.
- Oxidation of acyloins give diones.
- Some acyloins rearrange with positions swapped under the influence of base in the Lobry–de Bruyn–van Ekenstein transformation
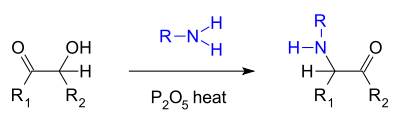
- A similar reaction is the so-called Voight amination [4] where an acyloin reacts with a primary amine and phosphorus pentoxide to an alpha-keto amine [5]:
- Indole synthesis[6], compare Bischler-Möhlau
References
- ^ Synthesis of .alpha.-hydroxycarbonyl compounds (acyloins): direct oxidation of enolates using 2 sulfonyloxaziridines Franklin A. Davis, Lal C. Vishwakarma, Joanne G. Billmers, John Finn J. Org. Chem.; 1984; 49(17); 3241-3243. Abstract
- ^ Asymmetric Oxidation of Ester and Amide Enolates Using New (Camphorylsulfony1)oxaziridines Davis, F. A.; Haque, M. S.; Ulatowski, T. G.; Towson, J. C. J. Org. Chem. 1986, 51, 2402. Abstract
- ^ An Electrochemical Approach to the Guanacastepenes Chambers C. Hughes, Aubry K. Miller, and Dirk Trauner ORGANIC LETTERS 2005 Vol. 7, No. 16 3425-3428 Article
- ^ E. von Meyer, Karl Voigt (1886). "Ueber die Einwirkung von primären aromatischen Aminen auf Benzoïn". Journal für Praktische Chemie 34 (1): 1–27. doi:10.1002/prac.18860340101.
- ^ Amines: Synthesis, Properties and Applications Stephen A. Lawrence 2004 Cambridge University Press ISBN 0-521-78284-8
- ^ Roth, Lepke (1971): Archiv der Pharmazie, 159
Categories:- Functional groups
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.