- Copper(I)-thiophene-2-carboxylate
-
"CuTC" redirects here. For other uses, see CUTC (disambiguation).
Copper(I)-thiophene-2-carboxylate[1] 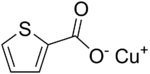 Copper(I) thiophene-2-carboxylateOther namesCuTC
Copper(I) thiophene-2-carboxylateOther namesCuTCIdentifiers CAS number 68986-76-5 PubChem 11194830 ChemSpider 9369899 
Jmol-3D images Image 1
Image 2- O=C([O-])C1=CC=CS1.[Cu+]
[Cu+].[O-]C(=O)c1sccc1
Properties Molecular formula C5H3CuO2S Molar mass 190.69 g mol−1 Hazards R-phrases R36/37/38 S-phrases S26 Main hazards Irritant (Xi)  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
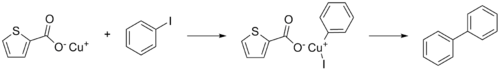
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Copper(I)-thiophene-2-carboxylate or CuTC is a thiophene and a reagent in organic chemistry that especially promotes the Ullmann reaction between aryl halides.[2]
References
- ^ Copper(I) thiophene-2-carboxylate at Sigma-Aldrich
- ^ Jwanro Hassan, Marc Sévignon, Christel Gozzi, Emmanuelle Schulz, and Marc Lemaire (2002). "Aryl-Aryl Bond Formation One Century after the Discovery of the Ullmann Reaction". Chem. Rev. 102 (5): 1359–1470. doi:10.1021/cr000664r. PMID 11996540. http://pubs.acs.org/spotlight/july2002/cr000664r.pdf.
Categories:- Reagents for organic chemistry
- Thiophenes
- Copper compounds
- O=C([O-])C1=CC=CS1.[Cu+]
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.