- DNA polymerase mu
-
Polymerase (DNA directed), mu 
PDB rendering based on 2dun.Available structures PDB 2DUN, 2HTF Identifiers Symbols POLM; FLJ35482; Pol Mu; Tdt-N External IDs OMIM: 606344 MGI: 1860191 HomoloGene: 41170 GeneCards: POLM Gene EC number 2.7.7.7 Gene Ontology Molecular function • DNA binding
• DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity
• DNA nucleotidylexotransferase activity
• transferase activity
• metal ion bindingCellular component • intracellular
• nucleusBiological process • DNA repair
• DNA recombination
• somatic hypermutation of immunoglobulin genes
• B cell differentiationSources: Amigo / QuickGO RNA expression pattern 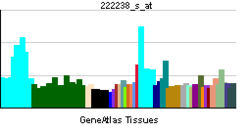
More reference expression data Orthologs Species Human Mouse Entrez 27434 54125 Ensembl ENSG00000122678 ENSMUSG00000020474 UniProt Q9NP87 Q7TN90 RefSeq (mRNA) NM_013284 NM_017401.2 RefSeq (protein) NP_037416 NP_059097.2 Location (UCSC) Chr 7:
44.11 – 44.12 MbChr 11:
5.73 – 5.74 MbPubMed search [1] [2] DNA polymerase mu is a human protein encoded by the POLM gene.[1]
Function
Pol μ is a member of the X family of DNA polymerases. It participates in resynthesis of damaged or missing nucleotides during the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway of DNA repair.[2] Pol μ interacts with Ku and DNA ligase IV, which also participate in NHEJ.[3] It is structurally and functionally related to pol λ, and, like pol λ, pol μ has a BRCT domain that is thought to mediate interactions with other DNA repair proteins.[4] Unlike pol λ, however, pol μ has the unique ability to add a base to a blunt end that is templated by the overhang on the opposite end of the double-strand break.[5] Pol μ is also closely related to terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT), a specialized DNA polymerase that adds random nucleotides to DNA ends during V(D)J recombination, the process by which B-cell and T-cell receptor diversity is generated in the vertebrate immune system. Like TdT, pol μ participates in V(D)J recombination, but only during heavy chain rearrangements.[6] This is distinct from pol λ, which is involved in light chain rearrangements.[7]
References
- ^ "Entrez Gene: POLM polymerase (DNA directed), mu". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=27434.
- ^ Daley JM, Laan RL, Suresh A, Wilson TE (August 2005). "DNA joint dependence of pol X family polymerase action in nonhomologous end joining". J. Biol. Chem. 280 (32): 29030–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.M505277200. PMID 15964833.
- ^ Mahajan KN, Nick McElhinny SA, Mitchell BS, Ramsden DA (July 2002). "Association of DNA polymerase mu (pol mu) with Ku and ligase IV: role for pol mu in end-joining double-strand break repair". Mol. Cell. Biol. 22 (14): 5194–202. doi:10.1128/MCB.22.14.5194-5202.2002. PMC 139779. PMID 12077346. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=139779.
- ^ Nick McElhinny SA, Ramsden DA (August 2004). "Sibling rivalry: competition between Pol X family members in V(D)J recombination and general double strand break repair". Immunol. Rev. 200: 156–64. doi:10.1111/j.0105-2896.2004.00160.x. PMID 15242403.
- ^ Nick McElhinny SA, Havener JM, Garcia-Diaz M, et al. (August 2005). "A gradient of template dependence defines distinct biological roles for family X polymerases in nonhomologous end joining". Mol. Cell 19 (3): 357–66. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2005.06.012. PMID 16061182.
- ^ Bertocci B, De Smet A, Berek C, Weill JC, Reynaud CA (August 2003). "Immunoglobulin kappa light chain gene rearrangement is impaired in mice deficient for DNA polymerase mu". Immunity 19 (2): 203–11. doi:10.1016/S1074-7613(03)00203-6. PMID 12932354.
- ^ Bertocci B, De Smet A, Weill JC, Reynaud CA (July 2006). "Nonoverlapping functions of DNA polymerases mu, lambda, and terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase during immunoglobulin V(D)J recombination in vivo". Immunity 25 (1): 31–41. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2006.04.013. PMID 16860755.
PDB gallery Categories:- Human proteins
- Chromosome 7 gene stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.