- Dresdner Verkehrsbetriebe
-
The Dresdner Verkehrsbetriebe AG (DVB), is the municipal transport company of the city of Dresden in Germany. It is a member of the Verkehrsverbund Oberelbe transport association that manages a common public transport structure for Dresden and its surrounding areas.[1]
The DVB operates a network comprising 12 tram lines, with a total length of approximately 200 kilometres (120 mi), and 28 bus lines, with a total length of approximately 300 kilometres (190 mi). It is also responsible for two funicular railways and three ferries across the River Elbe. It carries about 140 million passengers each year.[1][2]
The DVB network carries some 142 million passenger journeys each year. In 2007, it generated €96.5m of revenue, covering 76% of costs.[3]
Contents
Tramways
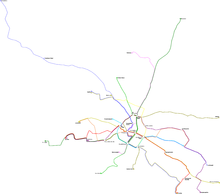
The tramway system is the backbone of public transport in Dresden. DVB operate twelve routes on a 200 km network, with a fleet of 160 tramsets.[2]
The origins of the Dresden tramway can be traced back to the year 1872, when the first horse-drawn line opened between the city centre and the former village of Blasewitz, now a borough of Dresden.
Tram network
The Dresden tramway is a mixed system of traditional street running, especially in the inner city boroughs close to the city centre, and modern light rail. The tramway uses the unusual gauge of 1.450 metres (4 ft 9.1 in), which is just 15 millimetres (0.59 in) wider than standard gauge.[4]
In recent years, street running has been replaced by independent right-of-way arrangements wherever possible, and new extensions created in the same form. In November 2008, a 2.8 kilometres (1.7 mi) extension of route 7 was opened from Gorbitz to Pennrich, in Dresden's south eastern suburbs. In May 2011, a 1.6 kilometres (0.99 mi) extension of route 10 opened from Friedrichstrasse to the city's Messe or exhibition centre, involving construction of a 315 metres (1,033 ft) long, 15 metres (49 ft) wide and 5.4 metres (18 ft) high bridge across the floodplain of the River Elbe.[3][5][6][7]
Unlike many other German cities of comparable size, no stadtbahn style tunnel sections or high platform stops have been created. However many tram stops have been rebuilt so as to be fully accessible to physically disabled persons, and to allow level boarding to the low floor trams that now operate most services.
Different routes can be identified by a route number and a colour code. The current routes are:[1][8]
Number Route Length Time Stops 1 Prohlis – Gruna – Straßburger Platz – Postplatz – Bahnhof Mitte – Friedrichstadt – Leutewitz 15.4 kilometres (9.6 mi) 47 min 34 2 Kleinzschachwitz – Gruna – Straßburger Platz – Postplatz – Bahnhof Mitte – Cotta – Gorbitz 18.2 kilometres (11.3 mi) 55 min 38 3 Coschütz – Plauen – Hauptbahnhof – Pirnaischer Platz – Albertplatz – Bahnhof Neustadt – Trachenberge – Wilder Mann 11.9 kilometres (7.4 mi) 38 min 25 4 Laubegast – Striesen – Straßburger Platz – Postplatz – Mickten – Radebeul – Coswig – Weinböhla 28.9 kilometres (18.0 mi) 79 min 56/57 6 Niedersedlitz – Blasewitz – Albertplatz – Bahnhof Neustadt – Bahnhof Mitte – Löbtau – Wölfnitz (– Gorbitz) 22.0 kilometres (13.7 mi) 67 min 44/45 (48/49) 7 Pennrich – Gorbitz – Löbtau – Hauptbahnhof – Pirnaischer Platz – Albertplatz – Klotzsche – Weixdorf 23.2 kilometres (14.4 mi) 63 min 43/44 8 Südvorstadt – Hauptbahnhof – Postplatz – Albertplatz – Hellerau 13.4 kilometres (8.3 mi) 40 min 27 9 Prohlis – Strehlen – Zoo – Hauptbahnhof – Postplatz – Mickten – Kaditz 17.0 kilometres (10.6 mi) 51 min 40 10 Striesen – Straßburger Platz – Hauptbahnhof – Bahnhof Mitte – Vorwerkstraße (Friedrichstadt)– Messe 11 kilometres (6.8 mi) 23 11 Zschertnitz – Hauptbahnhof – Postplatz – Bahnhof Neustadt – Albertplatz – Weißer Hirsch – Bühlau 15.9 kilometres (9.9 mi) 48 min 31 12 Striesen – Blasewitz – Straßburger Platz – Postplatz – Löbtau – Cotta – Leutewitz 14.5 kilometres (9.0 mi) 49 min 32/33 13 Prohlis – Strehlen – Zoo – Straßburger Platz – Neustadt – Pieschen – Mickten (– Kaditz) 14.7 kilometres (9.1 mi) 48 min 37 (43) Future plans, as part of the Stadtbahnprogrammn 2020, include 14.9 kilometres (9.3 mi) of new tram route, with work starting in 2014. Some 10.5 kilometres (6.5 mi) would be on reserved track, and the new routes would replace bus routes 61 and 62, some of the city's busiest, with an estimated cost of 223 million euros. The new routes comprise:[9]
- Prager Str to Plauen Bhf via Budapester Str and Chemnitzer Str
- Grosser Garten to Löblau via Technische Universität
- Statzentrum to Fetscheplatz via Pillnitzer Str and Striesener Str
- Sachsenallee to Max-Planck-Institute via Johannstadt
- Bühlau to Weissig
On all tramway routes except route 4, a general 10-minute headway is offered on weekdays, extending to 15 minutes on Saturday, Sunday and in the evening. On the main lines through the inner city, where different routes intertwine, vehicles run up to every two minutes. Route 4, which extends a considerable distance beyond the city boundary to the towns of Radebeul, Coswig and Weinböhla, operates the standard 10 or 15 minute interval service as far as Radebeul West, and a 30 minute service beyond that to Coswig and Weinböhla.[10]
Tram fleet
Most of the trams operating in Dresden are articulated low floor cars, of two different basic designs, each of which has several variants. The first generation of low floor cars was built by Deutsche Waggonbau (DWA) in Bautzen between 1995 and 2002; both 6 and 8 axle variants exist. The second generation of low floor cars have been built since 2003 by Bombardier Transportation, also in Bautzen, and are of that manufacturer's Flexity Classic design; both 8 and 12 axle variants exist. The articulated cars vary in length from 30 metres (98 ft) to 45 metres (148 ft) long; all run as single car sets.[11]
The fleet used to be composed of ČKD Tatra trams that provided service towards the end of the GDR era. At present some Tatra T4 cars built between 1968 and 1984 are still in service, but it is intended that they will all be replaced by 2010. The Tatra cars are all high floor, precluding level boarding from tram stops, and run in two car sets with a set length of some 30 metres (98 ft).[11][12]
The DVB tram fleet operates out of three depots; at Gorbitz on routes 2,6 and 7 in south west Dresden, at Trachenberge on route 3 in the north-west, and Reick on routes 1, 9 and 13 in the south-east. Gorbitz is new facility opened in 1996 and includes a new central workshops. Trachenberge and Reick are older facilities that have both been heavily rebuilt to similar standards, whilst several other older depots have been closed. The former central workshops at Trachenberge, adjacent to the current depot, now house the Dresden Tram Museum, which has a collection including examples of many former Dresden trams.[1][3][13]
CarGoTram
The CarGoTram is a freight carrying tram that supplies Volkswagen's Transparent Factory, crossing the city. The two trams, up to 60 meters long, are the longest vehicles allowed to use roads in Dresden. The connection by tram was established to reduce the number of trucks used. The factory is located to the east of the city centre, next to the Großer Garten, whilst the distribution depot that loads the parts is to the west of the city centre.[14]
Buses
The DVB operates 28 city bus routes, with a total route length of about 300 kilometres (190 mi). The routes are operated by a fleet of 145 buses.[2]
Two of the city bus routes, the 75 and 62, provide trunk cross-city service, serving parts of Dresden not served tram routes. Most of the remaining bus routes are intended as a supplement to the tramway network, and are designed to cross the main radial tram routes at a right or oblique angle.[1]
The modernization of the bus fleet has been significantly faster than that of the tram fleet. By 2001 the last GDR era Ikarus bus had been retired. Today, the DVB uses a fleet of buses manufactured by EvoBus (under the Mercedes-Benz bus brand), MAN and Solaris. The whole fleet has a low floor, and over 100 of the buses are articulated. One hybrid bus is operated.[1][15]
Most of the DVB's bus fleet operate out of the central bus depot at Gruna, south-east of the inner city. However some 30 to 40 vehicles are kept at the Trachenberge tram depot.[1]
Other modes
Besides the tram and bus networks, common to many German cities, the DVB also operates two less common modes of city transportation.
Funicular railways
The DVB operates two very different funicular railways within Dresden. Both start from lower terminals close to each other, in the district of Loschwitz and near to the famous Blue Wonder bridge over the River Elbe. The Standseilbahn Dresden is a conventional funicular that runs some 500 metres (1,600 ft) to Weisser Hirsch. The Schwebebahn Dresden is a unique cable operated suspension railway, a kind of hanging monorail, that covers about 250 metres (820 ft) to Oberloschwitz.[16][17]
Both funiculars are operated by two cars, which counter-balance each other. The Standseilbahn is single track with a passing loop, whilst the Schwebebahn has two parallel 'tracks' on its substantial elevated structure. Both are electrically propelled.[16][17]
Ferries
The DVB operates three ferry services across the River Elbe in Dresden. The Pillnitz to Kleinzschachwitz Ferry carries both passengers and cars. The Laubegast to Niederpoyritz Ferry and Johannstadt to Neustadt Ferry are both pedestrian only.[18]
The ferry services are maintained by a fleet of five passenger ferries and one car ferry. All the vessels are diesel propelled but of different designs. The oldest ferry dates from 1927 and the most recent from 2004. The smallest ferry carries a maximum of 40 passengers, whilst the largest passenger ferry carries up to 120. The car ferry can carry 140 passenger and 8 cars, or 350 passengers if no cars are carried. All ferries are painted in the DVB's yellow and white livery.[19]
References
- ^ a b c d e f g
- This article incorporates information from the revision as of March 3, 2009 of the equivalent article on the German Wikipedia.
- ^ a b c "Zahlen & Daten" (in German). DVB. http://www.dvb.de/de/Die-DVB-AG/Zahlen---Daten/. Retrieved 2009-03-03.
- ^ a b c Streeter, Tony (April 2008). "Dreseden trams heading west". Tramways & Urban Transit (Ian Allan Ltd / Light Rail Transit Association): pp. 133–136.
- ^ "World Systems List of LRT, Tramways and Metros - F-J". Light Rail Transit Association. http://www.lrta.org/world/worldf-j.html. Retrieved 2009-03-24.
- ^ "Urban rail news in brief - October 2010". Railway Gazette International. 2010-10-03. http://www.railwaygazette.com/nc/news/single-view/view/urban-rail-news-in-brief-october-2010.html. Retrieved 2010-10-05.
- ^ "Dresden Messe tram extension opens". Railway Gazette International. 2011-06-02. http://www.railwaygazette.com/nc/news/single-view/view/dresden-messe-tram-extension-opens.html.
- ^ "Dresden Messebahn opened". Today's Railways (Platform 5 Publishing Ltd): p. 16. July 2011.
- ^ "Liniennetz" (in German). DVB. http://www.dvb.de/de/Die-DVB-AG/Zahlen---Daten/Liniennetz/. Retrieved 2009-04-18.
- ^ "Dresden unveils tramway expansion". Tramways & Urban Transit (Ian Allan Ltd / Light Rail Transit Association): pp. 165. May 2011.
- ^ "Fahrplanbuchseite" (in German). DVB. http://www.dvb.de/de/Fahrplan/Fahrplanbuchseiten/. Retrieved 2009-03-16.
- ^ a b "Straßenbahnflotte" (in German). DVB. http://www.dvb.de/de/Die-DVB-AG/Zahlen---Daten/Strassenbahnflotte/. Retrieved 2009-03-10.
- ^ "Trams & Buses". City of Dresden. http://www.dresden.de/en/03/09/01/c_01.php. Retrieved 2009-03-10.
- ^ "Strassenbahnmuseum Dresden e.v." (in German). Strassenbahnmuseum Dresden e.v.. http://www.strassenbahnmuseum-dresden.de/. Retrieved 2009-03-23.
- ^ "CarGoTram Dresden" (in German). DVB. http://www.dvb.de/de/Die-DVB-AG/Zahlen---Daten/CarGoTram/. Retrieved 2009-03-03.
- ^ "Busflotte" (in German). DVB. http://www.dvb.de/de/Die-DVB-AG/Zahlen---Daten/Busflotte/. Retrieved 2009-03-11.
- ^ a b "Weißer Hirsch". Funiculars.net. http://www.funiculars.net/line.php?id=43. Retrieved 2009-03-23.
- ^ a b "Bergschwebebahn Loschwitz-Oberloschwitz". Funiculars.net. http://www.funiculars.net/line.php?id=42. Retrieved 2009-03-26.
- ^ "Elbfähren" (in German). DVB. http://www.dvb.de/de/Freizeit---Tourismus/Elbfaehren/. Retrieved 2009-03-26.
- ^ "Fährflotte" (in German). DVB. http://www.dvb.de/de/Die-DVB-AG/Zahlen---Daten/Faehrflotte/. Retrieved 2009-03-03.
External links
- Webpage of the DVB with route maps, construction works, facts, news and more
- History of tram routes
- Collection of photos of different trams
- Kategorie:Straßenbahn im Dresdner Stadtwiki
Categories:- Transport in Dresden
- Public transport operators of Germany
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.