- DMS-100
-
 A DMS-100, in a CO located in France
A DMS-100, in a CO located in France
The DMS-100 Switch is a line of Digital Multiplex System (DMS) telephone exchange switches manufactured by Nortel Networks.
The purpose of the DMS-100 Switch is to provide local service and connections to the PSTN public telephone network. It is designed to deliver services over subscribers' telephone lines and trunks. It provides Plain Old Telephone Service (POTS), mobility management for cellular phone systems, sophisticated business services such as Automatic Call Distribution (ACD), Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN), and Meridian Digital Centrex (MDC), formerly called Integrated Business Network (IBN). It also provides Intelligent Network functions (AIN, CS1-R, ETSI INAP). It is used in countries throughout the world.
Contents
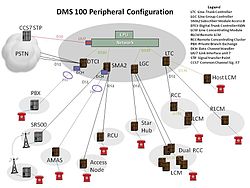
Hardware
All power distribution is at -48 VDC (nominal), from which DC to DC converters on every shelf provide other necessary voltages.
Analog lines are terminated on individual line cards, each with its own codec, in pull-out Line Drawers in frames. The original design of such frames was called the Line Module (LM) with 32 lines per drawer. LMs were not able to send caller-id information (CLASS services) and became rare late in the century, having been supplemented or replaced by the newer Line Concentrating Module (LCM). Duplicated ringing generators serve each LM or pair of LCM. For DC testing, each line card has a relay to connect it to a test bus.
LCM have smaller line cards, serving 64 lines per drawer of the same size as in the LM. The majority of line cards are 6x17, with three relays for loop start lines. Others include 6x18 which have four or more relays and a slide switch for ground start lines (a newer version of the 6x18 has eliminated the ground switch), and 6x19 line card which provides a higher voltage to operate neon message waiting lamps. Type 6x21 cards serve P-sets (Meridian Business Sets), a special analog telephone with a proprietary Nortel data link operating at 8 kHz to provide advanced call handling services. For example, a telephone number may appear on multiple P-sets even though each such telephone has only one pair of wires, thus providing a simpler replacement for key telephone systems. BX27 cards serve Basic Rate ISDN lines. LCMs are served by an Line Group Controller (LGC). The number of LCMs per LGC depends on traffic: 3-4 LCM per LGC but as few as two where traffic is heavy.
Remote offices, anywhere from a kilometer to 100 km from the host, can be served by Remote Switching Centre (RSC); a later vintage is known as RCC2. They use T1 links to the host LGC. Rcc's/Rcc2's work like LGC's in controlling LCMs. Large remotes may have 2+ Rcc/Rcc2's and they can be equipped with links between the Rcc's - Interlinks; so calls within the remote do not tie up host links. The Rcc's/ Rcc2 are usually equipped so they will provide calling within the remote office if the host links fail; this feature is called ESA; Emergency Stand Alone.
Another type of remote office is known as Remote Carrier Urban (RCU). Such units typically reside on the side of a road in a large box, approx 3 meters across, almost 2 meters high and almost a meter through. In the 1980s many telcos installed an early version of these instead of pulling more cable into a remote area. They were much cheaper and could provide up to approx 500 lines. Back then they needed two 'boxes' to work- a host box called a Central Terminal (CT) that had the dial tone lines wired into it and a remote box called a Remote terminal (RT) where the dial tone 'came out'. They used 2-6 T1 links on copper - i.e. LD-1 or fiber. As Telcos modernized, these same remote boxes were re-configured to work directly from a SMU peripheral at the host DMS. Typically each SMU can handle 3-6 RCUs.
Transmitters, receivers and other service circuits are in Trunk Module (TM) and Miscellaneous Trunk Module (MTM) shelves. Trunks are on DTC (Digital Trunk Controller) or DTCI (Digial Trunk Controller ISDN) or PDTC (PCM30 Digital Trunk Controller) shelves, usually two T-1 lines per card, ten cards per DTC for a total of 480 ds0 voice channels. At the turn of the century many original NT6X50AA cards were still in service that cannot perform T-carrier extended superframe signaling, this can be performed with a plug-in replacement NT6X50AB card, used for services such as PBX ISDN T1s. Trunks can also be provisioned on SPM (Spectrum Peripheral Module) capable of handling 2016 DS0s, nearly 4.2x more than the DTC.
Internal connections to the time switch are on 2.56 Mbit/s (DS-30) Speech Links, each carrying thirty channels plus synchronization and data channels, on four wires plus a ground wire. European PDTCs were complemented by the DTCOI2 and DTCO2. The DTCOI2 was designed to run PRI and DPNSS services as per existing PDTCOI and MSB7 peripherals. The DTCO2 was designed to carry CAS and SS7 as per existing PDTCO peripheral.
Time Division switching is performed in E-Net, similar to the Communication Module of 5ESS switch or the Switching Network of EWSD or the Group Switch of AXE telephone exchange.
There are also DMS-200 and DMS-250 variants for tandem switches. The successor to the DMS-100 is the Communication Server 2000 (CS2K), which shares many components and software with the DMS. The significant difference is the addition of VOIP technology into the CS2K.[1]
Hardware and maintenance are administered locally through cathode-ray terminals, through a multilevel menu system called MAPCI. There are various methods used to access the DMS remotely as well, including modem and telnet. Backups and other hard drive work are administered through a DISKUT command line program.
See also
References
External links
LAN - MAN - WAN Multiservice Switch * Virtual Service Platform 9000 (VSP9000) * MERS-8600 System * ERS-8600 System * ERS-5600 System * ERS-5500 SystemsOptical Optical Multiservice Edge 6500 (OME6500)Voice Systems Security Management Tools Unified Communications Management * Visualization Performance & Fault Manager * Enterprise Switch Manager * Device Manager * VLAN Manager * Multicast Manager * Security Manager * File & Inventory Manager * Routing Manager * Multi-link Trunking Manager * Proactive Voice Quality ManagementProtocols FAST Stacking * Nortel Discovery Protocol * MLT * DMLT * SMLT * DSMLT * RSMLT * IST * Simple Loop Prevention Protocol * PBT * PBB * UNIStim * VLACPNortel Certifications NANP Telephone Switches Early Automatic & Crossbar Switches
Strowger Switch • Panel Switch • Western Electric 1XB • Western Electric 5XBElectronic Switching Systems
Western Electric 1ESS/1AESS • Western Electric 4ESS • Western Electric 5ESS • Northern Electric SP1 • Northern Telecom DMS-100 • Stromberg-Carlson/Siemens DCO • Siemens EWSD • Automatic Electric GTD-5 EAXCategories:- Multiplexing
- Telephone exchanges
- Nortel products
- Nortel
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.