- PEG 400
-
Polyethylene glycol 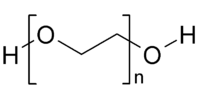 Polyethylene glycol
Polyethylene glycolIdentifiers CAS number 25322-68-3 
Properties Molecular formula C2nH4n+2On+1, n = 8.2 to 9.1 Molar mass 380-420 g/mol Density 1.128 g/cm³ Melting point 4-8 °C
Viscosity 90.0 cSt at 25 °C, 7.3 cSt at 99 °C Hazards Flash point 238 °C LD50 30 mL/kg, orally in rats  400 (verify) (what is:
400 (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references PEG 400 (polyethylene glycol 400) is a low molecular weight grade of polyethylene glycol. It is a clear, colorless, viscous liquid. Due in part to its low toxicity, PEG 400 is widely used in a variety of pharmaceutical formulations. More recently, it has been used to make "E-Liquid" for Electronic Cigarettes (Personal Vaporizers).
Chemical properties
PEG 400 is strongly hydrophilic. The partition coefficient of PEG 400 between hexane and water is 0.000015 (logP = − 4.8), indicating that when PEG 400 is mixed with water and hexane, there are only 1.5 parts of PEG 400 in the hexane layer per 100,000 parts of PEG 400 in the water layer.[1]
PEG 400 is soluble in water, acetone, alcohols, benzene, glycerin, glycols, aromatic hydrocarbons and is slightly soluble in aliphatic hydrocarbons.
References
- ^ T. Y. Ma, D. Hollander, P. Krugliak, K. Katz (1990). "PEG 400, a hydrophilic molecular probe for measuring intestinal permeability". Gastroenterology 98 (1): 39–46. PMID 2293598. http://www.gastrojournal.org/article/PII001650859091288H/abstract.
- The Merck Index, 11th Edition
- Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients
Categories:- Polyethers
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
