- Marine Facade
-
Sea Facade (reclaimed land)
Russian: Морской фасад
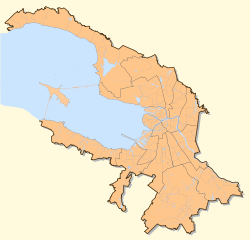
Намыв— The alluvial territories increasing a city territory — Marine Facade Morskoi Fasad transcription(s) Coordinates: 59°56′32″N 30°10′57″E / 59.94222°N 30.1825°E Russia St. Petersburg The decision on development of western part of Vasilievsky Island July, 1st, 2004[1] Marine Facade Management Company has begun October, 25th, 2006[2] Project of a lay-out of territory of the Neva Bay in the Gulf of Finland off the West coast of Vasilievsky Island is confirmed November, 13th 2007[3] Area - Total 4.767 km2 (1.8 sq mi) "Marine Facade Management Company Official Cite" (in en). Marine Facade Management Company. http://www.mfspb.ru/index.php?lang=en. Retrieved 2010-12-19. The Sea (Marine) Facade is a project of additional expansion of St. Petersburg, on Vasilievsky Island at the Neva river's mouth. In these new territories the New Sea Passenger port will be created along with a considerable amount of residential and commercial space. The Western Rapid Diameter highway [4] will be built across these lands.
This project is being implemented within the framework of a public-private partnership between the Saint Petersburg City Administration and Marine Facade Management Company. The primary goal of this project is to build the New Sea Passenger port by reclaiming new territories of 476 hectares from the Neva Bay in the Gulf of Finland. The total cost of the project is estimated 3 billion dollars. The project will reportedly build over 1.5 million square metres of office space, 3 million square metres of residential space, as well as retail, entertainment and social objects, two subway stations, a marina etc.
In 2008, the first phase of works has been finished, an area of 150 hectares was reclaimed for the port building. Reclamation of additional 20 hectares for the Western Rapid Diameter and the construction of buildings is now underway.[5]
Construction chronology
- 2006
- The area of 35 hectares have been reclaimed.
- The underwater channel for the moorings in the port's aquatic area has been built.
- Construction of the service access road has been finished.
- The dividing dam have been built.
- 2007
- The reclaimed area is about 80 hectares (half of this area is intended to be under the passenger terminal). As of July, more than 70% of work has been done.[6]
- By July, 28th (Navy Day) the training sailing ship named "Young Baltiets" has moored at berth 7.[7] New Sea Passenger port has been opened.
- 2008
- In May, the builders announced the beginning of sale of space for the residential and commercial buildings on the reclaimed lands.[8]
- 2009
- The sea passenger port accepts passenger cruise liners.
- In August, a hydrofoil line to Peterhof and the Winter Palace was launched.[9]
References
- ^ Matvienko, Valentina (2004-07-01). "The order of the government of St.-Petersburg Number 61-rp from July, 1st 2004 Russian: Распоряжение правительства Санкт-Петербурга № 61-рп от 1 июля 2004" (in ru). Saint Petersburg City Administration. http://www.mfspb.ru/docum/02.html. Retrieved 2009-09-13.[dead link]
- ^ "Law "About the target program "Realization of the investment project on development of the Sea passenger terminal on Vasilevsky island in St.-Petersburg"" Russian: ЗАКОН САНКТ-ПЕТЕРБУРГА О целевой программе Санкт-Петербурга "Реализация инвестиционного проекта по развитию морского пассажирского терминала на Васильевском острове в Санкт-Петербурге"" (in ru). Sankt-Peterburgskie Vedomosti. 2009-06-11. http://www.spbustavsud.ru/printdoc?tid=&nd=8438818&prevDoc=8461106. Retrieved 2009-09-13.
- ^ Matvienko, Valentina (2007-11-13). "The order of the government of St.-Petersburg Number 1430 from November, 13th 2007 Russian: Распоряжение правительства Санкт-Петербурга № 1431 от 13 ноября 2007" (in ru). Saint Petersburg City Administration. http://www.mfspb.ru/docum/02.html. Retrieved 2009-09-13.[dead link]
- ^ "Marine Facade Management Company Official Cite" (in en). Marine Facade Management Company. http://www.mfspb.ru/index_eng.html. Retrieved 2009-09-13.[dead link]
- ^ "Territory" (in en). Marine Facade Management Company Official Cite. http://www.mfspb.ru/island_eng.html. Retrieved 2009-09-13.[dead link]
- ^ These are the basic works financed from the federal budget, primarily dredging operations
- ^ "News. 28.07.2007" (in en). Marine Facade Management Company Official Cite. 2007-07-28. http://www.mfspb.ru/news_archive_eng.html. Retrieved 2009-09-13.[dead link]
- ^ "To buyers of the ground areas Russian: Покупателям земельных участков" (in en). Marine Facade Management Company Official Cite. http://www.mfspb.ru/develop.html. Retrieved 2009-09-13.[dead link]
- ^ ""Sea facade" have connected with fountains of Petrodvorets Russian: "Морской фасад" связали с фонтанами Петродворца" (in ru). City (fontanka.ru). 2009-08-21. http://www.fontanka.ru/2009/08/21/074/. Retrieved 2009-09-13.
External links
- "Marine Facade Management Company Official Cite" (in en). Marine Facade Management Company. http://www.mfspb.ru/index.php?lang=en.
Marine Facade of St. Petersburg "Marine Facade Management Company Official Cite" (in en). Marine Facade Management Company. http://www.mfspb.ru/index_eng.html. Retrieved 2009-09-13. Hydrofoil boats lines of St. Petersburg Winter palace-Petergof 
Winter palace-Sea Facade Sea Facade-Petergof Type of ships: Meteor Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.