- 2010 Alaska Turbo Otter crash
-
"2010 Alaska plane crash" redirects here. For the US Air Force crash, see 2010 Alaska C-17 crash.
2010 Alaska Turbine Otter crash 
The de Havilland Canada DHC-3T Turbine Otter following the crashAccident summary Date August 9, 2010 Type Undetermined; suspected pilot error Site Near Aleknagik
59°19′46″N 158°22′52″W / 59.32944°N 158.38111°WCoordinates: 59°19′46″N 158°22′52″W / 59.32944°N 158.38111°WPassengers 8 Crew 1 Injuries 4[1] Fatalities 4 passengers, 1 crew[2] Survivors 4[2] Aircraft type de Havilland Canada DHC-3T Turbine Otter Operator General Communication Tail number N455A[3] cn:206 Flight origin Nerka Lake, Alaska[4] Destination HRM Sports, a fish camp on the Nushagak River The 2010 Alaska Turbine Otter crash was a fatal accident that occurred on August 9, 2010, when a privately operated amphibious floatplane crashed near Aleknagik, Alaska, killing five of the nine passengers and crew. The fatalities included former United States Senator for Alaska Ted Stevens, while the survivors included former Administrator of NASA and current CEO of EADS North America, Sean O'Keefe, and his son. The aircraft, a de Havilland Canada single-engined turboprop-driven DHC-3T Turbo-Otter registered to General Communication Inc., crashed on a mountainside while on a flight between two fishing lodges. Stevens and O'Keefe had been on a fishing trip when their airplane was reported overdue. The wreckage was quickly located after an aerial search, but rescue efforts were hampered by poor weather. The cause of the crash is unknown.[5]
Contents
Accident
The floatplane crashed at around 2:30pm Alaska Daylight Time (UTC-8), 10 miles (16 km) northwest of Aleknagik.[4][6] After it was reported that the aircraft had not landed as scheduled, other pilots launched a search and located the wreckage on a 40-degree slope in the mountainous Dillingham region.[4] The flight was being conducted under visual flight rules and was not monitored by radar at the time of the accident, since there is no such coverage in the area under 4000 feet.[7] Other pilots who had flown in the same area during the course of the day described weather conditions in the region as "very bad" [8] with visibility at times being less than 1 mile (1.6 km).[9]
Rescue efforts
Local responders were on the mountain within a half hour of the plane being located around 6:30pm. A doctor, and a handful of local responders were dropped off by helicopter the same day[10] and spent the night providing aid to crash survivors.
Early in the morning as the Alaska Air National Guard arrived at the scene, also by helicopter, the first responders assisted rescuers in navigating to the site with rain and fog in the area hampering rescue and recovery efforts.[2][6][11]
U.S. Coast Guard assets from Air Station Kodiak were also launched. An MH-60J Jayhawk helicopter crew arrived on scene and deployed their rescue swimmer to the crash site to assist Air National Guard pararescuemen in extricating and treating patients for transport to medical care. Survivors were hoisted into and transported to Dillingham in both the Air National Guard and Coast Guard helicopters. The crew was met in Dillingham by an HC-130H Hercules aircraft and crew from Coast Guard Air Station Kodiak. They embarked and transported several patients including Mr. O'Keffe's son William. The aircrew also transported two Air National Guard pararescuemen so they could continue work on and monitor the medical conditions of the survivors. Due to the nature of the survivor's injuries the cabin could not be pressurized and the aircrew flew at a lower altitude. All patients were delivered to awaiting EMS in Anchorage at Kulis Air National Guard Base.
A spokesperson for the Alaska National Guard said that rescuers were giving medical aid to survivors of the crash,[12] and that three survivors were being airlifted to Providence Alaska Medical Center in Anchorage.[13] Upon examination of the wreckage it was discovered that the ELT antenna had separated from the ELT housing on impact, thus disabling the emergency signal.[14]
Passengers
The aircraft was carrying eight passengers and one pilot. Four of the passengers and the pilot died and two more were badly injured,[15] with the last two suffering only minor injuries.[4][14] Among the five fatalities was former U.S. Senator Ted Stevens. He had served as a Republican Senator from Alaska from 1968 to 2009. Also among the fatalities were a GCI executive and her 16 year old daughter.[16] Among the survivors were former NASA Administrator Sean O'Keefe and his teenage son, who both sustained non-life threatening injuries but were listed in critical and serious conditions respectively the night after the crash.[1] O'Keefe sustained leg and neck injuries,[17] and his teeth were broken.[18]
Stevens and O'Keefe had been fishing together before, and had been planning a fishing trip to a site near Dillingham at the time of the crash.[15] Stevens had survived a crash at Anchorage International Airport in 1978 that killed his first wife.[19] Pilot Theron "Terry" Smith, who also died, had lost his son in law in another plane crash less than two weeks before.[20]
Also among the dead was one of Stevens' former staff members, Bill Phillips. His youngest son, Willy, was seriously injured, and had to spend the night at the crash site with his dead father.[21]
Investigation
The National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) sent a team to the site of the accident to investigate the cause of the crash.[22] The team returned an inconclusive report in May, 2011. They speculated that the pilot, a recovered stroke victim, may have fallen asleep or had a seizure but there was no direct evidence to support these theories. The report was critical of the FAA's re-certification process, stating:
The Federal Aviation Administration's internal guidance for medical certification of pilots following stroke is inadequate because it is conflicting and unclear, does not specifically address the risk of recurrence associated with such an event, and does not specifically recommend a neuropsychological evaluation (formal cognitive testing) to evaluate potential subtle cognitive impairment.
The report went on to note that the plane was equipped with a Terrain Awareness and Warning System, but that the pilot had elected to fly with the system turned off. Because much of Alaska's terrain is highly variable bush pilots will often de-activate the system as it issues many false warnings. [23]
References
- ^ a b "Ex-NASA chief O'Keefe survives Alaska crash that killed Stevens". USA Today. August 10, 2010. http://content.usatoday.com/communities/ondeadline/post/2010/08/ex-nasa-chief-okeefe-survives-alaska-crash-that-killed-stevens/1.
- ^ a b c "Rescuers At Ted Stevens Alaska Crash Site". NPR. August 10, 2010. http://www.npr.org/blogs/thetwo-way/2010/08/10/129106215/alaska-ted-stevens-sean-o-okeefe-crash.
- ^ "Reports: Former Sen. Ted Stevens in Alaska Plane Crash". PBS Newshour. http://www.pbs.org/newshour/rundown/2010/08/reports-ted-stevens-in-alaska-plane-crash.html.
- ^ a b c d By the CNN Wire Staff (August 11, 2010). "Former U.S. senator may have been on plane that crashed in Alaska". CNN.com. http://www.cnn.com/2010/US/08/10/alaska.plane.crash/?hpt=T1. Retrieved August 10, 2010.
- ^ Halsey, Ashley III and Lonnae O'Neal Parker. "The Waiting: Survivors of the Ted Stevens plane crash in Alaska wondered if help would reach them in time." Washington Post. Sunday November 28, 2010. 3. Retrieved on November 24, 2010.
- ^ a b ""GCI executive recalls plane crash that killed Ted Stevens" - Alaska Dispatch". www.alaskadispatch.com. December 14, 2010. http://www.alaskadispatch.com/dispatches/news/6387-gci-executive-recalls-plane-crash-that-killed-ted-stevens. Retrieved August 14, 2010.
- ^ Yardley, William; Robbins, Liz (August 10, 2010). "Former Senator Ted Stevens Is in Plane Crash". New York Times. http://www.nytimes.com/2010/08/11/us/11crash.html?_r=1&hp.
- ^ Flying Conditions Had Been Poor in Crash Area Alaska Public Radio Network 8-10-10
- ^ Stevens Dies in Plane Crash; Some Survivors Flown to Anchorage Alaska Public Radio Network 8-10-10
- ^ Saul, Joshua; Craig Medred, Jill Burke and Patti Epler (August 11, 2010). "In GCI crash, grassroots search and rescue led to 'horrible' crash scene". Alaska Dispatch. http://www.alaskadispatch.com/projects/ted-stevens-1923-2010/6349-in-gci-crash-grassroots-search-and-rescue-led-to-horrible-crash-scene. Retrieved 17 August 2010.
- ^ Murphy, Kim (August 10, 2010). "Alaska plane crash: Former Sen. Ted Stevens feared dead in Alaska plane crash". latimes.com. http://www.latimes.com/news/nationworld/nation/la-na-alaska-crash-20100811,0,2706610.story.
- ^ BECKY BOHRER (August 10, 2010). "The Associated Press: Rescuers arrive to help Alaska plane crash victims". Google.com. http://www.google.com/hostednews/ap/article/ALeqM5iImeWBx3jNzOyQyuAiDaV67MSTXQD9HGNKAG0. Retrieved August 10, 2010.
- ^ "Plane carrying ex-Sen. Stevens crashes-TODAYshow.com". Today.msnbc.msn.com. http://today.msnbc.msn.com/id/38637072/ns/us_news-life. Retrieved August 10, 2010.
- ^ a b "Preliminary Report". NTSB. 2010-08-27. http://www.ntsb.gov/ntsb/GenPDF.asp?id=ANC10MA068&rpt=p. Retrieved 2010-09-06.
- ^ a b ""Former Senator Ted Stevens dies in Alaska plane crash" - BBC News". bbc.co.uk. December 14, 2004. http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-us-canada-10928024. Retrieved August 10, 2010.
- ^ "Former Alaska Sen. Ted Stevens dies in plane crash". Associated Press. August 10, 2010. http://news.yahoo.com/s/ap/us_alaska_plane_crash.
- ^ Halsey, Ashley III and Lonnae O'Neal Parker. "The Waiting: Survivors of the Ted Stevens plane crash in Alaska wondered if help would reach them in time." Washington Post. Sunday November 28, 2010. 5. Retrieved on November 24, 2010. "Emerging from his haze, Sean O'Keefe felt a bizarre sensation in his mouth. Like chewing on gravel without taking a bite. He explored that mystery with his tongue until it registered: His mouth was awash with his own broken teeth."
- ^ Halsey, Ashley III and Lonnae O'Neal Parker. "The Waiting: Survivors of the Ted Stevens plane crash in Alaska wondered if help would reach them in time." Washington Post. Sunday November 28, 2010. 1. Retrieved on November 24, 2010. "Emerging from his haze, Sean O'Keefe felt a bizarre sensation in his mouth. Like chewing on gravel without taking a bite. He explored that mystery with his tongue until it registered: His mouth was awash with his own broken teeth."
- ^ by Mark HosenballAugust 11, 2010. "NTSB Warned About Alaska Pilots' Risky Ways—and Ted Stevens Argued". Newsweek. http://www.newsweek.com/blogs/declassified/2010/08/11/ntsb-warned-about-alaska-pilots-risky-ways-and-ted-stevens-argued.html. Retrieved 2010-08-13.
- ^ Pilot in GCI plane crash lost son-in-law in C-17 crash last month Joshua Saul, Alaska Dispatch 8-10-2010
- ^ E:60 report, "Band of Brothers", November 8, 2011
- ^ Yardley, William; Robbins, Liz (August 10, 2010). "Former Senator Ted Stevens Is in Plane Crash". New York Times. http://www.nytimes.com/2010/08/11/us/11crash.html?_r=2&hp. "NTSB said it was sending a team of investigators to the crash site"
- ^ Investigators find no clear cause for crash that killed Ted Stevens Jim Burke, Alaska Dispatch, 5/24/2011
External links
 External images
External images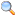
Photos of N455A at Airliners.net 
Photos of N455A at JetPhotos.net 
Photos of N455A at Flickr  News related to Former US Senator Ted Stevens dies in plane crash at Wikinews
News related to Former US Senator Ted Stevens dies in plane crash at Wikinews- Accident description at the Aviation Safety Network
- "Governor Remembers Victims of Plane Crash." Office of the Governor of Alaska
← 2009 · Aviation accidents and incidents in 2010 · 2011 → Jan 2–5 Danube Wings Flight 8230
Jan 21 Cargolux Flight 7933
Jan 24 Taban Air Flight 6437
Jan 25 Ethiopian Airlines Flight 409
Feb 11 Trigana Air Flight 168
Feb 18 Austin crash
Mar 22 Aviastar-TU Flight 1906
Apr 7 United Airlines Flight 663
Apr 10 Polish Air Force Tu-154
Apr 13 Merpati Nusantara Flight 836
Apr 13 Cathay Pacific Flight 780
Apr 13 AeroUnion Flight 302
Apr 14 – May 23 Eyjafjallajökull eruption
Apr 21 Interisland Airlines An-12
May 12 Afriqiyah Airways Flight 771May 15 Blue Wing Airlines An-28
May 17 Pamir Airways Flight 112
May 22 Air India Express Flight 812
Jun 19 Air Service Berlin C-47
Jun 20 Aéro Service CASA C-212 Aviocar
Jul 26 Israeli helicopter disaster
Jul 27 Lufthansa Cargo 8460
Jul 28 Airblue Flight 202
Jul 28 Alaska C-17 crash
Aug 3 Katekavia Flight 9357
Aug 9 JetBlue Flight 1052
Aug 10 Alaskan DHC-3 Turbo Otter
Aug 16 AIRES Flight 8250
Aug 24 Agni Air Flight 101
Aug 24 Henan Airlines Flight 8387Aug 25 Filair Let L-410
Sep 3 UPS Airlines Flight 6
Sep 4 New Zealand Fletcher FU24
Sep 7 Alrosa Mirny Air Enterprise Flight 514
Sep 13 Conviasa Flight 2350
Oct 6 Tajik National Guard Helicopter crash
Oct 12 Transafrik International Flight 662
Oct 29 Cargo plane bomb plot
Nov 4 Qantas Flight 32
Nov 4 Aero Caribbean Flight 883
Nov 5 Karachi Beechcraft 1900
Nov 11 Tarco Airlines crash
Nov 28 Sun Way Flight 4412
Dec 4 South East Airlines Flight 372
Dec 15 Okhaldhunga crashIncidents resulting in at least 50 deaths shown in italics. Deadliest incident shown in bold smallcaps.Categories:- Dillingham Census Area, Alaska
- Aviation accidents and incidents in the United States in 2010
- Aviation accidents and incidents in Alaska
- 2010 in Alaska
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
