- Dunstable North railway station
-
Dunstable North Location Place Dunstable Area Central Bedfordshire Grid reference TL012227 Operations Original company Dunstable & London & Birmingham Railway Pre-grouping London and North Western Railway Post-grouping London, Midland and Scottish Railway
London Midland Region of British RailwaysPlatforms 3 History 1 June 1848 Opened as Dunstable 25 September 1950 Renamed Dunstable North 26 April 1965 Closed to passengers 9 October 1967 Closed to goods Disused railway stations in the United Kingdom Closed railway stations in Britain
A B C D–F G H–J K–L M–O P–R S T–V W–ZDunstable North was a railway station on the London and North Western Railway's branch line from Leighton Buzzard which served Dunstable in Bedfordshire from 1848 to 1967. Originally the terminus of the London and North Western Railway's branch line from Leighton Buzzard, Dunstable became the point where the line met with the Great Northern's branch line from Luton in 1858. The station became the hub of a number of sidings connecting a variety of concerns to the line, including Waterlows, Bedfordshire County Council, Associated Portland Cement, Dunstable gasworks and a coal yard operated by the Great Northern. Against a background of falling passenger numbers and declining freight returns, the station closed to passengers in 1965 and to goods in 1967. Connections were retained with the cement works and coal yard, which became an oil depot, until 1988 and the line eventually closed in 1991. The site of the station is now occupied by the offices of South Bedfordshire District Council. A section of the former line to the west of the site has become part of route 6 of the National Cycle Network.
Contents
History
The passing of the Dunstable & London & Birmingham Railway Act on 30 June 1845 authorised the construction of a short branch line from Leighton Buzzard to connect Dunstable with the London and Birmingham's main line.[1] The proposals were devised by George and Robert Stephenson.[2] The line opened for freight on 29 May 1848 and to passengers on 1 June.[3] A station was opened beside the A5 Watling Street. It was constructed almost on the level with the road to allow a connection to be made with the Luton, Dunstable and Welwyn Junction Railway[4] which opened a line between Dunstable and Luton in May 1858.[5] The crossing of Watling Street would require the road to be raised by 3 feet 8 inches (1.12 m) and a level crossing to be constructed, but Parliament refused consent for the works.[4] A solution was found whereby the original Dunstable station would be reconstructed at a higher level to allow the road to be crossed by a bridge, whilst also lowering the road level to allow sufficient clearance.[6] This was accepted and a new station opened in January 1866.[7] The delay in opening the new station was caused by protracted negotiations between the two railway companies as to who would bear the costs of construction.[4] In the event, it was the London and North Western Railway, which had absorbed the Dunstable & London & Birmingham Railway.
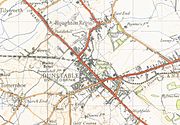
 A 1902 Railway Clearing House map of railways in the vicinity of Dunstable North (upper left)
A 1902 Railway Clearing House map of railways in the vicinity of Dunstable North (upper left)
The new Dunstable station had two platforms and a bay; the Down platform was used by Hatfield trains (the extension from Luton to Hatfield was completed in 1860[8]), the bay was used for Leighton services and the Up platform was, it is believed, used as a run-round loop.[9] The site of the original Dunstable station became the goods yard[10] This yard saw large quantities of coal and fertiliser traffic, in addition to general traffic.[11] To the south of the yard lay the town's gasworks which were served by sidings, whilst to the west was a signal box which controlled access to the yard as well as the level crossing over Brewer's Hill Road.[12] A rail-served Bedfordshire County Council depot was situated on the other side of the level crossing immediately to the north of the running lines.[13] Other sidings served Waterlow's printing works, the Great Northern coal yard from 1871, and the Associated Portland Cement works at Houghton Regis from 1925.[14] Due to subsidence a new 50-lever signal box replaced the LNWR one from 16 August 1958; it was only to have a short life as closure came just over a decade later on 23 March 1969.[15] At this time the station was still lit by gas lamps.[16]
Passenger traffic over the Dunstable branch in its later years was not great except on market days[10], and Dunstable North, as it became after 1950[7], was closed to passengers in 1965 and to goods in 1967.[17] The line to Leighton Buzzard closed from 1 January 1966, with tracklifting at Dunstable beginning in 1968.[18] The former Great Northern coal yard became an oil storage depot in October 1968 which, together with the cement works, was served by between one and three trains daily. The section of line across the A5 bridge was closed in 1969 as it had cracked and the costs of replacement were not justified by the line's remaining traffic. The remaining sidings were disconnected and the signal box closed and demolished. A new loop line was laid between Waterlow's siding and the cement works to provide a run-around.[19] From 1971 the coal for the cement works was shifted to road[20] and the rail connection was limited to the distribution of cement products.[21] Cement and oil traffic continued until 1988[22] and closure of the line was authorised from 16 December 1991.[23]
Preceding station Disused railways Following station Stanbridgeford London and North Western Railway
Dunstable Branch LineDunstable Town Present day
The station has been demolished and is now the site of the offices of South Bedfordshire District Council.[24][25] What remains of the line to the west has become part of the 3.5 km (2.2 mi) Sewell greenaway from French's Avenue to just short of Stanbridgeford. The route is part of National Cycle Network route 6 and includes a bridge over the A505.[26]
References
- ^ Davies & Grant 1984, pp. 74-75.
- ^ Woodward & Woodward 2008, p. 1.
- ^ Oppitz 2000, pp. 100-101.
- ^ a b c Woodward & Woodward 1994, p. 14.
- ^ Oppitz 2000, p. 110.
- ^ Simpson 1998, p. 111.
- ^ a b Butt 1995, p. 86.
- ^ Oppitz 2000, p. 111.
- ^ Woodward & Woodward 1994, p. 53.
- ^ a b Davies & Grant 1984, p. 75.
- ^ Woodward & Woodward 1994, p. 101.
- ^ Woodward & Woodward 2008, fig. 27.
- ^ Woodward & Woodward 2008, p. 23.
- ^ Woodward & Woodward 1994, pp. 100-101.
- ^ Woodward & Woodward 2008, fig. 28-29.
- ^ Woodward & Woodward 2008, fig. 35.
- ^ Clinker 1978, p. 42.
- ^ Woodward & Woodward 1994, p. 127.
- ^ Woodward & Woodward 1994, pp. 130-131.
- ^ Woodward & Woodward 1994, p. 131.
- ^ Leleux 1984, p. 30.
- ^ Simpson 1998, p. 112.
- ^ Woodward & Woodward 1994, p. 133.
- ^ Oppitz 2000, p. 103.
- ^ Shannon 1996, p. 89.
- ^ "Bedford Local Transport Plan Fourth Annual Progress Report" (PDF). Bedfordshire County Council. April 2004. para. 2.3.30. http://www.bedfordshire.gov.uk/Resources/PDF/TransportAndStreets/LocalTransportPlans/LTP1-AnnualProgressReportsPDFS/July2004/APR_2004Chapter2.pdf. Retrieved 2010-04-17.
Sources
- Butt, R. V. J. (1995). The Directory of Railway Stations: details every public and private passenger station, halt, platform and stopping place, past and present (1st ed.). Sparkford: Patrick Stephens Ltd. ISBN 1-8526-0508-1. OCLC 60251199.
- Clinker, C.R. (October 1978). Clinker's Register of Closed Passenger Stations and Goods Depots in England, Scotland and Wales 1830-1977. Bristol: Avon-Anglia Publications & Services. ISBN 0-90546-619-5.
- Davies, R.T.; Grant, M.D. (1984) [1975]. Forgotten Railways: Chilterns and Cotswolds (Vol. 3). Newton Abbot, Devon: David St John Thomas. ISBN 0-946537-07-0.
- Leleux, Robin (1984) [1976]. A Regional History of the Railways of Great Britain: The East Midlands (Volume 9). Newton Abbot, Devon: David St. John Thomas. ISBN 978-0-946537-06-8.
- Oppitz, Leslie (2000). Lost Railways of the Chilterns (Lost Railways Series). Newbury, Berkshire: Countryside Books. ISBN 978-1-85306-643-6.
- Shannon, Paul (1996) [1995]. British Railways Past and Present: Buckinghamshire, Bedfordshire and West Hertfordshire (No. 24). Wadenhoe, Peterborough: Past & Present Publishing Ltd. ISBN 978-1-85895-073-0.
- Simpson, Bill (1998). The Dunstable Branch. Witney, Oxon: Lamplight Publications. ISBN 978-1-89924-603-8.
- Woodward, Sue; Woodward, Geoff (May 2008). Branch Line to Dunstable from Leighton Buzzard to Hatfield. Midhurst, West Sussex: Middleton Press. ISBN 978-1-9060-0827-7.
- Woodward, Sue; Woodward, Geoff (1994). The Hatfield, Luton and Dunstable Railway (Locomotion Papers No. 44). Headington, Oxford: The Oakwood Press. ISBN 978-0-85361-458-6.
External links
- BBC feature on Dunstable's railways.
- Recent images of the remains of the line between Leighton Buzzard to Dunstable.
- Pre-bypass images of the line.
- Dunstable North station on navigable 1946 O. S. map.
- Photographs of removal of rail bridge near Dunstable North Station.
Coordinates: 51°53′34″N 0°31′56″W / 51.89286°N 0.53218°W
Closed railway stations in Bedfordshire Midland Main Line Varsity Line Husborne Crawley Halt · Wootton Broadmead Halt · Kempston and Elstow Halt · Bedford St John's (1st) · Willington · Blunham · Girtford Halt · Sandy (LNWR) · PottonBedford to Hitchin Line Cardington · Cardington Workmen's Platform · Southill · Shefford · Henlow CampDunstable Branch Line Other lines Categories:- Disused railway stations in Bedfordshire
- Former London and North Western Railway stations
- Railway stations opened in 1866
- Railway stations closed in 1967
- Transport in Luton/Dunstable Urban Area
- Dunstable
- Beeching closures in England
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.