- NFRKB
-
Nuclear factor related to kappaB binding protein Identifiers Symbols NFRKB; DKFZp547B2013; INO80G External IDs OMIM: 164013 MGI: 2442410 HomoloGene: 4492 GeneCards: NFRKB Gene Gene Ontology Molecular function • protease binding
• DNA bindingCellular component • nucleus
• nucleolus
• Ino80 complex
• Ino80 complexBiological process • DNA repair
• DNA recombination
• regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
• transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter
• inflammatory responseSources: Amigo / QuickGO RNA expression pattern 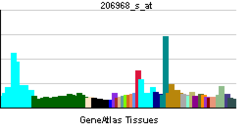
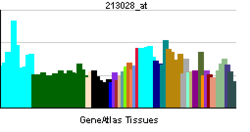
More reference expression data Orthologs Species Human Mouse Entrez 4798 235134 Ensembl ENSG00000170322 ENSMUSG00000042185 UniProt Q6P4R8 Q3UV62 RefSeq (mRNA) NM_001143835.1 NM_172766.3 RefSeq (protein) NP_001137307.1 NP_766354.2 Location (UCSC) Chr 11:
129.73 – 129.77 MbChr 9:
31.19 – 31.23 MbPubMed search [1] [2] Nuclear factor related to kappa-B-binding protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NFRKB gene.[1][2]
References
- ^ Adams BS, Leung K, Meltzer PS, Lewis KA, Wagner-McPherson C, Evans GA, Nabel GJ (Dec 1992). "Localization of the gene encoding R kappa B (NFRKB), a tissue-specific DNA binding protein, to chromosome 11q24-q25". Genomics 14 (2): 270–4. doi:10.1016/S0888-7543(05)80216-2. PMID 1427843.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: NFRKB nuclear factor related to kappaB binding protein". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=4798.
Further reading
- Olsen JV, Blagoev B, Gnad F et al. (2006). "Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks". Cell 127 (3): 635–48. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.026. PMID 17081983.
- Nousiainen M, Silljé HH, Sauer G et al. (2006). "Phosphoproteome analysis of the human mitotic spindle". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103 (14): 5391–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.0507066103. PMC 1459365. PMID 16565220. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1459365.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA et al. (2004). "The Status, Quality, and Expansion of the NIH Full-Length cDNA Project: The Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=528928.
- Beausoleil SA, Jedrychowski M, Schwartz D et al. (2004). "Large-scale characterization of HeLa cell nuclear phosphoproteins". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101 (33): 12130–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.0404720101. PMC 514446. PMID 15302935. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=514446.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=139241.
- Urban MB, Schreck R, Baeuerle PA (1991). "NF-kappa B contacts DNA by a heterodimer of the p50 and p65 subunit". EMBO J. 10 (7): 1817–25. PMC 452856. PMID 2050119. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=452856.
- Adams BS, Leung KY, Hanley EW, Nabel GJ (1992). "Cloning of R kappa B, a novel DNA-binding protein that recognizes the interleukin-2 receptor alpha chain kappa B site". New Biol. 3 (11): 1063–73. PMID 1777480.
Categories:- Human proteins
- Chromosome 11 gene stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
