- Multi-link trunking
-
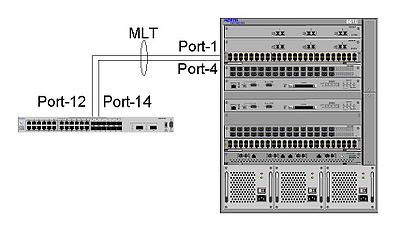
Nortel Multi-Link Trunking MLT between ERS 5530 switch and an ERS 8600 switch Multi-Link Trunking (MLT) is a link aggregation or IEEE 802.3ad port trunking technology designed by Nortel (now Avaya). It allows grouping several physical Ethernet links into one logical Ethernet link to provide fault-tolerance and high-speed links between routers, switches, and servers. In the past redundant links were unused due to Spanning Tree’s loop protection.
Using this technology allows or enables the use of several links (from 2 up to 8) and combined them to create increased bandwidth and several fail-over paths. This produces server to switch or switch to switch connections that are up to 8 times faster.
Fault-tolerant design is an important aspect of Multi-Link Trunking technology. Should any one or more than one link fail, the MLT technology will automatically redistribute traffic across the remaining links. This automatic redistribution is accomplished in less than half a second (typically less than 100 millisecond[1]) so no outage is noticed by end users. This high speed recovery is required by many critical networks where outages can cause loss of life or very large monetary losses in critical networks. Combining MLT technology with DMLT, SMLT, DSMLT and RSMLT technologies create networks that support the most critical applications.
A general limitation of standard MLT is that all the physical ports in the link aggregation group must reside on the same switch. SMLT, DSMLT and RSMLT technologies removes this limitation by allowing the physical ports to be split between two switches.
Contents
See also
- Avaya
- Avaya Government Solutions
- Link aggregation
- R-SMLT
- Distributed Split Multi-Link Trunking
- Split multi-link trunking
- Avaya Multi-link Trunking Manager
- Nortel
References
Further reading
- Knapp, James R. (2001). Nortel networks: The Complete Reference (Second Edition ed.). McGraw-Hill. pp. 92–93, 116–117, 228–233. ISBN 007219281X.
- Nortel Ethernet Routing Switch Solutions (First ed.). Research Triangle Park, NC: Nortel Press. October 2008. pp. 92, 116–119, 220–225, 423–424, 399, 480–490, 479, 481. ISBN 978-09-9815218-1-7.
- Edwards, James; Jensen, Matthews S. (2001). Nortel Networks: A Beginner's Guide. McGraw-Hill. pp. 113, 353–354, 364. ISBN 0-07-213089-x.
- Roebuck, Kevin (May 30, 2011). Ethernet MAN Services. Tebbo. ISBN 978-1743044261.
- Duffy, Jim (May 18, 1998). In light of buy, Bay builds. 15. Network World. p. 64. http://books.google.com/books?id=aB4EAAAAMBAJ&pg=PA64&dq=%22Multi-Link+Trunking%22&hl=en&ei=LSxjTqqlNZKSgQeOhonDCg&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=4&ved=0CDYQ6AEwAw#v=onepage&q=%22Multi-Link%20Trunking%22&f=false. Retrieved 3 Sept 2011.
External links
- Tolly Benchmarks -Retrieved 29 July 2011
- See IEEE.org for info on 802.3ad standard -Retrieved 29 July 2011
Avaya Data
telecommunications
systemsRouters
SwitchesVSP-9000 • ERS-8800 Systems • Metro ERS-8600 System • ERS-8600 Systems
VSP-7000 • ERS-5600 Systems • ERS-5500 Systems • ERS-2500 SystemsSecure
RoutersSecurityUnified Communications Aura
ServersSystems
ApplicationsAgile Communication Environment • Communications ManagerIP Phones 1100 Series IP Deskphones (1140E, 1120E, 1120SA) • Avaya 9600 Series IP DeskphonesManagement Tools Protocols Auto Detection Auto Configuration • FAST Stacking • Nortel Discovery Protocol • Simple Loop Prevention Protocol
MLT • DMLT • SMLT • DSMLT • RSMLT • IST • PBT • IP-VPN Lite • VLACP • UNIStimRetired Products Categories:- Avaya
- Communication circuits
- Ethernet
- Link protocols
- Network topology
- Nortel protocols
- Bonding protocols
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.