- Deforestation in Papua New Guinea
-
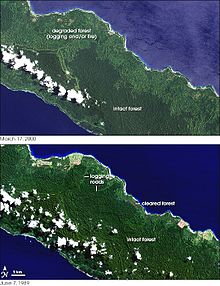 Satellite images exemplify massive loss of forest cover in New Ireland between 1989 (bottom) and 2000 (top)
Satellite images exemplify massive loss of forest cover in New Ireland between 1989 (bottom) and 2000 (top)
Deforestation in Papua New Guinea has been extensive in recent decades and is continuing at an estimated rate of 1.4% of tropical forest being lost annually.[1] Deforestation in Papua New Guinea is mainly a result of illegal logging, which contributed to 70-90 % of all timber exports, one of the highest rates in the world.[2] Illegal logging is linked to corruption, environmental issues and human rights concerns.[3]
The PNG Government is interested in turning the asset into carbon trading revenue through the REDD programme.[4]
Contents
Environment and human rights
PNG’s logging industry negatively affects food sources, water supply and the cultural property of communities.
According to Transparency International PNG’s logging industry is synonymous with political corruption, police racketeering and the brutal repression of workers, women and those who question its ways.[2]
Land rights
On 28 May 2010 PNG’s Parliament amended the Environment and Conservation Act, removing the rights of indigenous people to challenge deals concerning the country’s natural resources.[2]
Corruption
The logging industry has influence in PNG through political donations, public sponsorship, lobbying and media ownership.[3]
According to the governmental report (1989) corruption included bribery, non-compliance with regulations, extensive violations of landowners’ rights and extreme environmental destruction. Logging companies are roaming the countryside with the self assurance of robber barons; bribing politicians and leaders, creating social disharmony and ignoring laws in order to gain access to, rip out, and export valuable timber. Logging industry provide a ground for arms smuggling.[2]
There are human rights abuses of the forest communities and labour. A review of fourteen logging operations 2001- 2006 was highly critical, with the exception of a Japanese company. Forest minister, Belden Namah, addressed logging and corruption in the parliament for the first time in 2008. He found that many responsible persons for monitoring forestry operations had ignored the law and were ‘in the pockets’ of logging companies. He suspended two forestry licences and announced that no permits are to be issued for log exports after 2010. Unnamed PNG politicians are linked in the media to US$45 million in a Singapore bank account, allegedly money earned through secret logging deals.[3]
Logging industry
Malaysian timber conglomerate Rimbunan Hijau (RH) is one of the main logging companies. In October 2008 it admitted in court that it had been awarded logging rights in PNG illegally.[2] Operating subsidiary of Rimbunan Hijau include Wawoi Guavi Timbers.
REDD programme
There is no domestic policy or legislation on carbon trading in PNG. The Office for Climate Change and Environmental Sustainability (OCCES) was created in 2008 under the Prime Minister’s Office, to manage the REDD funds. In March 2008 PNG signed an agreement with Australia to cooperate on REDD. In 2009 the OCCES issued certificates for at least 40 future REDD credits for 1 million tonnes of carbon each. One of the projects is in the 800,000 hectares (ha) of virgin rainforest in Kamula Duso. The controversies and complexity pose management and governance challenges.[4]
According to IUCN weak forest governance is a factor of forest degradation. If it is unresolved, the success of REDD is uncertain and may reinforce corruption, undermine human rights and threaten forest biodiversity. Friends of the Earth questions: ” Why should complex REDD policies involving large amounts of money work in countries unable to contain illegal logging and forest conversion in the first place?”[5]
See also
References
- ^ Shearman et al.: The State of Forests of Papua New Guinea, University of Papua New Guinea, 2008
- ^ a b c d e Global Corruption Report 2011: Climate Change, Corruption A root cause of deforestation and forest degradation Patrick Alley (director of Global Witness). pg.299-311
- ^ a b c corruption report 2009 Corruption and the Private Sector Transparency International August 2009 page 288-289
- ^ a b Global Corruption Report 2011: Climate Change Hypothetical offsets Carbon trading and land rights in Papua New Guinea, Sarah Dix (Transparency International Papua New Guinea) 345-347
- ^ REDD myths Friends of the Earth december 2008 page 26, 11
External links
Deforestation by region Africa America Amazon · Argentina · Bolivia · Brazil · Canada · Central America · Colombia · Costa Rica · Guatemala · Haiti · Mexico · Panama · Peru · Venezuela · United StatesAsia Australia and Oceania Europe Russia · Roman EmpireCategories:- Environment of Papua New Guinea
- Deforestation by region
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

