- PCGEM1
-
Prostate-specific transcript 1 (non-protein coding) Identifiers Symbols PCGEM1; NCRNA00071 External IDs OMIM: 605443 GeneCards: PCGEM1 Gene Gene Ontology Orthologs Species Human Mouse Entrez 64002 n/a Ensembl n/a n/a UniProt n/a n/a RefSeq (mRNA) NR_002769 n/a RefSeq (protein) n/a n/a Location (UCSC) n/a n/a PubMed search [1] n/a Prostate-specific transcript 1 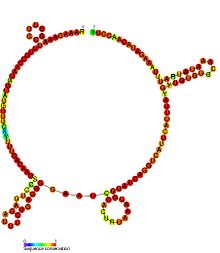
Predicted secondary structure and sequence conservation of PCGEM1 Identifiers Symbol PCGEM1 Rfam RF01981 Other data RNA type Gene; Domain(s) Eukaryota; GO 0042981 SO 0001463 Prostate-specific transcript 1 (non-protein coding), also known as PCGEM1, is a long non-coding RNA gene. In humans, it is located on chromosome 2q32. It is over-expressed in prostate cancer.[1][2] In a study of prostate tumours from 88 men, levels of PCGEM1 were found to be higher in prostate cancer cells in African-American men than in Caucasian-American men. The mortality rate of prostate cancer is highest in African-American men.[3]
PCGEM1 inhibits doxorubicin-induced apoptosis of cells, via delayed induction of p53 and p21.[4]
Contents
See also
- Long noncoding RNA
- Prostate cancer
References
- ^ Srikantan V, Zou Z, Petrovics G, et al. (October 2000). "PCGEM1, a prostate-specific gene, is overexpressed in prostate cancer". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97 (22): 12216–21. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.22.12216. PMC 17321. PMID 11050243. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=17321.
- ^ Bialkowska-Hobrzanska H, Driman DK, Fletcher R, Harry V, Razvi H (February 2006). "Expression of human telomerase reverse transcriptase, Survivin, DD3 and PCGEM1 messenger RNA in archival prostate carcinoma tissue". Can J Urol 13 (1): 2967–74. PMID 16515751.
- ^ Petrovics G, Zhang W, Makarem M, et al. (January 2004). "Elevated expression of PCGEM1, a prostate-specific gene with cell growth-promoting function, is associated with high-risk prostate cancer patients". Oncogene 23 (2): 605–11. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1207069. PMID 14724589.
- ^ Fu X, Ravindranath L, Tran N, Petrovics G, Srivastava S (March 2006). "Regulation of apoptosis by a prostate-specific and prostate cancer-associated noncoding gene, PCGEM1". DNA Cell Biol. 25 (3): 135–41. doi:10.1089/dna.2006.25.135. PMID 16569192.
Further reading
- Ifere GO, Barr E, Equan A, et al. (2009). "Differential effects of cholesterol and phytosterols on cell proliferation, apoptosis and expression of a prostate specific gene in prostate cancer cell lines.". Cancer Detect. Prev. 32 (4): 319–28. doi:10.1016/j.cdp.2008.12.002. PMID 19186008.
- Enciso-Mora V, Hosking FJ, Houlston RS (2010). "Risk of breast and prostate cancer is not associated with increased homozygosity in outbred populations.". Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 18 (8): 909–14. doi:10.1038/ejhg.2010.53. PMID 20407466.
- Romanuik TL, Wang G, Morozova O, Delaney A, Marra MA, Sadar MD (2010). "LNCaP Atlas: gene expression associated with in vivo progression to castration-recurrent prostate cancer". BMC Med Genomics 3: 43. doi:10.1186/1755-8794-3-43. PMC 2956710. PMID 20868494. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2956710.
- Ifere GO, Ananaba GA (November 2009). "Prostate cancer gene expression marker 1 (PCGEM1): a patented prostate- specific non-coding gene and regulator of prostate cancer progression". Recent Pat DNA Gene Seq 3 (3): 151–63. PMID 19891595.
External links
Categories:- Human proteins
- Non-coding RNA
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
