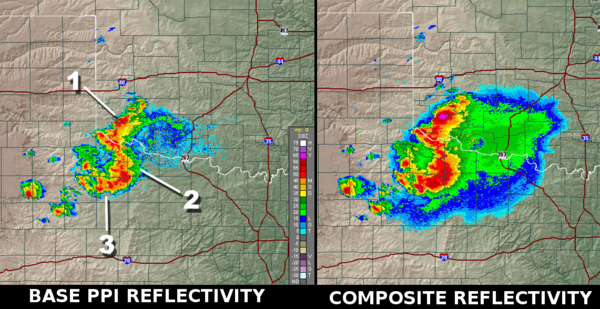
- Composite reflectivity
-
The composite reflectivity is the maximum dBZ reflectivity from any of the reflectivity angles of the NEXRAD weather radar[1]. The reflectivity on individual PPI angles show the precipitation intensity at that specific angle above the horizon. Some of these angles are .5,1.45,2.4, and 3.35 degrees with the Doppler radar having up to 14 angles when it's in Severe Mode. In the Composite, the highest intensities amongst those available in the different angles above each point of the image will be displayed . In the Canadian weather radar network, this is called MAXR, for Maximum reflectivity in the column.
Use
When compared to the base angle reflectivity, the lowest angle of elevation sounding, the composite reflectivity, including higher elevation scan information, may appear to indicate more widespread rain. This could indicate one of two things :
- Virga : the precipitation (rain or snow) is probably not reaching the ground but evaporating as it falls from very high in the atmosphere. This is a regular situation in winter as snowflakes can easily sublimate in dry air near the ground.
- Strong updrafts : air rising in a thunderstorm updraft will saturate at higher level than the rest of the cloud forming an overhang region. In case of a very strong updraft, a Bounded weak echo region (BWER) will form and lead to the possibility of severe weather.
External links
- Oklahoma Climatological Survey Training Materials - Composite Reflectivity
- http://weather.noaa.gov/radar/radinfo/radinfo.html
References
- ^ National Weather Service (August 29, 2007). "Composite Reflectivity". JetStream - Online School for Weather. NOAA. http://www.srh.noaa.gov/jetstream/doppler/comprefl.htm. Retrieved 2008-10-03.
Categories:- Atmospheric science stubs
- Radar meteorology
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.