- Phenyl-C61-butyric acid methyl ester
-
Phenyl-C61-butyric acid methyl ester 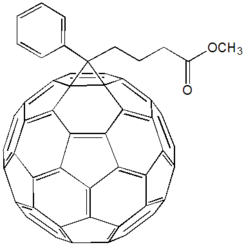 Phenyl-C61-butyric acid methyl ester
Phenyl-C61-butyric acid methyl esterIdentifiers ChemSpider 21170152 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - COC(=O)CCCC1(C23=C14c5c6c7c8c9c1c%10c%11c%12c%13c%14c%10c%10c9c7c7c5c5c2c2c9c%15c(c%13c%13c%12c%12c%16c%11c1c1c8c8c6c4c4c6c8c1c%16c1c%12c8c%13c%15c%11c8c(c16)c4c3c%112)c1c%14c%10c7c5c19)c1ccccc1
- InChI=1S/C72H14O2/c1-74-11(73)8-5-9-70(10-6-3-2-4-7-10)71-66-58-50-40-30-22-14-12-13-16-20-18(14)26-34-28(20)38-32-24(16)25-17(13)21-19-15(12)23(22)31-37-27(19)35-29(21)39-33(25)43-42(32)52-46(38)56-48(34)54(44(50)36(26)30)62(66)64(56)68-60(52)61-53(43)47(39)57-49(35)55-45(37)51(41(31)40)59(58)67(71)63(55)65(57)69(61)72(68,70)71/h2-4,6-7H,5,8-9H2,1H3

Key: FIGVSQKKPIKBST-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Properties Molecular formula C72H14O2 Molar mass 910.88 g mol−1 Exact mass 910.099379692 g mol−3  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references PCBM is the common abbreviation for the fullerene derivative [6,6]-phenyl-C61-butyric acid methyl ester. It is being investigated in organic solar cells[1].
PCBM is a fullerene derivative of the C60 buckyball that was first synthesized in the 1990s.[2] It is an electron acceptor material and is often used in plastic solar cells or flexible electronics in conjunction with electron donor materials such as P3HT or other polymers. It is a more practical choice for an electron acceptor when compared with fullerenes because of its solubility in chlorobenzene. This allows for solution processable donor/acceptor mixes, a necessary property for "printable" solar cells. However, considering the cost of fabricating fullerenes, it is not certain that this derivative can be synthesized on a large scale for commercial applications.
See also
References
- ^ Björström, Cecilia; Bernasik, Andrzej; Rysz, Jakub; Budkowski, Andrzej; Nilsson, Svante; Svensson, Mattias; Andersson, Mats; Magnusson, Kjell et al. (December 21, 2005). "Multilayer formation in spin-coated thin films of low-bandgap polyfluorene: PCBM blends". Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter 17 (50): L529–L534. doi:10.1088/0953-8984/17/50/L01.
- ^ Hummelen, Jan C.; Knight, Brian W.; Lepeq, F.; Wudl, Fred; Yao, Jie; Wilkins, Charles L. (1995). "Preparation and Characterization of Fulleroid and Methanofullerene Derivatives". The Journal of Organic Chemistry 60 (3): 532–538. doi:10.1021/jo00108a012.
This article about an ester is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
