- Octahydroxyanthraquinone
-
Octahydroxyanthraquinone 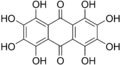
 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8-Octahydroxy-9,10-anthracenedioneOther namesOctahydroxyanthracenedione
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8-Octahydroxy-9,10-anthracenedioneOther namesOctahydroxyanthracenedioneIdentifiers CAS number 169132-62-1 
PubChem 9840703 ChemSpider 8016420 
ChEBI CHEBI:190016 
ChEMBL CHEMBL293801 
Jmol-3D images Image 1
Image 2- OC1=C(O)C(O)=C2C(=O)C3=C(O)C(O)=C(O)C(O)=C3C(=O)C2=C1O
OC1=C(O)C(O)=C(O)C2=C1C(C3=C(O)C(O)=C(O)C(O)=C3C2=O)=O
Properties Molecular formula C14H8O12 Molar mass 368.21 g mol−1 Exact mass 336.011746476 g mol-1 log P -0.291 Acidity (pKa) 5.358  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Octahydroxyanthraquinone is an organic compound with formula C14H8O12, formally derived from anthraquinone by replacement of 8 hydrogen atoms by hydroxyl groups.
The compound was obtained in 1911 by Georg von Georgievics[1] [2] and can be obtained through oxidation of rufigallol (1,2,3,5,6,7-hexahydroxyanthraquinone) with boric acid and mercuric oxide in sulfuric acid at 250 °C.[3]
Esters of octahydroxyanthraquinone, where all eight hydroxyls are replaced by straight-chain 1-alkanecarboxylate groups H3C-(CH2)n-COO-, with n between 6 and 14, are liquid crystals and have been studied for possible LCD applications.[3]
Octahydroxyanthraquinone is active against the malaria parasite, but rufigallol (1,2,3,5,6,7-hexahydroxyanthraquinone) is 22 times more potent.[4]
References
- ^ Georgievics, G. v. (1911). "Darstellung und Eigenschaften des Octooxyanthrachinons". Monatshefte für Chemie 32: 347. doi:10.1007/BF01518160.
- ^ Wahl, Andre; Atack, F. W (1919) The Manufacture Of Organic Dyestuffs. G. Bell And Sons, Limited. Online version accessed on 2010-01-22.
- ^ a b Kumar, Sandeep (2008). "Rufigallol-based self-assembled supramolecular architectures". Phase Transitions 81: 113. doi:10.1080/01411590701601610.
- ^ Winter, R (1995). "Hydroxy-anthraquinones as antimalarial agents". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 5: 1927. doi:10.1016/0960-894X(95)00326-O.

This article about an aromatic compound is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. - OC1=C(O)C(O)=C2C(=O)C3=C(O)C(O)=C(O)C(O)=C3C(=O)C2=C1O
