- Cyclopentadienylindium(I)
-
Cyclopentadienylindium(I)  Other namesindium cyclopentadienyl, cyclopentadienyl indium
Other namesindium cyclopentadienyl, cyclopentadienyl indiumIdentifiers CAS number 34822-89-4 ChemSpider 9270356 Properties Molecular formula C5H5In Molar mass 179.913 g/mol Appearance off-white solid Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) Infobox references Cyclopentadienylindium(I), C5H5In, is an organoindium compound containing indium in the +1 oxidation state. Commonly abbreviated to CpIn, it is a cyclopentadienyl complex with a half-sandwich structure. It was the first (1957[1]) low valent organoindium compound reported.
Preparation and chemistry
CpIn can be readily prepared by reacting indium(I) chloride with cyclopentadienyllithium:[2]
- InCl + CpLi → CpIn + LiCl
InCp reacts with BF3, BCl3, BBr3, BI3 and trimethylborane B(CH3)3 to form adducts,[3] e. g.:
- CpIn + BF3 → CpIn.BF3
In these adducts the bonding of the Cp ligand to the indium atom changes from η5 (π complexing) to η1 (σ bonding).
Salts containing the InX2− anion containing indium in the +1 oxidation state have been prepared, for example:[4]
Structure and bonding
Solid CpIn is polymeric consisting of zigzag chains of alternating indium atoms and C5H5 units. Two indium atoms interact with the opposite faces of each C5H5− ring, nearly perpendicularly to the ring plane, and two rings interact with each indium atom, forming an angle of about 128°.[5] In the CpIn monomer present in the vapour phase the indium atom sits on the central axis of the aromatic cyclopentadienyl anion, C5H5−.
Bonding studies have shown that the aromatic ring electrons of the cyclopentadienyl anion interact with the indium 5s and 5p atomic orbitals, and that the lone pair on the indium atom is a dominant feature.[6]
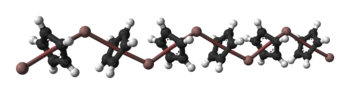
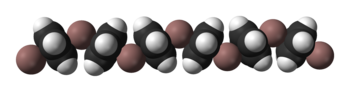
Ball-and-stick and space-filling models of CpIn chains
in the crystal structure of cyclopentadienylindium(I)References
- ^ Fischer E.O., Hofmann H.P. (1957). "Metall-cyclopentadienyle des Indiums". Angew. Chemie 69 (20): 639. doi:10.1002/ange.19570692008.
- ^ Peppe C., Tuck D.G., Victoriano L. (1981). "A simple synthesis of cyclopentadienylindium(I)". J. Chem. Soc.Dalton Trans. 69 (12): 2592. doi:10.1039/DT9810002592.
- ^ Contreras J. G., Tuck D. G. (1973). "Coordination compounds of indium. XXIII. Adducts of cyclopentadienylindium(I) with boron trihalides or trimethylboron". Inorganic Chemistry 12 (11): 2596–2599. doi:10.1021/ic50129a021.
- ^ Habeeb J.J., Tuck D.G. (1976). "Co-ordination compounds of indium. Part XXXI. Further studies of anionic complexes of indium(I)". J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans. (10): 866–869. doi:10.1039/DT9760000866.
- ^ Beachley O. T., Pazik J. C., Glassman T. E., Churchill M. R., Fettinger J.C., Blom R. (1988). "Synthesis, characterization and structural studies of In(C5H4Me) by x-ray diffraction and electron diffraction techniques and a reinvestigation of the crystalline state of In(C5H5) by x-ray diffraction studies". Organometallics 7 (5): 1051–1059. doi:10.1021/om00095a007.
- ^ Lin C.S., Tuck D.G. (1982). "The electronic structure of cyclopentadienylindium". Can. J. Chem. 60 (6): 699–702. doi:10.1139/cjc-60-6-699.
Categories:- Indium compounds
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
