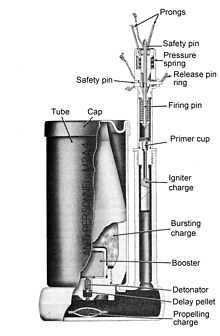
- M2 mine
-
The M2 is a US bounding anti-personnel mine used during the Second World War. A number of variants of the mine were produced and although the mine is no longer in US service, it can be found in Cyprus, Iran, Iraq, Korea, Laos, Oman, Rwanda, Tunisia and the Western Sahara. Copies of the mine were produced by Belgium (as the PRB M966), Pakistan (P7), Portugal (M/966) and Taiwan.
The mine consists of a cylindrical steel main body containing a 60 millimeter mortar shell body (originally the M49A2), linked to a tall thin fuze stand. The fuze stand held either a pin based tripwire fuze or a combination pressure tripwire fuze with a pronged pressure cap. Later fuzes were sensitive to pressure or pull and could be used with a tripwire. When the mine is triggered a black powder charge launches the mortar shell out of the main body of the mine and into the air. A pyrotechnic delay fuse triggers the mine when it has risen to between two and three meters in height. The lethal radius of the mine is reported to be approximately ten meters.
Contents
Development
The US began development of the anti-personnel mines in the summer of 1940 spurred on by events in the Second World War. A French officer, Major Pierre Delalande (sometimes Paul Delalande) who had escaped the fall of France came to the US with the plans of the Modele 1939 bounding mine.[1] The M2 series of mines were based on this design, and were first fielded in April 1942.[2]
Status
The mine has not been in US service for some time, having been replaced by the M16 mine soon after the Second World War. The M2 was not considered a successful design, and was replaced with more successful German-based designs.[3]
With the advent of the Ottawa Treaty, large stockpiles of this mine have been eliminated. As of 2006[update] Cyprus,[4]Greece,[5]Turkey,[6] and possibly Taiwan[7] hold stockpiles of this mine. Cyprus, Greece and Turkey are expected to have destroyed their stockpiles of the mine by March 2008.
Variants
The variants of the mine differ in detail of the fuze and base section of the mine. The early mines had a large thin flat circular base while later mines had a smaller thicker base. Later version of the mine were also better waterproofed.
- M2A1
- M2A1B
- M2A1B1 - A variant of the mine using the same shell - however the fuze holder and body of the mine are merged into a single piece of cast iron intended to simplify mass production. The mine was 3.78 inches wide at the widest point and 8.63 inches high, weighing a total of 7.16 pounds.[8]
- M2A2
- M2A3 - This variant was in service during the second world war. The principal difference between this mine and later variants appears to have been the use of an increased propellent charge in this variant.[9]
- M2A3B2
- M2A4
- M2A4B2
Specifications
- Height: 244 mm
- Width: 104 mm
- Weight: 2.95 kg
- Explosive content: 154 g of TNT
- Operating pressure: 9 kg or 1.5 to 3 kg pull
References
- M2 mine at ORDATA
- Jane's Mines and Mine Clearance 2005-2006
- Brassey's Essential Guide to Anti-personnel Landmines
- US Army FM 20-43
Notes
- ^ The mine was patented in the United States under the name "Paul Delalande" US Patent 2,374,179 at GooglePatents
- ^ AxisHistory forum, contributor WSchneck
- ^ Lieutenant-Colonel John Ingraham & Col. Dalton Jones. Technical Intelligence Bulletins 8(5), 2003. (available online)
- ^ Is in the process of eliminating its mine stockpile, and currently has an uncertain number of M2A1 and M2A3 mines in its stockpile. It has also kept approximately 100 each of the M2A1 and M2A3 types for research and training 2006 ICBL report
- ^ A reported stockpile of 214,374 mines ICBL report 2006
- ^ Stockpile of 146,882 mines 2006 ICBL report
- ^ The government refuses to release details of their stockpiles and they have produced the M2 under license 2006 ICBL report 2004 ICBL report
- ^ Standard Ordnance Items Catalog 1944 volume 3, page 596
- ^ This diagram shows a cross section of the mines - note that the M2A3 has a double charge indicated. Diagram at ORDATA mines
Categories:- Anti-personnel mines
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.