- Drainage research
-
Drainage research is the study of agricultural drainage systems and their effects to arrive at optimal system design.
Contents
Aspects to be covered
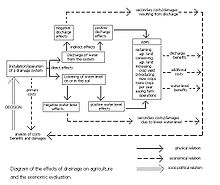
Agricultural land drainage has agricultural, environmental, hydrological, engineering, economical, social and socio-political aspects (Figure 1).
All these aspects can be subject of drainage research.
The aim (objective, target) of agricultural land drainage is the optimized agricultural production related to:- reclamation of agricultural land
- conservation of agricultural land
- optimization of crop yield
- crop diversification
- cropping intensification
- optimization of farm operations.
Systems analysis
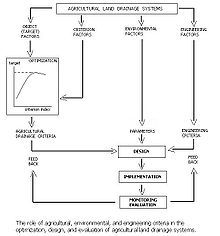
The role of targets, criterion, environmental, and hydrological factors is illustrated in Figure 2.
In this figure criterion factors are factors influenced by drainage on the one hand and the agricultural performance on the other.
An example of a criterion factor is the depth of the water table:- A drainage system influences this depth; the relation between drainage system design and depth of water table is mainly physical and can be described by drainage equations, in which the drainage requirements are to be found from a water balance.[1]
- The depth of the water table as a criterion factor needs to be translated into a criterion index to be given a numerical value that represents the behavior of the water table on the one hand and that can be related to the target (e.g. crop production) on the other hand.
- The relation between criterion index and target can often be optimized, the maximum value providing the ultimate aim while the corresponding value of the criterion index can be used as an agricultural drainage criterion in the design procedure.
Crop response processes
The underlying processes in the optimization (as in the insert of Figure 2) are manifold. The processes can be grouped into mutually dependent soil physical, soil chemical/biological, and hydrological processes (Figure 3):
- The soil physical processes include soil aeration, soil structure, soil stability, and soil temperature
- The chemical processes include soil salinity, soil acidity and soil alkalinity.
- The hydrological processes include evaporation, runoff, and soil salinity.
Examples of processes can be found in.[2]
Field data
In drainage research the collection and analysis of field data is important.[3]
In dealing with field data one must expect considerable random variation owing to the large number of natural processes involved and the large variability of plant and soil properties and hydrological conditions.
An example of a relation between crop yield and depth of water table subject to random natural variation is shown in the attached graph. The graph was made with the SegReg program, see segmented regression.
When analysing field data with random variation a proper application of statistical principles like in regression and frequency analysis is necessary.
Soil salinity control
In irrigated lands, subsurface drainage may be required to leach the salts brought into the soil with the irrigation water to prevent soil salination.
Agro-hydro-salinity and leaching models like SaltMod [4] may be helpful to determine the drainage requirement.
See also
Agricultural water management Irrigation Surface irrigation · Tidal irrigation · Irrigation of alluvial fans · Irrigation statistics · Irrigation management · Irrigation environmental impactsSubsurface drainage Tile drainage · Drainage equation · Drainage system (agriculture) · Watertable control · Drainage research · Drainage by wellsSurface water/runoff Groundwater Groundwater flow · Groundwater energy balance · Groundwater model · Hydraulic conductivity · WatertableProblem soils Agro-hydro-salinity group Hydrology (agriculture) · Soil salinity control · Leaching model (soil) · SaltMod integrated model · SahysMod polygonal model: Saltmod coupled to a groundwater modelRelated topics Sand dam ·References
- ^ Drainage for Agriculture: Hydrology and Water Balances. Lecture notes, International Course on Land Drainage (ICLD), International Institute for Land Reclamation and Improvement (ILRI), Wageningen, The Netherlands. Download at : [1]
- ^ Agricultural Drainage Criteria. Chapter 17 in: H.P.Ritzema (ed., 1994), Drainage Principles and Applications, Publication 16, p.635-690. International Institute for Land Reclamation and Improvement (ILRI), Wageningen, The Netherlands. ISBN 90 70754 3 39. Download at : [2]
- ^ Drainage Research in Farmers' Fields: Analysis of Data. Part of project “Liquid Gold” of the International Institute for Land Reclamation and Improvement (ILRI), Wageningen, The Netherlands. Download at : [3]
- ^ SaltMod: A tool for interweaving of irrigation and drainage for salinity control. In: W.B.Snellen (ed., 1997), Towards integration of irrigation, and drainage management. Special report, p. 41-43, International Institute for Land Reclamation and Improvement (ILRI), Wageningen, The Netherlands. Download at : [4]
External links
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.