- Mucolipidosis
-
Mucolipidosis Classification and external resources ICD-10 E77.0-E77.1 ICD-9 272.7 MeSH D009081 Mucolipidosis (ML) is a group of inherited metabolic disorders that affect the body's ability to carry out the normal turnover of various materials within cells.
When originally named, the mucolipidoses derived their name from the similarity in presentation to both mucopolysaccharidoses and sphingolipidoses.[1] A biochemical understanding of these conditions has changed how they are classified. Although four conditions (I, II, III, and IV) have been labeled as mucolipidoses, type I (sialidosis) is now classified as a glycoproteinosis,[1] and type IV (Mucolipidosis type IV) is now classified as a gangliosidosis.[2]
Contents
ML II and III
- For details, see I-cell disease (type II) and Pseudo-Hurler polydystrophy (type III)
The other two types are closely related.
Mucolipidosis types II and III (ML II and ML III) result from a deficiency of the enzyme N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphotransferase, which phosphorylates target carbohydrate residues on N-linked glycoproteins. Without this phosphorylation, the glycoproteins are not destined for lysosomes, and they escape outside the cell.
Genetics
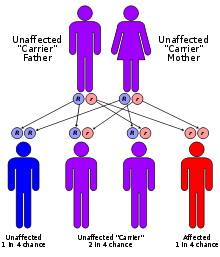
The mucolipidoses are inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, that is, they occur only when a child inherits two copies of the defective gene, one from each parent. When both parents carry a defective gene, each of their children faces a one in four chance of developing one of the MLs. At the same time, each child also faces a one in two chance of inheriting only one copy of the defective gene. People who have only one defective gene are known as carriers. These individuals do not develop the disease but they can pass the defective gene on to their own children. Because the defective genes involved in certain forms of ML are known, tests can identify people who are carriers in some instances.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of ML is based on clinical symptoms, a complete medical history, and certain laboratory tests.
See also
- Medical genetics of Ashkenazi Jews
- mucolipidoses at NINDS
References
- ^ a b Julia A. McMillan; Ralph D. Feigin; Catherine DeAngelis; M. Douglas Jones (1 April 2006). Oski's pediatrics: principles & practice. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 1–. ISBN 9780781738941. http://books.google.com/books?id=VbjFQiz8aR0C&pg=RA1-PA2211. Retrieved 3 November 2010.
- ^ "ICD-10:". http://apps.who.int/classifications/apps/icd/icd10online/?ge70.htm+e751. Retrieved 2010-11-03.
(LSD) Inborn error of carbohydrate metabolism: glycoproteinosis (E77, 271.8) Anabolism Post-translational modification
of lysosomal enzymesCatabolism Aspartylglucosaminuria · Fucosidosis · mannosidosis (Alpha-mannosidosis, Beta-mannosidosis) · Sialidosis · Schindler diseaseOther Categories:- Glycoprotein metabolism disorders
- Autosomal recessive disorders
- Ashkenazi Jews topics
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.