- Culture of Latvia
-
The culture of Latvia combines traditional Latvian and Livonian heritage with influences of the country's varied historical heritage.
Contents
History
The territory of Latvia has been populated since 9000 BC. Baltic tribes, the ancestors of present day Latvians, arrived around 3000 BC. In the 13th century after conquest of today's Latvia, Baltic Germans settled here and gradually became the upper class and rulers of Latvia, while Latvians and Livonians lost their positions finally becoming serfs in 16th century. This caused the Germanisation of the educated inhabitants of other nationalities, yet preserved some local traditions. In the 19th century, when serfdom was abolished, a Latvian nationalist movement, the first "Latvian National Awakening", begun. Led by "Young Latvians", it encouraged Latvians to become artists and scholars, while preserving their cultural heritage and the language. The movement was countered by a period of Russification, followed by the leftist movement New Current at the beginning of the 20th century; it is regarded as a period in which Latvian culture thrived. This caused the second "Latvian National Awakening", leading ultimately to the proclamation of an independendent Latvia in 1918.
On 15 May 1934, Kārlis Ulmanis seized power in a coup d'etat and established an authoritarian regime, which lasted only until the outbreak of war and Soviet occupation in 1939-40. In cultural terms, however, this period is seen as a "golden age" for Latvia. During the war, with a period of German occupation from 1941-45, Latvia lost its independence as it was occupied by the USSR and became the Latvian SSR. Soviet rule ended in 1991 during the third "Latvian National Awakening".
People
The majority of inhabitants are Latvians. There is a culturally and linguistically distinct subgroup, the Latgalians, who inhabit the Latgale region in eastern Latvia. Another indigenous group are the Livonians, whose Finnic Livonian language is nearly extinct. The largest minority group is the Slavic people, notably Russians. Other well known minorities are Roma people, Baltic Germans and Jews, whose population decreased significantly after the Second World War, as well as Lithuanians and Estonians.
Regions
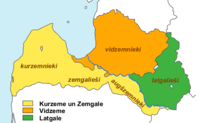
Latvia is divided into several cultural and historical regions - Vidzeme, Latgale, Courland and Zemgale. Sometimes, Sēlija and Maliena are also distinguished.
Folklore
Latvians have the rich heritage of traditional folklore, especially folk songs. Dating back well over a thousand years, more than 1.2 million texts and 30,000 melodies of folk songs have been identified.[1]
Music
Main article: Music of LatviaArchitecture
 Modern architecture in Riga
Modern architecture in Riga
A form of traditional architecture in Latvia is log houses. The position of houses differs between regions. In western Latvia, single farms are more popular and in villages, the houses are positioned in a circle around a central square. In eastern Latvia, villages are more popular and houses are positioned along a main street. This is seen as an influence of nearby Russia.
References
Culture of Europe Sovereign
states- Albania
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Georgia
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Kazakhstan
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macedonia
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Russia
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- United Kingdom
- (England
- Northern Ireland
- Scotland
- Wales)
- Vatican City
States with limited
recognition- Abkhazia
- Kosovo
- Nagorno-Karabakh
- Northern Cyprus
- South Ossetia
- Transnistria
Dependencies
and other territories- Åland
- Faroe Islands
- Gibraltar
- Guernsey
- Jan Mayen
- Jersey
- Isle of Man
- Svalbard
Other entities - European Union
Categories:- Latvian culture
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.