- Diffusion-limited aggregation
-
Diffusion-limited aggregation (DLA) is the process whereby particles undergoing a random walk due to Brownian motion cluster together to form aggregates of such particles. This theory, proposed by Witten and Sander in 1981,[1] is applicable to aggregation in any system where diffusion is the primary means of transport in the system. DLA can be observed in many systems such as electrodeposition, Hele-Shaw flow, mineral deposits, and dielectric breakdown.
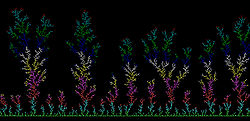
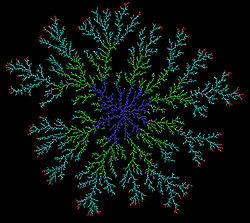
The clusters formed in DLA processes are referred to as Brownian trees. These clusters are an example of a fractal. In 2-D these fractals exhibit a dimension of approximately 1.71 for free particles that are unrestricted by a lattice, however computer simulation of DLA on a lattice will change the fractal dimension slightly for a DLA in the same embedding dimension. Some variations are also observed depending on the geometry of the growth, whether it be from a single point radially outward or from a plane or line for example. Two examples of aggregates generated using a microcomputer by allowing random walkers to adhere to an aggregate (originally (i) a straight line consisting 1300 particles and (ii) one particle at center) are shown on the right.
Computer simulation of DLA is one of the primary means of studying this model. Several methods are available to accomplish this. Simulations can be done on a lattice of any desired geometry of embedding dimension, in fact this has been done in up to 8 dimensions,[2] or the simulation can be done more along the lines of a standard molecular dynamics simulation where a particle is allowed to freely random walk until it gets within a certain critical range at which time it is pulled onto the cluster. Of critical importance is that the number of particles undergoing Brownian motion in the system is kept very low so that only the diffusive nature of the system is present.
Contents
Artwork based on diffusion-limited aggregation
 High-voltage dielectric breakdown within a block of plexiglas creates a fractal pattern called a Lichtenberg figure. The branching discharges ultimately become hairlike, but are thought to extend down to the molecular level.[3]
High-voltage dielectric breakdown within a block of plexiglas creates a fractal pattern called a Lichtenberg figure. The branching discharges ultimately become hairlike, but are thought to extend down to the molecular level.[3]
The intricate and organic forms that can be generated with diffusion-limited aggregation algorithms have been explored by artists. Andy Lomas' 'Aggregation' series features ray-traced images and animations of aggregates containing more than 50 million particles.[4] Lomas has presented the series at more than nine galleries and as a sketch at SIGGRAPH 2005, in which he describes his technique.[5]
 Sunflow rendered image of a point cloud created using toxiclibs/simutils with the DLA process applied to a spiral curve
Sunflow rendered image of a point cloud created using toxiclibs/simutils with the DLA process applied to a spiral curve
Simutils, part of the toxiclibs open source library for the Java programming language developed by Karsten Schmidt, allows users to apply the DLA process to pre-defined guidelines or curves in the simulation space and via various other parameters dynamically direct the growth of 3D forms.[6]
See also
External links
- Diffusion-Limited Aggregation: A Model for Pattern Formation
- A Java applet demonstration of DLA from Hong Kong University
- Another DLA java applet
References
- ^ T. A. Witten Jr, L. M. Sander, Phys. Rev. Lett. 47, 1400 (1981)
- ^ R. Ball, M. Nauenberg, T. A. Witten, Phys. Rev. A 29, 2017 (1984)
- ^ Bert Hickman
- ^ Robertson, B. Once a Mathematician, Always an Artist, CGSociety.org Artist Profile, accessed June 2007, [1]
- ^ Lomas, A. Aggregation: Complexity out of Simplicity, SIGGRAPH 2005 Sketch Session, accessed June 2007, [2]
- ^ Schmidt, K. simutils-0001: Diffusion-limited aggregation
Categories:- Stochastic processes
- Computer art
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.