- Chaconine
-
Chaconine 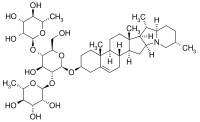 beta-D-Glucopyranoside, (3beta)-solanid-5-en-3-yl O-6-deoxy-alpha-L-mannopyranosyl-(1-2)-O-(6-deoxy-alpha-L-mannopyranosyl-(1-4))-
beta-D-Glucopyranoside, (3beta)-solanid-5-en-3-yl O-6-deoxy-alpha-L-mannopyranosyl-(1-2)-O-(6-deoxy-alpha-L-mannopyranosyl-(1-4))-Identifiers CAS number 20562-03-2 PubChem 104750 Beilstein Reference 77396 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - C[C@H]1CC[C@@H]2[C@H]([C@H]3[C@@H](N2C1)C[C@@H]4[C@@]3(CC[C@H]5[C@H]4CC=C6[C@@]5(CC[C@@H](C6)O[C@H]7[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O7)CO)O[C@H]8[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H](O8)C)O)O)O)O)O[C@H]9[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H](O9)C)O)O)O)C)C)C
Properties Molecular formula C45H73NO14 Molar mass 852.06 g mol−1 Melting point 243°C
 (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references α-Chaconine is a steroidal glycoalkaloid chemical compound that occurs in plants of the Solanaceae family. It is a natural toxicant produced in green potatoes and gives the potato a bitter taste.[1] Tubers produce this glycoalkaloid in response to stress, providing the plant with insecticidal and fungicidal properties.[1]
See also
- Solamargine
- Solanine
References
- ^ a b Kuiper-Goodman, T. and Nawrot, P.S. "Toxin profile:Solanine and Chaconine" IPCS, INCHEM
Categories:- Biochemistry stubs
- Alkaloids
- Plant toxins
- Potatoes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
