- Diphenylmercury
-
Diphenylmercury 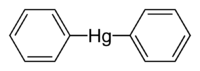

Identifiers CAS number 587-85-9 
UNII 9JF9FUI57J 
Properties Molecular formula C12H10Hg Molar mass 354.80 g mol−1 Density 2.318 g cm−3[1] Boiling point 204 °C[1]
Solubility in water slightly soluble in ethanol, diethyl ether; soluble in benzene, chloroform[1]  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Diphenylmercury is a colourless, crystalline[2] organomercury compound with the chemical formula C12H10Hg. It can be synthesised by the reaction of a 2:1 molar ratio of mercury(II) chloride and methyltriphenyltin in ethanol.[2] As with almost all organomercury compounds, the coordination geometry at mercury is linear.[2]
Preparation
Commercially available, the synthesis of this compound has been variously described in the literature. Diphenylmercury may be prepared by the reaction of phenylmercury acetate with benzene in the presence of sodium stannite,[3] by the reaction of mercury halides with phenylmagnesium bromide,[4] and the reaction of bromobenzene with sodium amalgam.[5]
References
- ^ a b c Lide, David R. (2008). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 89th Edition. CRC Press. p. 3–518. ISBN 978-0849304880.
- ^ a b c C. Glidewell, J. N. Low, J. L. Wardell (2005). "Diphenylmercury, redetermined at 120 K: sheets built from a single C-H…π(arene) hydrogen bond". Acta Cryst. C61 (Pt 2): m107–m108. doi:10.1107/S0108270104034134. PMID 15695887.
- ^ Maynard, J. Lewis (1924). "The Direct Mercuration of Benzene and the Preparation of Mercury Dipheny". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 46 (6): 1510. doi:10.1021/ja01671a024.
- ^ Borgstrom, P.; Dewar, Margaret M. (1929). "The Preparation of Mercury Diphenyl by use of the Grignard Reagent". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 51 (11): 3387. doi:10.1021/ja01386a030.
- ^ H. O. Calvery, "Diphenylmercury", Org. Synth., http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=cv1p0228; Coll. Vol. 1: 228
Categories:- Organomercury compounds
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
