- Lunar node
-
"Dragon's Tail" redirects here. For the Dragon's Tail stretch of road in North Carolina, see Deals Gap, North Carolina.
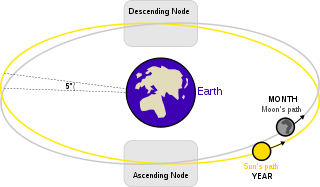
The lunar nodes are the orbital nodes of the Moon, that is, the points where the orbit of the Moon crosses the ecliptic (which is the apparent path of the Sun across the heavens against the background stars). The ascending node is where the moon crosses to the north of the ecliptic. The descending node is where it crosses to the south.
Eclipses occur only near the lunar nodes: Solar eclipses occur when the passage of the Moon through a node coincides with the new moon; lunar eclipses occur when passage coincides with the full moon. A Lunar Eclipse may occur if there is a full moon within 11° 38' (Celestial Longitude), of a Node, and a Solar Eclipse may occur if there is a new moon within 17° 25' of a Node.
The lunar nodes precess rather quickly around the ecliptic, completing a revolution (called a draconitic or nodical period, the period of nutation) in 6793.5 days or 18.5996 years (note that this is not the same length as a saros).
Contents
Names and symbols
The nodes are called by different names in different areas of the world.
Since the ascending node is the point of intersection between the ecliptic and the plane of the lunar orbit where the Moon is ascending from the South to the North, it is sometimes called the North node. In ancient European texts, it is referred to as the dragon's head (Caput Draconis, or Anabibazon). The symbol of the ascending node is
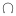 , the astronomical and astrological symbol for the Dragon's head. Similarly the descending node is the point where the Moon is descending from North to South, and is sometimes referred to as South node. It is also known as the dragon's tail (Cauda Draconis, or Catabibazon), and its symbol is the inversion of that of the ascending node:
, the astronomical and astrological symbol for the Dragon's head. Similarly the descending node is the point where the Moon is descending from North to South, and is sometimes referred to as South node. It is also known as the dragon's tail (Cauda Draconis, or Catabibazon), and its symbol is the inversion of that of the ascending node: 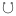 . Note that the so-called North node may in fact lie South of the South node in the course of the nodal cycle.
. Note that the so-called North node may in fact lie South of the South node in the course of the nodal cycle.In Hindu astronomy, the ascending node ☊ is called Rahu and the descending node ☋ is called Ketu.
Extreme declinations
See also: Lunar standstillThe lunar orbit is inclined by about 5 degrees on the ecliptic: hence the Moon can be up to about 5 degrees north or south of the ecliptic. The ecliptic is inclined by about 23.4° on the celestial equator, the plane that is perpendicular to the rotation axis of the Earth. As a consequence, once during the 18.6-year nodal period, when the ascending node of the Moon's orbit coincides with the vernal equinox, then the Moon reaches extreme northern and southern declinations. Then it also has its extreme northern and southern azimuth points of rising and setting on the horizon; its extreme lowest and highest altitude when crossing the meridian; and potentially extreme late first sightings of the new moon. Furthermore, occultations by the Moon of the bright star group the Pleiades, which are over 4° North of the ecliptic, occur during a comparatively brief period once every nodal period.
Astrological significance
In Western Astrology only the north node is usually marked in horoscopes, as the south node is by definition at the opposite point in the chart. In Vedic Astrology, the north and south nodes are called Rahu and Ketu respectively, and both are marked in the chart.
Nodes always move retrograde and are considered natural malefics. There is no consensus on their special aspects.
In Tibetan Astrology (partially based on the Kalacakra Tantra) the southern node is named Kalagni.
See also
References
External links
- Sun and Moon Polar Applet, showing moonrise/moonset azimuths
- Astronomy Answers: What are the standstills of the Moon?
- Eclipses, Cosmic Clockwork of the Ancients
Categories:- Orbit of the Moon
- Technical factors of astrology
- Celestial mechanics
- Hindu astrology
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.