- PAOX
-
Polyamine oxidase (exo-N4-amino) Identifiers Symbols PAOX; DKFZp434J245; MGC45464; PAO External IDs MGI: 1916983 HomoloGene: 72096 GeneCards: PAOX Gene EC number 1.5.3.11 Gene Ontology Molecular function • oxidoreductase activity
• polyamine oxidase activityCellular component • peroxisome Biological process • electron transport Sources: Amigo / QuickGO RNA expression pattern 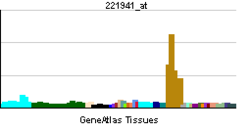
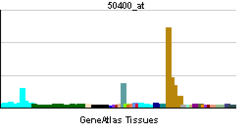
More reference expression data Orthologs Species Human Mouse Entrez 196743 212503 Ensembl ENSG00000148832 ENSMUSG00000025464 UniProt Q6QHF9 Q4GX45 RefSeq (mRNA) NM_152911.2 NM_153783.4 RefSeq (protein) NP_690875.1 NP_722478.2 Location (UCSC) Chr 10:
135.19 – 135.21 MbChr 7:
147.31 – 147.32 MbPubMed search [1] [2] Peroxisomal N(1)-acetyl-spermine/spermidine oxidase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PAOX gene.[1][2]
References
- ^ Wu T, Yankovskaya V, McIntire WS (Jun 2003). "Cloning, sequencing, and heterologous expression of the murine peroxisomal flavoprotein, N1-acetylated polyamine oxidase". J Biol Chem 278 (23): 20514–25. doi:10.1074/jbc.M302149200. PMID 12660232.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: PAOX polyamine oxidase (exo-N4-amino)". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=196743.
Further reading
- Järvinen A, Keinänen TA, Grigorenko NA et al. (2006). "Guide molecule-driven stereospecific degradation of alpha-methylpolyamines by polyamine oxidase". J. Biol. Chem. 281 (8): 4589–95. doi:10.1074/jbc.M509959200. PMID 16354669.
- Pledgie A, Huang Y, Hacker A et al. (2006). "Spermine oxidase SMO(PAOh1), Not N1-acetylpolyamine oxidase PAO, is the primary source of cytotoxic H2O2 in polyamine analogue-treated human breast cancer cell lines". J. Biol. Chem. 280 (48): 39843–51. doi:10.1074/jbc.M508177200. PMID 16207710.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=528928.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Clark HF, Gurney AL, Abaya E et al. (2003). "The secreted protein discovery initiative (SPDI), a large-scale effort to identify novel human secreted and transmembrane proteins: a bioinformatics assessment". Genome Res. 13 (10): 2265–70. doi:10.1101/gr.1293003. PMC 403697. PMID 12975309. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=403697.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=139241.
- Vujcic S, Liang P, Diegelman P et al. (2003). "Genomic identification and biochemical characterization of the mammalian polyamine oxidase involved in polyamine back-conversion". Biochem. J. 370 (Pt 1): 19–28. doi:10.1042/BJ20021779. PMC 1223169. PMID 12477380. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1223169.
Categories:- Human proteins
- Chromosome 10 gene stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
