- 2.2.2-Cryptand
-
2.2.2-Cryptand  Systematic name4,7,13,16,21,24-Hexaoxa-1,10-diazabicyclo[8.8.8]hexacosane[1]Other namesCryptating agent 222[citation needed]
Systematic name4,7,13,16,21,24-Hexaoxa-1,10-diazabicyclo[8.8.8]hexacosane[1]Other namesCryptating agent 222[citation needed]Identifiers Abbreviations Crypt-222 CAS number 23978-09-8 
PubChem 72801 ChemSpider 65637 
EC number 245-962-4 MeSH Cryptating+agent+222 RTECS number MP4750000 Beilstein Reference 620282 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - C1COCCN2CCOCCOCCN(CCO1)CCOCCOCC2
Properties Molecular formula C18N2H36O6 Molar mass 376.4882 g mol-1 Exact mass 376.257336894 g mol-1 Melting point 68-71 °C, 341-344 K, 154-160 °F
Hazards GHS pictograms 
GHS signal word WARNING GHS hazard statements H315, H319, H335 GHS precautionary statements P261, P305+351+338 EU classification  Xi
XiR-phrases R36/37/38 S-phrases S26, S36  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references 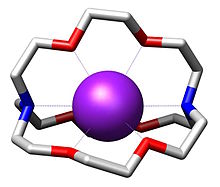 Structure of a [2.2.2]cryptand encapsulating a potassium cation (purple). At crystalline state, obtained with an X-ray diffraction.[2]
Structure of a [2.2.2]cryptand encapsulating a potassium cation (purple). At crystalline state, obtained with an X-ray diffraction.[2]
2,2,2-Cryptand is one of the most important members of the cryptand family of chelating agents. In Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry (2005), IUPAC recommends the abbreviation "crypt-222".
References
- ^ "cryptating agent 222 - PubChem Public Chemical Database". The PubChem Project. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. Descriptors Computed from Structure. http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/summary/summary.cgi?cid=72801.
- ^ Alberto, R.; Ortner, K.; Wheatley, N.; Schibli, R.; Schubiger, A. P. (2001). "Synthesis and properties of boranocarbonate: a convenient in situ CO source for the aqueous preparation of [99mTc(OH2)3(CO)3]+". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 121 (13): 3135–3136. doi:10.1021/ja003932b.
This article about an organic compound is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
