- Penrose graphical notation
-
In mathematics and physics, Penrose graphical notation or tensor diagram notation is a (usually handwritten) visual depiction of multilinear functions or tensors proposed by Roger Penrose[1]. A diagram in the notation consists of several shapes linked together by lines, much like tinker toys. The notation has been studied extensively by Predrag Cvitanović, who used it to classify the classical Lie groups [2]. It has also been generalized using representation theory to spin networks in physics, and with the presence of matrix groups to trace diagrams in linear algebra.
Contents
Interpretations
Multilinear algebra
In the language of multilinear algebra, each shape represents a multilinear function. The lines attached to shapes represent the inputs or outputs of a function, and attaching shapes together in some way is essentially the composition of functions.
Tensors
In the language of tensor algebra, a particular tensor is associated with a particular shape with many lines projecting upwards and downwards, corresponding to abstract upper and lower indices of tensors respectively. Connecting lines between two shapes corresponds to contraction of indices. One advantage of this notation is that one does not have to invent new letters for new indices. This notation is also explicitly basis-independent[3]
Matrices
Each shape represents a matrix, and tensor multiplication is done horizontally, and matrix multiplication is done vertically.
Examples
The identity function on a vector space is a vertical line.
Representation of special tensors
Metric tensor
The metric tensor is represented by a U-shaped loop or an upside-down U-shaped loop, depending on the type of tensor that is used.
Levi-Civita tensor
The Levi-Civita antisymmetric tensor is represented by a thick horizontal bar with sticks pointing downwards or upwards, depending on the type of tensor that is used.
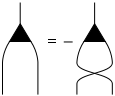
Structure constant
The structure constants (
 ) of a Lie algebra are represented by a small triangle with one line pointing upwards and two lines pointing downwards.
) of a Lie algebra are represented by a small triangle with one line pointing upwards and two lines pointing downwards.Tensor operations
Contraction of indices
Contraction of indices is conveniently represented by joining the index lines together.
Symmetrization
Symmetrization of indices is represented by a thick zig-zag or wavy bar crossing the index lines horizontally.
Antisymmetrization
Antisymmetrization of indices is represented by a thick straight line crossing the index lines horizontally.
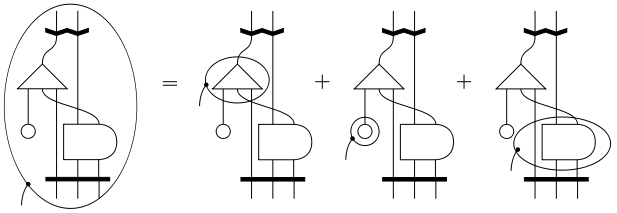
Covariant derivative
The covariant derivative (
 ) is represented by a circle around the tensor(s) to be differentiated and a line joined from the circle pointing downwards to represent the lower index of the derivative.
) is represented by a circle around the tensor(s) to be differentiated and a line joined from the circle pointing downwards to represent the lower index of the derivative.Tensor manipulation
The diagrammatic notation is very useful in manipulating tensor algebra. It usually involves a few simple "identities" of tensor manipulations.
For example,
 , where n is the number of dimensions, is a common "identity".
, where n is the number of dimensions, is a common "identity".See also
- Braided monoidal category
- Spin networks
- Trace diagram
- Abstract index notation
Notes
- ^ see e.g. Quantum invariants of knots and 3-manifolds" by V. G. Turaev (1994), page 71
- ^ Predrag Cvitanović (2008). Group Theory: Birdtracks, Lie's, and Exceptional Groups. Princeton University Press. http://birdtracks.eu/.
- ^ Roger Penrose, The Road to Reality: A Complete Guide to the Laws of the Universe, 2005, ISBN 0-099-44068-7, Chapter Manifolds of n dimensions.
Categories:- Tensors
- Theoretical physics
- Mathematical notation
- Diagram algebras
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.










![{}_{= Q^{[ab]}}](1/af19c747bc6e208e34c47380f90024f6.png)
 )
)
![E_{[ab\ldots n]}](8/0d8161ef738cbe0640be765fe357c5a2.png)

![{}_{= E_{[ab]}}](d/1fd0c04afc81bbcc887c2310936a620d.png)
 )
)
![12\nabla_a\left\{ \xi^f\,\lambda^{(d}_{fb[c}\,D^{e)b}_{gh]} \right\}](3/f838b2d0038cd16a54969d9ca93cebbb.png)