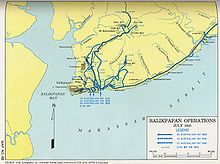
- Battle of Balikpapan (1945)
-
Battle of Balikpapan (1945) Part of the Pacific Theatre of World War II 
American manned Alligators during the landing of Australian troops at Balikpapan, BorneoDate 1–21 July 1945 Location Balikpapan, Netherlands East Indies Result Allied victory Belligerents  Australia
Australia
 United States
United States
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom Empire of JapanFor other uses, see Battle of Balikpapan (disambiguation).
Empire of JapanFor other uses, see Battle of Balikpapan (disambiguation).The Battle of Balikpapan was the concluding stage of the Borneo campaign (1945). The landings took place on 1 July 1945. The Australian 7th Division, composed of the 18th, 21st and 25th Infantry Brigades, with support troops, made an amphibious landing, codenamed Operation Oboe Two a few miles north of Balikpapan, on the island of Borneo. The landing had been preceded by heavy bombing and shelling by Australian and US air and naval forces. The Japanese were outnumbered and out gunned, but like the other battles of the Pacific War, many of them fought to the death.
Major operations had ceased by July 21. The 7th Division's casualties were significantly lighter than they had suffered in previous campaigns. The battle was one of the last to occur in World War II, beginning a few weeks before the bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki effectively ended the war. Japan surrendered while the Australians were combing the jungle for stragglers.
Following the surrender the three Brigades were committed to occupation duties until around February 1946. The 21st Brigade was detached to Makassar in the Celebes Islands to accept surrender of the Japanese forces, release POWs and maintain civil order.
Contents
Order of battle
Allied Units ("Oboe Two Force")
Land forces
- 7th Australian Division
- Divisional Units
- 2/7 Cavalry (Commando) Regiment
- 2/1 Pioneer Battalion
- 2/1 Machine Gun Battalion
- B Company 2/1 Guard Regiment (4 platoons)
- Divisional Artillery
- 2/4 Field Regiment (25 pounder guns)
- 2/5 Field Regiment (25 pounder guns)
- 2/6 Field Regiment (25 pounder guns)
- 2/2 Tank Attack Regiment
- Divisional Engineers
- 2/4 Field Company
- 2/5 Field Company
- 2/6 Field Company
- 2/9 Field Company
- 2/25 Field Park Company
- 18 Infantry Brigade
- 2/9 Battalion
- 2/10 Battalion
- 2/12 Battalion
- 21 Infantry Brigade
- 2/14 Battalion
- 2/16th Battalion
- 2/27 Battalion
- 25 Infantry Brigade
- 2/25 Battalion
- 2/31 Battalion
- 2/33 Battalion
- Divisional Units
- I Australian Corps units
- (Attached to the 7th Division for operational purposes.)
- 1st Armoured Regiment (Matilda II tanks)
- Armoured Squadron (Special Equipment) (-)
- 2/1 Composite Anti-Aircraft Regiment
- 2 Beach Group
- 2/2 Pioneer Battalion
- 2/11 Field Company
- 12 Aust. Light Wireless Section
- 2/11 Field Company
- 2/2 Pioneer Battalion
- (Attached to the 7th Division for operational purposes.)
- Royal Netherlands East Indies Army
- 1 Company, 1 NEI Battalion
- United States Army
- 727 Amphibious Tractor Battalion (less one company)
- One company, 672 Amphibious Tractor Battalion
- One boat company, Boat Battalion, 593 Engineer Boat and Shore Regiment
Air Units
- 79 (General Reconnaissance – Bomber) Wing Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF)
- No. 2 Squadron (B-25)
- No. 18 (NEIAF, Australian-Dutch) Squadron (B-25)
- 78 (Fighter) Wing RAAF (from June 30)
- No. 75 Squadron (Kittyhawk)
- No. 78 Squadron (Kittyhawk)
- No. 80 Squadron (Kittyhawk)
- No. 452 Squadron (Spitfire)
- 82 (Bomber) Wing RAAF
- No. 21 Squadron (B-24)
- No. 23 Squadron (B-24)
- No. 24 Squadron (B-24)
- Detachment, 83 (Army Co-Operation) Wing
- Detachment, No. 4 Squadron (CAC Boomerang)
- Detachment, No. 16 Air Observation Post Flight
- Det, 9 Local Air Supply Unit
- No. 54 Squadron RAF (Spitfire)
- 13th Air Force
- 42d Bombardment Group (B-25)
- 69, 70, 75, 100, 390 Bombardment Squadrons (Palawan Island)
- 5th Bombardment Group (B-24)
- 23, 31, 72, 394 Bombardment Squadrons (Samar Island)
- 307th Bombardment Group (B-24)
- 370, 371, 372, 424 Bombardment Squadrons (Morotai Island)
- 868th Bombardment Squadron (SB-24, LAB: Low Altitude radar Bomb.) flew maritime surveillance patrols
- 18th Fighter Group (P-38)
- 12, 44, 70 Fighter Squadrons (Zamboanga)
- 347th Fighter Group (P-38)
- 67, 68, 339 Fighter Squadrons (Palawan Island)
- 419th Night Fighter Squadron (P-61) (Zamboanga and Palawan)
- 4 Reconnaissance Group (F-5 and B-25)
- 17th Photographic Reconnaissance Squadron Det. (Palawan Island)
- 42d Bombardment Group (B-25)
- 5th Air Force
- 22d Bombardment Group (B-24)
- 38th Bombardment Group (B-25)
- Attached to 42nd Bombardment Group
- 90th Bombardment Group (B-24)
- 380th Bombardment Group (B-24)
- VMB-611 (PBJ) flying from Zamboanga
- Marine Air Group 2 (flying from the USN escort carriers)
- Marine Escort Carrier Group 1 (MCVEG-1) on USS Block Island (CVE-106)
- VMF-511 (FG-1D Corsair) & F6F-5N Hellcat
- VMTB-233 (TBM-3)
- Marine Escort Carrier Group 2 (MCVEG-2) on carrier USS Gilbert Islands (CVE-107)
- VMF-512 (FG-1D)
- VMTB-143 (TBM-3)
- Marine Escort Carrier Group 1 (MCVEG-1) on USS Block Island (CVE-106)
- Fleet Air Wing 17 (Palawan Island)
- Patrol Bombing Squadron 128 (VPB-128) (PV-1)
- Patrol Bombing Squadron 106 (VPB-106) (PB4Y-2)
- Patrol Bombing Squadron 111 (VPB-111) (PB4Y-2)
- Navy Escort Carrier Group 40 (CVEG-40) on carrier Suwannee
- Fighting Squadron 40 (VF-40) (F6F-5)
- Torpedo Squadron 40 (VT-40) (TBM-3)
- Attack Group 78.2
- Transports: 1 AGC USS Wasatch, 1 CGC, 3 LSI (HMAS Manoora, HMAS Westralia, HMAS Kanimbla), 1 AKA (USS Titania), 1 LSD (USS Carter Hall), 5 APD, 1 LCF(F), 22 LSM, 35 LST, 16 LCI(L), 2 PC, 3 SC
- Close Support: 10 LCS(L), 8 LCI(R), 6 LCI(R), 3 LCI(M)
- Screen: 10 Destroyers (USS Robinson, Saufley, Waller, Philip, Bailey, Frazier, Flusser, Drayton, Conyngham, Smith), 5 Destroyer Escorts (USS Chaffee, Destroyer escorts: USS Mitchell, Donaldson, Cloues, Lamons and Kyne
- 8 USN PT boats arrived with the tender USS Mobjack on 27 June, and this force was expanded to two PT boat squadrons (10 and 27) on 6 July.
Japanese Units
- 22 Base Force
- 454 Independent Infantry Battalion
References
- Australian Official Histories of World War II
- Gavin Long (1963), The Final Campaigns. Australian War Memorial, Canberra.
- G. Hermon Gill (1968), Royal Australian Navy 1942–45. Australian War Memorial, Canberra.
- George Odgers (1968), Air War Against Japan, 1943–45. Australian War Memorial, Canberra.
- ‘Japanese Monograph Number 26: Borneo Operations. 1941–1945’ in War in Asia and the Pacific. Volume 6. The Southern Area (Part I).
- Wesley Craven and James Cate (1953), The Army Air Forces in World War Two. Volume V: Matterhorn to Nagasaki. Government Printing Office, Washington D.C.
- Major General R.N. Hopkins (Retired). Australian Armour. A History of the Royal Australian Armoured Corps 1927–1972. Australian Government Publishing Service. 1978.
- Samuel Eliot Morison (1989), The Liberation of the Philippines: Luzon, Mindanao, the Visayas 1944–1945. Little, Brown and Company, Boston.
- Gordon L. Rottman, US Marine Corps Order of Battle. Ground and Air Units in the Pacific War, 1939–1945. Greenwood Press. Westport. 2002.
- Royal Navy (1959), Naval Staff History Second World War: War with Japan, Volume VI; The Advance to Japan. British Admiralty, London.
- James J. Fahey (1992), Pacific War Diary, 1942–1945: The Secret Diary of an American Sailor Houghton Mifflin ISBN 0-395-64022-9 (gives a shipboard view of the naval operations around the island, in particular the terrible beating the minesweepers took in clearing the harbour)
External links
Categories:- Conflicts in 1945
- 1945 in Indonesia
- South West Pacific theatre of World War II
- Japanese Occupation of Indonesia
- Battles of World War II involving Australia
- United States Marine Corps in World War II
- 7th Australian Division
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.