- North Baddesley
-
Coordinates: 50°58′40″N 1°26′15″W / 50.9779°N 1.4375°W
North Baddesley 
St John the Baptist, North Baddesley
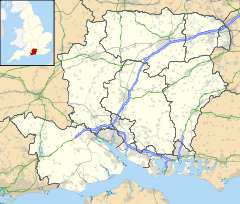
 North Baddesley shown within Hampshire
North Baddesley shown within HampshirePopulation 12,878 [1] OS grid reference SU395199 Parish North Baddesley District Test Valley Shire county Hampshire Region South East Country England Sovereign state United Kingdom Post town SOUTHAMPTON Postcode district SO52 Dialling code 023 Police Hampshire Fire Hampshire Ambulance South Central EU Parliament South East England UK Parliament Romsey and Southampton North List of places: UK • England • Hampshire North Baddesley is a large village and civil parish in Hampshire, England. It is situated 3 miles (4.5 km) east of the town of Romsey and 6 miles (10 km) north of Southampton. It occupies an area of approximately 9.15 square kilometres, and is home to a population of just over 10,000 people.[1] It is located in the Test Valley; a river famous for trout fishing. North Baddesley is one of the largest villages in the South of England.
Administratively it is represented by the two-tier system of councils with responsibilities divided between Hampshire County Council and Test Valley Borough Council.
North Baddesley is twinned with Authie and Carpiquet, France and was home to Keith Harris and Orville the Duck.
Contents
Location
Nearby towns and cities: Romsey, Southampton, Eastleigh, Winchester
Nearby villages: Rownhams, Chandler's Ford, Ampfield, Chilworth, Nursling
Development
North Baddesley, although still a village, has many of the features, though few of the facilities, of a small town. In 1921 the population was fewer than 400, but by the outbreak of war in 1939 it was almost 1,000. Its proximity to Southampton and Eastleigh gave rise to considerable pressure for development after the war and large estates of modern houses were built. The most recent of the parish's developments is Knights Grove.
There is a Community Centre on Fleming Avenue.
Valley Park, which straddles the borough boundary with Eastleigh is now a community of 3000 dwellings, with a population of 7,500. Built from 1981 onwards, it was part of the parish of North Baddesley, but after much debate, it formed its own parish in 2006.
The old village lies to the north, and the manor house incorporates part of the Preceptory of the Knights Hospitaller, which was the Hampshire headquarters of the Order after 1365. Reminders of this are found in the local place-names of Zionshill and Knightwood. The parish church is also of mediaeval foundation, and is dedicated to St. John the Baptist, the patron saint of the Knights Hospitaller
History
The Domesday Book of 1086 shows North Baddesley or Badeslei as it was then called (Ley meaning a wood, and Baed or Baeddi being a proper name, i.e. Baeddi's Wood) as a small hamlet with a church, four farms, seven small holdings and a wood sufficient for ten hogs valued at 60 shillings (£3). The most notable event in North Baddesley's past was the arrival in the 12th Century of the Knights of St John of Jerusalem, later known as the Knights Hospitaller, and their acquisition of the overlordship rights in the late 14th century. However, long before this, half the manor had already been transferred to the Knights as early as 1304, when the little church of All Saints was re-dedicated to St John the Baptist, the patron Saint of Hospitallers. The Church was almost opposite the Hospitallers preceptory, on the site now occupied by the present Manor House. The Black Death of 1348-49 resulted in the transfer of the Hospitallers Hampshire headquarters from Godsfield near New Alresford to North Baddesley.
The Knights Hospitaller were a medieval order dedicated to the care and protection of pilgrims, and tending the sick and infirm, including the Crusaders in their quest to return the Holy Land to the Christian world. A Europe-wide order, they became extremely large and wealthy landowners thanks to the patronage of rich and noble families.
The Knights Hospitaller were in Baddesley for about 400 years until 1541. Following the Dissolution of the Monasteries they were at odds with Henry VIII, as they still recognised the supremacy of Rome and were themselves suppressed. Their possessions were made forfeit to the crown.
After the departure of the Hospitallers the Manor changed hands several times. The Civil War of 1642-46 came and went without leaving any physical scars and there is no record of any significant happenings in Baddesley during this time. However, the then Lord of the Manor, Samuel Dunch was a strong parliamentarian. He was later related to the Cromwell family through the marriage of his son John in 1650 to Ann Major of Hursley Park, whose sister Dorothy was married to Richard Cromwell.
In 1767 the manor was bought by Thomas Dummer of Cranbury Park, Otterbourne, from whom it devolved to the Chamberlayne family. The Joyce family bought the Manor house from the Chamberlaynes in 1981 and have lived there ever since.
Baddesley gradually expanded down Nutburn Road and in 1876 the first buildings south of the crossroads were erected. The school opened to serve both Baddesley and Chilworth, with Mr Dibble the headmaster living in the adjoining school house.
The modern village (south of Botley Road), was built on open farmland and common-land belonging formerly to the Willis Fleming family, who were major local landowners.[2] This is reflected in the names of local roads, Willis Avenue and Fleming Avenue.
The arrival of the 20th century was to change Baddesley forever, propelling it from a small hamlet with a population of 393 in 1901 to that of the largest village in the Test Valley. In 2001, 100 years later, it had a population in excess of 10,000, akin to that of a small town, consisting predominantly of 1960s / 70s style small housing. The most recent development is a new estate off Rownhams Road which was completed in 2008.
Baddesley Common
Baddesley Common and Emer Bog are areas of New Forest style grassland heath and bog. There is a wide variety of the plants which thrive in this environment and it is a Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI).
Marsh Gentian, Cross-leaved Heath, Lousewort, Heath Spotted orchid and Petty Whin are some specialist plants that occur in the wet heath areas.
White Admiral and Purple Emperor butterflies glide through the woods and dragonflies chase over the bog and ponds. Several hundred different species of moth have been recorded.
There is also a boardwalk trail towards the back of the bog, which can be strolled in order to observe the woodland wildlife.
St John's Church is a mainly 17th century building set on a hill-brow with a view over countryside. Baddesley Manor, opposite the church, is an 18th century building as the successor of the medieval Preceptory of the Knights Hospitaller. The village was a stronghold of the Knights of St John.
Geocaching
North Baddesley has a collection of Geocaches located in and around the area, Geocaching is an entertaining adventure game for gps users. The following caches are located here:
Hoe Lane by penguinhunters
Baddesley Common by Krazy Kats
Emer Bog by harryatkinsReferences
- ^ a b "Parish Headcounts, Area: North Baddesley CP (2001, including Valley Park)". Neighbourhood Statistics. Office for National Statistics. http://www.neighbourhood.statistics.gov.uk/dissemination/LeadTableView.do?a=3&b=795169&c=North+Baddesley&d=16&e=15&g=452858&i=1001x1003x1004&m=0&r=0&s=1204114409812&enc=1&dsFamilyId=779. Retrieved 2008-02-27.
- ^ "The Fleming Estate in Hampshire & the Isle of Wight". Willis Fleming Historical Trust. http://www.willisfleming.org.uk/estates/hants_and_iow/. Retrieved 2009-07-01.
- "BaddesleyNET" by Matthew Langridge & Steve Cole, BaddesleyNET, 1996–2005, retrieved December 1, 2005
- The Changing Face of North Baddesley, Una Lonergan & Beryl Green, 1996
External links
- North Baddesley Cricket Club
- Official North Baddesley website Now Defunct
- St. John's Church website
- North Baddesley history
- A new N.Baddesley site
- Streetmap.co.uk map of North Badddesley
Towns, villages and hamlets in the Test Valley District of Hampshire, England  Abbotswood · Abbotts Ann · Abbotts Ann Down · Ampfield · Amport · Andover · Andover Down · Anna Valley · Appleshaw · Ashfield · Awbridge · Barton Stacey · Bossington · Braishfield · Broughton · Charlton · Chattis Hill · Chilbolton · Chilbolton Down · Clanville · Crampmoor · Dunbridge · Dunley · East Anton · Embley · East Cholderton · East Dean · East Tytherley · Faberstown · Faccombe · Finkley · Finkley Down · Forton · Fox Amport · Foxcotte · Freefolk · Fullerton · Fyfield · Goodworth Clatford · Gore End · Grateley · Hatherden · Hillyfields · Houghton · Houghton Down · Hurstbourne Tarrant · Kimbridge · Kimpton · King's Somborne · Knights Enham · Leckford · Lickenholt · Little Down · Little Hatherden · Little Somborne · Lockerley · Longparish · Longstock · Longstock Park · Lower Wyke · Marsh Court · Michelmersh · Middle Wallop · Monxton · Mottisfont · Nether Wallop · Newton Stacey · North Baddesley · North Houghton · Nursling · Over Wallop · Ower · Penton Corner · Penton Grafton · Picket Piece · Picket Twenty · Pill Heath · Plaitford · Quarley · Ragged Appleshaw · Ramridge Park · Red Post Bridge · Red Rice · Redenham · Romsey · Sherfield English · Shipton Bellinger · Shootash · Smannell · South Harewood · Stockbridge · Tangley · Thruxton · Up Somborne · Upper Clatford · Upper Enham · Vernhams Dean · Vernham Street · Wellow · West Tytherley · Wherwell · Wherwell Wood · WildhernCategories:
Abbotswood · Abbotts Ann · Abbotts Ann Down · Ampfield · Amport · Andover · Andover Down · Anna Valley · Appleshaw · Ashfield · Awbridge · Barton Stacey · Bossington · Braishfield · Broughton · Charlton · Chattis Hill · Chilbolton · Chilbolton Down · Clanville · Crampmoor · Dunbridge · Dunley · East Anton · Embley · East Cholderton · East Dean · East Tytherley · Faberstown · Faccombe · Finkley · Finkley Down · Forton · Fox Amport · Foxcotte · Freefolk · Fullerton · Fyfield · Goodworth Clatford · Gore End · Grateley · Hatherden · Hillyfields · Houghton · Houghton Down · Hurstbourne Tarrant · Kimbridge · Kimpton · King's Somborne · Knights Enham · Leckford · Lickenholt · Little Down · Little Hatherden · Little Somborne · Lockerley · Longparish · Longstock · Longstock Park · Lower Wyke · Marsh Court · Michelmersh · Middle Wallop · Monxton · Mottisfont · Nether Wallop · Newton Stacey · North Baddesley · North Houghton · Nursling · Over Wallop · Ower · Penton Corner · Penton Grafton · Picket Piece · Picket Twenty · Pill Heath · Plaitford · Quarley · Ragged Appleshaw · Ramridge Park · Red Post Bridge · Red Rice · Redenham · Romsey · Sherfield English · Shipton Bellinger · Shootash · Smannell · South Harewood · Stockbridge · Tangley · Thruxton · Up Somborne · Upper Clatford · Upper Enham · Vernhams Dean · Vernham Street · Wellow · West Tytherley · Wherwell · Wherwell Wood · WildhernCategories:- Villages in Hampshire
- Test Valley
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.