- Lake Manitoba
-
Lake Manitoba 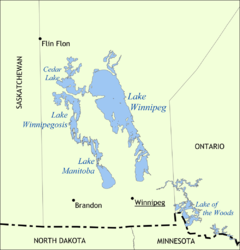
Location Manitoba Coordinates 51°00′N 98°50′W / 51°N 98.833°WCoordinates: 51°00′N 98°50′W / 51°N 98.833°W Primary inflows Waterhen River Whitemud River Primary outflows Fairford River Catchment area 54,630 km2 (21,090 sq mi) Basin countries Canada Max. length 200 km (120 mi) Max. width 45 km (28 mi) Surface area 4,624 km2 (1,785 sq mi) Max. depth 7 m (23 ft) Water volume 14.1 km3 (3.4 cu mi) Residence time North basin: 2 years; South basin: 28 years [1] Surface elevation 812 ft (247 m) Settlements Fairford, Steep Rock, St. Laurent, Sandy Bay Lake Manitoba is Canada's thirteenth largest lake (4,624 km2) and the world's 33rd largest freshwater lake. It is in central North America, in the Canadian province of Manitoba, which is named after the lake. It is located about 75 km northwest of the province's capital, Winnipeg, at 51°0′N 98°45′W / 51°N 98.75°W.
Contents
History
The lake, its shores populated by the Assiniboine and Cree, was made known to Europeans by La Vérendrye in the mid-1730s. He and his sons travelled from Fort La Reine through this lake to explore the Saskatchewan River and its environs. Forts were established on both the Saskatchewan and Cedar Lake. It also was part of the route of the fur trade to Hudson Bay.
The name derives from Cree manitou-wapow or Ojibwa manidoobaa, both meaning "straits of Manitou, the Great Spirit", a toponym referring to what are now called The Narrows in the centre of the lake. The lake was known to French explorers as Lac des Prairies.
Geography
The irregularly shaped lake, about 200 km long, is the smallest of a group of three large lakes, the other two being Lake Winnipeg (the largest) and Lake Winnipegosis, which are found on the floor of the prehistoric Glacial Lake Agassiz. The lake is subdivided into two connected but distinctly different basins: a small, irregular-shaped north basin and a much larger south basin. It is part of the watershed of the Nelson River and Hudson Bay.
The southern tip of the lake, 24 km north of Portage la Prairie, Manitoba, ends in the Delta Marsh, an important staging ground for migrating birds.
Communities on the lake include Fairford, Steep Rock, St. Laurent, and Sandy Bay.
River basins
The lake is primarily fed by Lake Winnipegosis to its northwest via the Waterhen River, with an average annual contribution of 1,900,000 acre feet (2.3 km3). The Whitemud River and local overland flow average about 257,000 acre feet (317,000,000 m3). Precipitation contributes about 1,800,000 acre feet (2.2 km3). From 1970 to 2003 the Portage Diversion has contributed an average annual volume of 246,800 acre feet (304,400,000 m3) from the Assiniboine River. Lake Manitoba drains northeast into Lake Winnipeg through the Fairford River to Lake St. Martin and then to the Dauphin River. The average annual river outflow is 2,030,000 acre feet (2.50 km3). Average evaporation is 2,020,000 acre feet (2.49 km3) per year. Most of the water inflow is from the Waterhen River (42% of the inflow) and from precipitation directly on the lake's surface (40%), while nearly 50% of the outflow is by evaporation.[2] This explains its hyposaline nature.[3]
Fishing
Lake Manitoba is one of the three main lakes in Manitoba's $30-million annual commercial fishing industry.[4]
The main marketable fish species caught on Lake Manitoba has changed from whitefish in the late 19th century to walleye, sauger and yellow perch today. There has been a large increase in rough fish like carp and mullet. Tulibee catch remains high, although it is not considered a commercial species.
The total recorded catch of the commercial winter fishery on the lake has declined from 15 million pounds (6.8 kt) annually in the late 1940s to less than 4.5 million pounds (2.0 kt) in 2002.
Regulation
Severe flooding around the lake led to the excavation of an improved outlet channel between 1899 and 1901. In 1933 following dry years in the late 1920s and early 1930s, the Province constructed a concrete control dam across the Fairford River immediately downstream of the channel. A new dam was constructed in 1961. The new structure is operated to try to control levels between 810.5 and 812.5 feet (247.0 and 247.7 m) above sea level.
Period Max level Average level Min level Av. annual range Pre 1960 816.25 ft (248.79 m) 812.17 ft (247.55 m) 809.92 ft (246.86 m) 1.4 ft (0.43 m) 1960–1999 813.48 ft (247.95 m) 811.92 ft (247.47 m) 810.36 ft (247.00 m) 1.27 ft (0.39 m) Manipogo
For many years there have been claims that a monster similar to Scotland's Loch Ness Monster and British Columbia's Ogopogo lives in the lake. It has been named Manipogo. Sightings of this serpent like sea monster have been going on since roughly 1908.
2011 Flooding
Due to above average snowfall over the winter of 2010-2011, and above average precipitation in the spring in the Lake Manitoba watershed, forecasted water levels on Lake Manitoba called for levels above the regulated upper range of 812.5 feet (247.7 m) above sea level and around the flood stage of 814 feet (248 m) above sea level. With the added inflows of the Portage Diversion due to high water levels on the Assiniboine River and it tributaries, of up to 34,000 cu ft/s (960 m3/s) of water, the forecast for Lake Manitoba was revised on numerous occasions until the predicted peak was between 817.3–817.5 feet (249.1–249.2 m) above sea level in mid-July. On May 31, 2011 a strong wind storm occurred on the lake with winds from the north and the north-west of 70 km/h gusting to 90 km/h causing major damage to beaches and communities on the south basin of the lake including Twin Lakes Beach, St. Laurent, St. Ambroise, Delta Beach, Lynch's Point, Big Point, and large areas of farmland.
Gallery
See also
Twin Lakes Beach, Manitoba Delta Marsh
References
- ^ http://www.gov.mb.ca/waterstewardship/pdf/rpt_shoal_lakes_report_fnl_2010_10_18_dsb.pdf
- ^ Volumes provided by Alf Warkentin Manitoba Water Stewardship
- ^ http://home.cc.umanitoba.ca/~mlast/publications/page1/assets/1988hydrobiol.pdf
- ^ http://www.gov.mb.ca/conservation/fish/
External links
Categories:- Lakes of Manitoba
- Hudson's Bay Company trading posts
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.










