- Chamazulene
-
Chamazulene 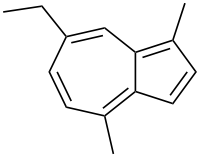 7-Ethyl-1,4-dimethylazuleneOther names1,4-Dimethyl-7-ethylazulene; Ba 2784; Camazulene; Chamazulen; Dimethulen; Dimethulene
7-Ethyl-1,4-dimethylazuleneOther names1,4-Dimethyl-7-ethylazulene; Ba 2784; Camazulene; Chamazulen; Dimethulen; DimethuleneIdentifiers CAS number 529-05-5 
PubChem 10719 ChemSpider 10268 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - c1(ccc(c2ccc(c2c1)C)C)CC
- InChI=1S/C14H16/c1-4-12-7-5-10(2)13-8-6-11(3)14(13)9-12/h5-9H,4H2,1-3H3
Key: GXGJIOMUZAGVEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
InChI=1/C14H16/c1-4-12-7-5-10(2)13-8-6-11(3)14(13)9-12/h5-9H,4H2,1-3H3
Key: GXGJIOMUZAGVEH-UHFFFAOYAM
Properties Molecular formula C14H16 Molar mass 184.28 g mol−1 Appearance Blue oil[1] Density 0.9883 (at 20 °C)[1] Boiling point 161 °C (at 12 mmHg)[1]
Hazards LD50 3 g/kg (i.m., mouse)[1] Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) Infobox references Chamazulene is an aromatic chemical compound with the molecular formula C14H16 found in a variety of plants including in chamomile (Matricaria chamomilla), wormwood (Artemisia absinthium), and yarrow (Achillea millefolium).[1] It is a blue-violet derivative of azulene which is biosynthesized from the sesquiterpene matricin.[2]
Chamazulene has anti-inflammatory properties in vivo.[2]
References

This article about an aromatic compound is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
