- Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi
-
The native form of this personal name is Csíkszentmihályi Mihály. This article uses the Western name order.
Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi (
 /ˈmiːhaɪ ˌtʃiːksɛntməˈhaɪ.iː/ mee-hy cheek-sent-mə-hy-ee; Hungarian: Csíkszentmihályi Mihály [ˈtʃiːksɛntmihaːji ˈmihaːj]; born September 29, 1934, in Fiume, Italy – now Rijeka, Croatia) is a Hungarian psychology professor, who emigrated to the United States at the age of 22. Now at Claremont Graduate University, he is the former head of the department of psychology at the University of Chicago and of the department of sociology and anthropology at Lake Forest College.
/ˈmiːhaɪ ˌtʃiːksɛntməˈhaɪ.iː/ mee-hy cheek-sent-mə-hy-ee; Hungarian: Csíkszentmihályi Mihály [ˈtʃiːksɛntmihaːji ˈmihaːj]; born September 29, 1934, in Fiume, Italy – now Rijeka, Croatia) is a Hungarian psychology professor, who emigrated to the United States at the age of 22. Now at Claremont Graduate University, he is the former head of the department of psychology at the University of Chicago and of the department of sociology and anthropology at Lake Forest College.He is noted for both his work in the study of happiness and creativity and also for his notoriously difficult name, in terms of pronunciation for non-native speakers of the Hungarian language, but is best known as the architect of the notion of flow and for his years of research and writing on the topic. He is the author of many books and over 120 articles or book chapters. Martin Seligman, former president of the American Psychological Association, described Csikszentmihalyi as the world's leading researcher on positive psychology.[1] Csikszentmihalyi once said "Repression is not the way to virtue. When people restrain themselves out of fear, their lives are by necessity diminished. Only through freely chosen discipline can life be enjoyed and still kept within the bounds of reason."[2] His works are influential and are widely cited.[3]
Contents
Personal background
He received his B.A. in 1960 and his Ph.D. in 1965, both from the University of Chicago.
He is the father of MIT Media Lab researcher Christopher Csikszentmihalyi and University of California - Berkeley[4] professor of philosophical and religious traditions of China and East Asia, Mark Csikszentmihalyi.
In 2009, he was awarded the Clifton Strengths Prize [5] and received the Széchenyi Prize at a ceremony in Budapest in 2011[6].
Flow
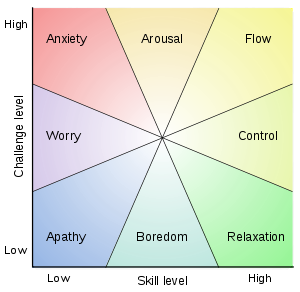
Main article: Flow (psychology)Mental state in terms of challenge level and skill level, according to Csikszentmihalyi.[7] (Click on a fragment of the image to go to the appropriate article)
In his seminal work, Flow: The Psychology of Optimal Experience, Csíkszentmihályi outlines his theory that people are most happy when they are in a state of flow— a state of concentration or complete absorption with the activity at hand and the situation. It is a state in which people are so involved in an activity that nothing else seems to matter (Csikszentmihalyi,1990). The idea of flow is identical to the feeling of being in the zone or in the groove. The flow state is an optimal state of intrinsic motivation, where the person is fully immersed in what he or she is doing. This is a feeling everyone has at times, characterized by a feeling of great absorption, engagement, fulfillment, and skill—and during which temporal concerns (time, food, ego-self, etc.) are typically ignored.[8]
In an interview with Wired magazine, Csíkszentmihályi described flow as "being completely involved in an activity for its own sake. The ego falls away. Time flies. Every action, movement, and thought follows inevitably from the previous one, like playing jazz. Your whole being is involved, and you're using your skills to the utmost."[9]
To achieve a flow state, a balance must be struck between the challenge of the task and the skill of the performer. If the task is too easy or too difficult, flow cannot occur. Both skill level and challenge level must be matched and high; if skill and challenge are low and matched, then apathy results.[7]
The flow state also implies a kind of focused attention, and indeed, it has been noted that mindfulness, meditation, yoga, the Alexander Technique, and martial arts seem to improve a person's capacity for flow. Among other benefits, all of these activities train and improve attention.[citation needed]
In short, flow could be described as a state where attention, motivation, and the situation meet, resulting in a kind of productive harmony or feedback.[citation needed]
See also
- Creativity
- Motivation
- Attention
- Psychology
- Cognitive Science
- John Neulinger
- Experience Sampling Method
Publications
- Csikszentmihalyi, Mihaly (1975). Beyond Boredom and Anxiety: Experiencing Flow in Work and Play, San Francisco: Jossey-Bass. ISBN 0-87589-261-2
- Csikszentmihalyi, Mihaly (1978) Intrinsic Rewards and Emergent Motivation in The Hidden Costs of Reward : New Perspectives on the Psychology of Human Motivation eds Lepper, Mark R;Greene, David, Erlbaum: Hillsdale: NY 205-216
- Csikszentmihalyi, Mihaly and Csikszentmihalyi, Isabella Selega, eds. (1988). Optimal Experience: Psychological studies of flow in consciousness, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-34288-0
- Csikszentmihalyi, Mihaly (1990). Flow: The Psychology of Optimal Experience. New York: Harper and Row. ISBN 0-06-092043-2
- Csikszentmihalyi, Mihaly (1994). "The Evolving Self", New York: Harper Perennial . ISBN 0060921927
- Csikszentmihalyi, Mihaly (1996). Creativity : Flow and the Psychology of Discovery and Invention. New York: Harper Perennial. ISBN 0-06-092820-4
- Csikszentmihalyi, Mihaly (1998). Finding Flow: The Psychology of Engagement With Everyday Life. Basic Books. ISBN 0-465-02411-4 (a popular exposition emphasizing technique)
- Gardner, Howard, Csikszentmihalyi, Mihaly, and Damon, William (2002). Good Work: When Excellence and Ethics Meet. New York, Basic Books.
- Gardner, Howard, Csikszentmihalyi, Mihaly, and Damon, William (2002). Good Business: Leadership, Flow, and the Making of Meaning. Basic Books. ISBN 0465026087
References
- ^ Thinker of the Year Award
- ^ http://www.focusdep.com/quotes/topics/virtue/start/0/
- ^ Nigel King & Neil Anderson (2002). Managing Innovation and Change. Cengage Learning EMEA. p. 82. (ISBN 1861527837)
- ^ http://eall.wisc.edu/?q=node/28 East Asian Languages and Literature
- ^ http://strengths.org/prize.shtml
- ^ http://www.cgu.edu/pages/4546.asp?item=5242
- ^ a b Csikszentmihalyi, M., Finding Flow, 1997.
- ^ Csikszentmihalyi, M. (1990). Flow: The Psychology of Optimal Experience. New York: Harper and Row. ISBN 0-06-092043-2
- ^ Geirland, John (1996). "Go With The Flow". Wired magazine, September, Issue 4.09.
External links
Categories:- American psychologists
- Hungarian psychologists
- American science writers
- Positive psychologists
- Creativity researchers
- Psychology educators
- Members of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences
- University of Chicago faculty
- University of Chicago alumni
- Hungarian expatriates in Italy
- Hungarian scientists
- American people of Hungarian descent
- People from Rijeka
- 1934 births
- Living people
- Claremont Graduate University faculty
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.