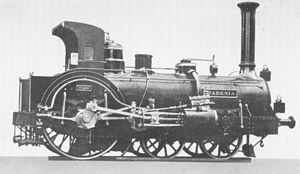
- Crampton locomotive
-
For other uses of the name "Crampton", see Crampton.
A Crampton locomotive is a type of steam locomotive designed by Thomas Russell Crampton and built by various firms from 1846. The main British builders were Tulk and Ley and Robert Stephenson and Company.
Notable features were a low boiler and large driving wheels. The crux of the Crampton patent was that the single driving axle was placed behind the firebox, so that the driving wheels could be very large. This helped to give this design a low centre of gravity, so that it did not require a very broad-gauge track to travel safely at high speeds. Its wheel arrangement was usually 4-2-0 or 6-2-0.
Contents
Design variations
Because the single driving axle was behind the firebox, Crampton locomotives usually had outside cylinders. However, some inside cylinder versions were built using indirect drive, then known as a jackshaft. The inside cylinders drove a crankshaft located in front of the firebox and the crankshaft was connected to the driving wheels by outside rods. Some long-wheelbase 0-4-0 tank locomotives were also built using this crankshaft system. The boiler feed-pump was often driven from the crankshaft as well because many Cramptons were built before the injector was invented.
Another peculiarity on some Crampton locomotives was the use of a boiler of oval cross-section, to lower the centre of gravity. It would nowadays be regarded as bad engineering practice because the internal pressure would tend to push the boiler into a circular cross-section and increase the risk of metal fatigue.
Usage
Crampton locomotives were used by some British railways and speeds of up to 120km/h (75mph) were achieved on the LNWR. They were more popular in France, southern Germany and the US. In France the expression "prendre la Crampton" meant to catch an express. One of the French examples has been preserved in the Cité du Train (the French Railway Museum) at Mulhouse and is still in working order. This is number 80 of the Chemin de Fer de l'Est, the Paris-Strasbourg line, which is named "Le Continent".
Locomotive list
Approximate numbers of Crampton-type locomotives built in Europe were:
- Great Britain 51
- France 127
- Germany 135
Below is a list of British-built Crampton locomotives:
Built by: Tulk and Ley, all of 4-2-0 wheel arrangement:
Date built Works no. Railway Name/no. Notes 1846 10 Namur and Liege Railway Namur (1) 1846 11 Namur and Liege Railway Liege (1) 1847 12 LNWR 200 London (2)(3) 1847 14 D&P&AJR Kinnaird (4) 1847 13 South Eastern Railway 81 1847 15 South Eastern Railway 83 1847 16 South Eastern Railway 85 1854 17 Maryport and Carlisle Railway 12 Notes
- Namur was tested over 2,300 miles (3,700 km) on the Grand Junction Railway and ultimately purchased by SER,[1] speeds up to 62 miles per hour (100 km/h) were recorded. Delivery of Liege to Belgium was delayed, and her ultimate fate is uncertain.
- The LNWR obtained two other Crampton-type locomotives: Courier, 4-2-0, built at Crewe Works in 1847 and Liverpool, 6-2-0, built by Bury, Curtis, and Kennedy.
- LNWR No.200 London, larger boiler and cylinders than Namur. Later rebuilt as an 0-4-2.[1]
- Dundee and Perth and Aberdeen Junction Railway, absorbed by the Scottish Central Railway in 1863
Built by: Robert Stephenson and Company
Robert Stephenson and Company built a number of Crampton type locomotives for the South Eastern Railway and the London, Chatham and Dover Railway. These were all of 4-2-0 wheel arrangement with inside cylinders and indirect drive. The inside cylinders drove a crankshaft located in front of the firebox and the crankshaft was coupled to the driving wheels by outside rods.Date built Works no. Railway No./Name Notes 1851 785 South Eastern Railway 134 1851 786 South Eastern Railway 135 1851 787 South Eastern Railway 136 Folkstone (1) 1851 788 South Eastern Railway 137 1851 789 South Eastern Railway 138 1851 790 South Eastern Railway 139 1851 791 South Eastern Railway 140 1851 792 South Eastern Railway 141 1851 793 South Eastern Railway 142 1851 794 South Eastern Railway 143 1851 Prussian Eastern Railways England[2] 1851 Prussian Eastern Railways 1851 Prussian Eastern Railways 1851 Prussian Eastern Railways 1851 Prussian Eastern Railways 1851 Prussian Eastern Railways 1862 1381 London, Chatham and Dover Railway Coquette (2) 1862 1382 Echo 1862 1383 Flirt 1862 1384 Flora 1862 1385 Sylph Notes:
- The name should have read Folkestone but was mis-spelled on the plate. This locomotive was displayed at The Great Exhibition of 1851. [1] Bogie wheels 3 feet 6 inches (1.07 m) diameter, driving wheels 6 feet (1.83 m) diameter. Cylinders 15"x 22" (380mmx560mm). Weight 26¼ Tons.[3]
- Bury, Curtis, and Kennedy, all 4-2-0 except Liverpool which was 6-2-0.
Date built Works no. Railway No./Name Notes 1848 355 LNWR Liverpool (1) 1848 ? South Eastern Railway 68 1848 ? South Eastern Railway 69 1848 ? South Eastern Railway 72 1848 ? South Eastern Railway 74 1848 ? South Eastern Railway 75 1848 ? South Eastern Railway 78 - Liverpool, 6-2-0, built by Bury, Curtis, and Kennedy works number 355/1848. Driving wheels 8 feet (2.44 m) diameter, grate area 21.5 square feet (2.00 m2), heating arear 2,290 square feet (213 m2), boiler pressure 120 lb/in2, cylinders 18"x24" (460mm x 610mm). The locomotive was awarded a Gold Medal at the Great Exhibition of 1851.[1][5]
Built by: E. B. Wilson and CompanyDate built Works no. Railway Name/no. Notes 1847 ? North British Railway 55 (1) 1847 ? Eastern Counties Railway 108 1847 ? Eastern Counties Railway 109 1847 ? Eastern Counties Railway 110 1847 ? Eastern Counties Railway 111 1847 ? Eastern Counties Railway 112 1847 ? Aberdeen Railway 26 1847 ? Aberdeen Railway 27 - Hauled the Royal Train in 1850, withdrawn from service in 1907.[2]
Built by: R and W Hawthorn 4-4-0STDate built Works no. Railway Name/no. Notes 1857 - East Kent Railway 62 Lake (1) 1857 - East Kent Railway 59 Sondes (1) 1858 - East Kent Railway 63 Faversham (1) 1858 - East Kent Railway 64 Chatham (1) 1858 - East Kent Railway 61 Crampton (1) 1858 - East Kent Railway 63 Faversham (1) - Rebuilt as Kirtley F class 2-4-0T 1865[6]
Built by: various builders
Builder Date built Works no. Railway Name/no. Notes Nasmyth, Gaskell and Company 1846 ? South Eastern Railway 92 (1) Crewe Works 1847 ? LNWR Courier Kitson and Company 1848 ? Midland Railway 130 Kitson and Company 1848 ? Midland Railway 131 Timothy Hackworth 1848 ? LB&SCR 56 Timothy Hackworth 1848 ? LB&SCR 58 A. Horlock & Co. 1848 Padarn Railway Fire Queen (2) A. Horlock & Co. 1848 Padarn Railway Jenny Lind 1848 Chemin de fer du Nord R. B. Longridge and Company 1851 ? Great Northern Railway 200 (3) 1855 Chemins de fer de Paris à Lyon et à la Méditerranée (4) 1855 Chemin de fer du Nord 162 Alma (5) Maschinenbaugesellschaft Karlsruhe 1863 Baden State Railway Phoenix (6) Notes:
- Originally built as a 2-2-2, rebuilt as a Crampton 2+2-2-0 December 1848.[7]
- 0-4-0 locomotives, 4 ft (1,219 mm) gauge, Fire Queen preserved at Penrhyn Castle Railway Museum. Jenny Lind named after the opera singer, a friend of Crampton's wife Louisa.
- Sources differ on how many Crampton locomotives Longridge built for the Great Northern Railway. Number 200 was later converted from a 4-2-0 to a conventional 2-2-2. There were nine similar 2-2-2 locomotives numbered 91-99 and it is uncertain whether these were built as 2-2-2 or whether they were converted from 4-2-0 like number 200.
- 40 locomotives built for the PLM between 1855 and 1864.[8]
- A 6-2-0 locomotive, converted to the Petiet system in the 1860s, withdrawn and scrapped in 1873.[9]
- In service until 1903, length 12.90 metres (42 ft 4 in), top speed 120 kilometres per hour (75 mph), weight 28½ tonnes. Preserved in the Deutsches Bundesbahn Museum, Nuremberg.[10]
See also
- Long Boiler locomotive
- 6-2-0 for Crampton locomotives in the USA
References
- ^ a b c "London & North Western Railway locomotives: Introduction & pre-Ramsbottom". Steam Index. http://www.steamindex.com/locotype/lnwr.htm#j154. Retrieved 2008-03-22.
- ^ a b "LOCOMOTIVES". Crampton Tower Museum. http://www.cramptontower.co.uk/about.htm. Retrieved 2008-03-22.
- ^ "The South Eastern and Chatham Railway and the London , Chatham and Dover Railway Amalgamated 1899 LOCOMOTIVES: Their Description, History, distinctive features and interest". The Percy Whitlock Trust. http://www.percywhitlock.org.uk/trains.htm. Retrieved 2008-03-22.
- ^ Bradley 1960, pp. 15–16.
- ^ "Thomas Russell Crampton". Steam Index. http://www.steamindex.com/people/crampton.htm. Retrieved 2008-03-22.
- ^ Bradley, D. L. (1960). The Locomotives of the London, Chatham and Dover Railway. Railway Correspondence and Travel Society. pp. 19-22.
- ^ D.L. Bradley, The Locomotives of the South Eastern Railway, Railway Correspondence and Travel Society, 1963, pp.4-3.
- ^ "The Crampton steam locomotive". tgveurofrance.com. http://pagesperso-orange.fr/tgveurofrance.com/traincapitale/cramptonen.htm. Retrieved 2008-03-22.
- ^ "Petiet's French Experiments". The Douglas Self Site. http://www.aqpl43.dsl.pipex.com/MUSEUM/LOCOLOCO/petiet/frexp.htm. Retrieved 2008-03-22.
- ^ "In the days when locomotives still had poetic names - the Phoenix". Deutsche Bahn Group. https://www.db.de/site/bahn/en/db__group/db__museum/exhibitions/vehicles/phoenix.html. Retrieved 2008-03-22.
Sources
- Bradley, D. L. (1960). The Locomotives of the London, Chatham and Dover Railway. Railway Correspondence and Travel Society.
- Sharman, M. (1983). The Crampton Locomotive. Oakwood Press. ISBN 0 9509067 0 0.
External links
Categories:- Steam locomotive types
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.