- Midostaurin
-
Midostaurin 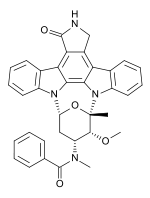
Systematic (IUPAC) name (9S,10R,11R,13R)-2,3,10,11,12,13-Hexahydro-10-methoxy-9-methyl-11-(methylamino)-9,13-epoxy-1H,9H-diindolo[1,2,3-gh:3',2',1'-lm]pyrrolo[3,4-j][1,7]benzodiamzonine-1-one Clinical data Pregnancy cat. ? Legal status Investigational Routes Oral Identifiers CAS number 120685-11-2 ATC code None PubChem CID 9829523 UNII ID912S5VON 
Synonyms 4'-N-benzoylstaurosporine Chemical data Formula C35H30N4O4 Mol. mass 570.637 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem - InChI=1S/C35H30N4O4/c1-35-32(42-3)25(37(2)34(41)19-11-5-4-6-12-19)17-26(43-35)38-23-15-9-7-13-20(23)28-29-22(18-36-33(29)40)27-21-14-8-10-16-24(21)39(35)31(27)30(28)38/h4-16,25-26,32H,17-18H2,1-3H3,(H,36,40)/t25-,26-,32-,35+/m1/s1
Key:BMGQWWVMWDBQGC-IIFHNQTCSA-N
Midostaurin (PKC412) is a multi-target protein kinase inhibitor being investigated for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). It is a semi-synthetic derivative of staurosporine, an alkaloid from the bacterium Streptomyces staurosporeus, and is active in patients with mutations of CD135 (FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 receptor).[1]
After successful Phase II clinical trials, a Phase III trial for AML has started in 2008. It is testing midostaurin in combination with daunorubicin and cytarabine.[2] In another trial, the substance has proven ineffective in metastatic melanoma.[3]
References
- ^ Fischer, T.; Stone, R. M.; Deangelo, D. J.; Galinsky, I.; Estey, E.; Lanza, C.; Fox, E.; Ehninger, G. et al. (2010). "Phase IIB Trial of Oral Midostaurin (PKC412), the FMS-Like Tyrosine Kinase 3 Receptor (FLT3) and Multi-Targeted Kinase Inhibitor, in Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia and High-Risk Myelodysplastic Syndrome with Either Wild-Type or Mutated FLT3". Journal of Clinical Oncology 28 (28): 4339. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.28.9678. PMID 20733134.
- ^ ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00651261 Daunorubicin, Cytarabine, and Midostaurin in Treating Patients With Newly Diagnosed Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- ^ Millward, M. J.; House, C.; Bowtell, D.; Webster, L.; Olver, I. N.; Gore, M.; Copeman, M.; Lynch, K. et al. (2006). "The multikinase inhibitor midostaurin (PKC412A) lacks activity in metastatic melanoma: a phase IIA clinical and biologic study". British Journal of Cancer 95 (7): 829. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6603331. PMC 2360547. PMID 16969355. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2360547.
This antineoplastic or immunomodulatory drug article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. - InChI=1S/C35H30N4O4/c1-35-32(42-3)25(37(2)34(41)19-11-5-4-6-12-19)17-26(43-35)38-23-15-9-7-13-20(23)28-29-22(18-36-33(29)40)27-21-14-8-10-16-24(21)39(35)31(27)30(28)38/h4-16,25-26,32H,17-18H2,1-3H3,(H,36,40)/t25-,26-,32-,35+/m1/s1
