Cytidine diphosphate glucose
- Cytidine diphosphate glucose
-
| Cytidine diphosphate glucose |
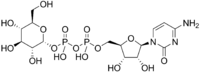 |
[[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(4-amino-2-oxopyrimidin-1-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl] [(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl] hydrogen phosphate
|
|
|
| Identifiers |
| CAS number |
2906-23-2  Y Y |
| PubChem |
439244 |
| ChemSpider |
388381  N N |
| Jmol-3D images |
Image 1 |
- O=P(O[C@H]1O[C@@H]([C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O)CO)(O)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]3O[C@@H](N2/C=C\C(=N/C2=O)\N)[C@H](O)[C@@H]3O
|
- InChI=1S/C15H25N3O16P2/c16-7-1-2-18(15(25)17-7)13-11(23)9(21)6(31-13)4-30-35(26,27)34-36(28,29)33-14-12(24)10(22)8(20)5(3-19)32-14/h1-2,5-6,8-14,19-24H,3-4H2,(H,26,27)(H,28,29)(H2,16,17,25)/t5-,6-,8-,9-,10+,11-,12-,13-,14-/m1/s1
 N N
Key: CGPHZDRCVSLMCF-JZMIEXBBSA-N  N N
|
| Properties |
| Molecular formula |
C15H25N3O16P2 |
| Molar mass |
565.32 g mol−1 |
 N diphosphate glucose (verify) (what is: N diphosphate glucose (verify) (what is:  Y/ Y/ N?) N?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) |
| Infobox references |
Cytidine diphosphate glucose, often abbreviated CDP-glucose, is a nucleotide-linked sugar consisting of cytidine diphospahte and glucose.[1][2]
Biosynthesis
CDP-glucose is produced from CTP and glucose-1-phosphate by the enzyme glucose-1-phosphate cytidylyltransferase.
References
| v · nucleotide sugars |
|
|
|
|
biochemical families: prot · nucl · carb (glpr, alco, glys) · lipd (fata/i, phld, strd, gllp, eico) · amac/i · ncbs/i · ttpy/i
|
|
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
Glucose-1-phosphate cytidylyltransferase — In enzymology, a glucose 1 phosphate cytidylyltransferase (EC number|2.7.7.33) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:CTP + alpha D glucose 1 phosphate ightleftharpoons diphosphate + CDP glucoseThus, the two substrates of this enzyme… … Wikipedia
Adénosine diphosphate — Pour les articles homonymes, voir ADP. Adénosine diphosphate … Wikipédia en Français
Thymidine diphosphate — IUPAC name [(2R,3S,5R) 3 hydroxy 5 (5 methyl 2,4 dioxopyrimidin 1 yl)oxolan 2 yl]methyl pho … Wikipedia
metabolism — /meuh tab euh liz euhm/, n. 1. Biol., Physiol. the sum of the physical and chemical processes in an organism by which its material substance is produced, maintained, and destroyed, and by which energy is made available. Cf. anabolism, catabolism … Universalium
LIPIDES — Le terme de lipides recouvre un ensemble de composés naturels qui ont la propriété d’être insolubles dans l’eau, en raison de la présence, dans leurs molécules, de longues chaînes hydrocarbonées d’acides gras ou de dérivés. À l’inverse, ils sont… … Encyclopédie Universelle
Metabolism — Cell metabolism redirects here. For the journal, see Cell Metabolism. Structure of adenosine triphosphate, a central intermediate in energy metabolism Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē , change or Greek: μεταβολισμός metabolismos,… … Wikipedia
CDP-paratose 2-epimerase — In enzymology, a CDP paratose 2 epimerase (EC number|5.1.3.10) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:CDP 3,6 dideoxy D glucose ightleftharpoons CDP 3,6 dideoxy D mannoseHence, this enzyme has one substrate, CDP 3,6 dideoxy D glucose,… … Wikipedia
CDP-4-dehydro-6-deoxyglucose reductase — In enzymology, a CDP 4 dehydro 6 deoxyglucose reductase (EC number|1.17.1.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:CDP 4 dehydro 3,6 dideoxy D glucose + NAD(P)+ + H2O ightleftharpoons CDP 4 dehydro 6 deoxy D glucose + NAD(P)H + H+The… … Wikipedia
Uracil — Uracil … Wikipedia
List of EC numbers (EC 2) — This list contains a list of EC numbers for the second group, EC 2, transferases, placed in numerical order as determined by the Nomenclature Committee of the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.EC 2.1: Transferring One… … Wikipedia
 [[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(4-amino-2-oxopyrimidin-1-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl] [(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl] hydrogen phosphateOther namesCDP-glucose
[[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(4-amino-2-oxopyrimidin-1-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl] [(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl] hydrogen phosphateOther namesCDP-glucose

 diphosphate glucose (verify) (what is:
diphosphate glucose (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)