- Mauna Loa Observatory
-
The Mauna Loa Observatory (MLO) is an atmospheric baseline station on Mauna Loa volcano, on the big island of Hawaii.
Contents
The observatory
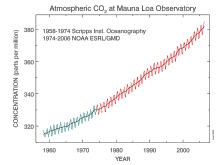
Since 1956 Mauna Loa Observatory (MLO) has been monitoring and collecting data relating to atmospheric change, and is known especially for the continuous monitoring of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2), which is sometimes referred to as the Keeling Curve. The observatory is under the Earth System Research Laboratory which is part of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
The latest observation of CO2 concentrations from MLO can be found at web sites along with data from other sites,[1] and trends at Mauna Loa.[2] The MLO levels can be compared with other sites in the global monitoring network.
MLO has activities at five locations on the Big Island. The primary observing site is located at the 3397 m (11,141 ft) level on Mauna Loa's north slope, 19°32′10″N 155°34′34″W / 19.53611°N 155.57611°WCoordinates: 19°32′10″N 155°34′34″W / 19.53611°N 155.57611°W about 5 km north of the summit Mokuaweoweo. The Mauna Loa Solar Observatory shares this site. The administration and some data processing are done in the Hilo, Hawaii office. Kulani Mauka is a rain collection site. Cape Kumukahi is a flask sample site located on the eastern-most point of Hawaii. At the Hilo airport weekly balloon-borne instruments are prepared and launched to measure ozone from the surface to usually over 30 km.[3] The observatory site is also a temporary home to a cosmic microwave background observatory called AMiBA.[4]
Mauna Loa was originally chosen as a monitoring site because, located far from any continent, the air sampled is a good average for the central pacific. Being high, it is above the inversion layer where most of the local effects are present. There was already a rough road to the summit built by the military. The contamination from local volcanic sources is sometimes detected at the observatory, and is then removed from the background data.[5]
See also
References
- ^ "Carbon Cycle-Greenhouse Gases Observatory Measurements". National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration. http://www.cmdl.noaa.gov/ccgg/insitu.html. Retrieved 2009-07-04.
- ^ "Trends in Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide - Mauna Loa". http://www.esrl.noaa.gov/gmd/ccgg/trends/. Retrieved 2009-07-04.
- ^ "Ozonesone". NOAA Ozone Layer web site. http://www.ozonelayer.noaa.gov/action/ozonesonde.htm. Retrieved 2009-07-04.
- ^ "Mauna Loa Solar Observatory". official web site. http://mlso.hao.ucar.edu. Retrieved 2009-07-04.
- ^ Steven Ryan (1995). "Quiescent Outgassing of Mauna Loa Volcano 1958-1994". Mauna Loa Revealed: Structure, Composition, History, and Hazards Geophysical Monograph 92, American Geophysical Union. Archived from the original on 1998-01-14. http://web.archive.org/web/19980114152259/http://mloserv.mlo.hawaii.gov/publish/steve/VolcCO2.htm. Retrieved 2009-07-04.
External links
- NOAA Mauna Loa Observatory official web site
- Global Monitoring Division, Boulder, CO, USA
- Worldwide Carbon Dioxide concentrations - in real time
Categories:- Geophysical observatories
- Meteorological observatories
- Buildings and structures in Hawaii County, Hawaii
- Western United States building and structure stubs
- Hawaii stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.