- Magnetic field imaging
-
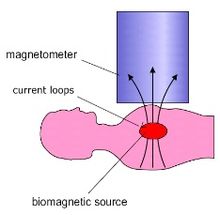
Magnetic Field Imaging (MFI) is a non-invasive and side-effect-free cardiac diagnostic method. It detects and records the electromagnetic signals that are associated with the heartbeat using a multi channel magnetic sensor array. The electric signals are known from the ECG and recordings of the magnetic signals are also known from Magnetocardiography (MCG). In comparison to MCG, MFI, among others, always records the whole relevant area above the chest of the person, is focused on clinical routine application and supplies convenient and easy to use parameters for the clinician based on images.
Background
The general principal of MFI is based on two facts:
- Cell activity in the human body is connected to electric activity (based on Galvani, Italy 1786).
- Electric current is associated with a corresponding magnetic field (based on Ørsted, Denmark 1819).
The difference between the electric and the magnetic signals:
In comparison to the electric signals, which are influenced by the differently conductive tissue of the body and varying resistance of the skin before they can be recorded, the magnetic signals travel through the body almost without disturbance. The differences in the electric potentials, that are recorded by the ECG, are directly depending on the inhomogeneity and geometry of the thorax, the magnetic signals outside of the thorax depend primarily on the intracellular currents of the cardiac tissue and only secondarily on the secondary currents generating the electric signal. Furthermore, the magnetic signals of so called vortex currents, which occur regularly in every heartbeat and include important information for an advanced and more accurate cardiac diagnosis (first theoretically described by John Wikswo),[1][2] can be acquired with an MFI system, but cannot be recorded electrically on the body surface (First experimental hint by Brockmeier et al. 1994[3] and comprehensive demonstration Brockmeier et al. 1997).[4]
Recording technology
The magnetic field changes detected by the MFI are about one million times weaker than the magnetic field of the earth. High end acquisition electronics and noise reduction concepts are necessary. As sensors the most sensitive magnetic sensors presently available, Superconducting Quantum Interference Devices (SQUID), which are cooled down to 4 K (-269 °C) with liquid helium, are used to acquire the signals.
Applications
The main fields of use are the risk stratification of ventricular tachycardia (VT) and the detection of stress induced ischemia. The MFI system can detect the onset of arrhythmic and ischemic diseases in a very early stage with high accuracy for both acute and asymptomatic patients.
- Early Detection: Arrhythmia; Ischemia; Angina pectoris; Cardiac microvascular diseases
- Direct diagnosis of heart function after myocardial infarction (MI) and surgery of heart transplantation
- On-going monitoring of patients with heart surgical intervention: Patients with a stent or who underwent a balloon dilatation; post bypass patients; post heart transplantation patients
As MFI is absolutely risk free and harmless for the patient, the procedure can be repeated without any negative effects for the patient, which gives the cardiologist the opportunity to observe a patient's progressive changes. The non-invasiveness of MFI makes it an ideal tool for the diagnosis of pregnant women as well as it can in addition detect the cardiac signal of an unborn child starting from the 4th month of pregnancy.
References
- ^ Wikswo, J.P., Barach, J.P. "Possible sources of new information in the magnetocardiogram" in J. Theoret. Biol. Vol. 95 pp. 721 - 729, 1982
- ^ Roth, B.J., Wikswo, J.P. "Electrically silent magnetic fields" in Biophys. J. Vol. 50 pp. 739 - 745, 1986
- ^ Brockmeier, K., Chomani, S., Erné, S.N. "Magnetocardiography and exercise test" in J. Electrocardiol. Vol. 27 pp. 137 - 142, 1994
- ^ Brockmeier, K. et al "Magnetocardiography and 32 lead potential mapping: Repolarisation in normal subjects during pharmacologically induced stress" in J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. Vol. 8 pp. 615 - 625, 1997
Medical test: Electrodiagnosis Electrocardiography Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Eyes Digestive system Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.