- Dzongkhag
-
Bhutan 
This article is part of the series:
Politics and government of
Bhutan- Constitution
- King (List)
- Dratshang Lhentshog
- Parliament
- Royal Court of Justice
- Supreme Court
- High Court
- Dzongkhag Courts
- Dungkhag Courts
- Council of Ministers
- Dzongkhags (List)
- Political parties
- Elections
- Foreign relations
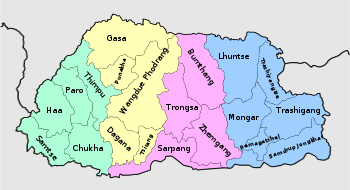
A dzongkhag (Dzongkha: རྫོང་ཁག་; Wylie: rjong-khag) is an administrative and judicial district of Bhutan. The twenty dzongkhags of Bhutan are further divided into 205 gewogs. Some larger dzongkhags have one or more of an intermediate judicial division, known as dungkhags (sub-districts), which themselves comprise two or more gewogs. The Parliament of Bhutan passed legislation in 2002 and 2007 on the status, structure, and leadership of local governments, including dzongkhags. Its most recent legislation regarding dzongkhags is the Local Government Act of 2009.[2][3][4]
Contents
Dzongkhag administration
Under the Local Government Act of 2009, the Dzongkhag Tshogdu (District Council) is the non-legislative executive body of the Dzongkhag. The Dzongkhag Thromde is composed of the Gup and Mangmi (elected leaders) from each gewog, one representative from that Dzongkhag Thromde, and one representative from the Dxongkhag Yenlag Thromdes.[4][nb 1] Dzongkhag Tshogdus are tasked with balancing socio-economic development; promoting business; protecting consumers; coordinating government agency activities; reviewing Gewog regulations and ordinances; and representing the Dzongkhags in national referenda. The Dzongkhag Tshogdus are empowered to enforce rules on health and public safety; to regulate environmental pollution, advertising in regard to environmental aesthetics; to regulate broadcast media in accordance with the Information, Communications, and Media Act; and to regulate gambling. Dzongkhag Tshogdus also bear the responsibility for their own finances.[4][nb 2] The Dzongkhag Tshogdus also oversee Dzongdags (governors), royal appointees who are the executive of each Dzongkhag. Dzongdags, in turn, are responsible for maintaining law and order, and for enforcing the driglam namzha laws.[4][nb 3]
History
Until 1956, Bhutan had nine provinces headed by the penlops: Byakar (centered in present day Bumthang), Dukye, Haa, Paro, Punakha, Dagana, Thimphu, Trongsa, and Wangdue Phodrang. Later, the country was reorganized into dzongkhags. Under the initiative of fourth Druk Gyalpo King Jigme Singye Wangchuk, the process of decentralisation of local administration started in 1981. the formation of the incipient Dzongkhag Yargye Tshogchung (district development committee, "DYT") in each dzongkhag. The DYT of each dzongkhag consisted of all the Gups (headmen), Mangmis (deputies), and Chimis (National Assembly representatives) of the dzongkhag. The Chairperson is elected from the DYT members by themselves. The DYT may also include the representatives of the municipalities and the towns within the dzonkhag. The DYTs also have non-voting members, which include the dzongdag, the dungpa (where a dungkhag exists) and the dzongkhag officials from various sectors such as the dzongkhag planning officer, the dzongkhag finance officer, the dzongkhag education officer, the dzongkhag chief engineer, the dzongkhag agriculture officer, the dzongkhag forestry officer, the dzongkhag animal husbandry officer, and the dzongkhag health officer.[3][2]
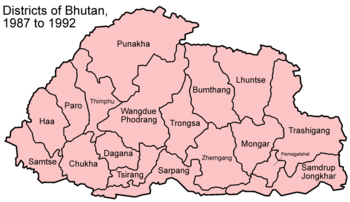
In August 1987, the territory of Gasa dzongkhag was divided between Punakha and Thimphu; Chhukha dzongkhag was formed by merging the parts of Samtse, Paro, and Thimphu.[5][6] In 1992, Gasa dzongkhag was re-established and carved out from Punakha; the same year, Trashi Yangtse dzongkhag was carved out from Trashigang.[5][6]
Under the Dzongkhag Yargay Tshogdu Chathrim of 2002, dzongkhags were already headed by Dzongdags assisted by a Dzongrabs (deputy district collectors) in carrying out the administrative activities the dzongdag. The dzongkhag administration coordinated all developmental activities within the district. Under the DYT, Dzongkhag Yargye Tshogchungs consisted of people's representatives and government officials in the dzongkhags that assisted the dzongdags in the discharge their developmental activities. A dzongdag was also assisted by the Gups elected from constituent gewogs.[2]
The Constitution of 2008 laid basic provisions for an elected Dzongkhag Tshogdu (district council) in each dzongkhag. It further codified the appointment process of dzongdags and the role of Dzongkhag Courts within the judicial system of Bhutan.[7]
See also
- Dungkhag
- Gewog
- Thromde
- Chiwog
- Districts of Bhutan
- Dzongkhag Court
- Local Government Act of Bhutan 2009
- List of terms for country subdivisions
Notes
References
- ^ "Delimitation". Election Commission, Government of Bhutan. 2011. http://www.election-bhutan.org.bt/index.php?option=com_content&id=132&Itemid=84. Retrieved 2011-07-31.
- ^ a b c "Dzongkhag Yargay Tshogdu Chathrim 2002" (PDF). Government of Bhutan. 2002-07-23. http://www.nationalcouncil.bt/images/stories/DYT_En_02.pdf. Retrieved 2011-01-20.
- ^ a b "Local Government Act of Bhutan 2007" (PDF). Government of Bhutan. 2007-07-31. http://www.nab.gov.bt/downloadsact/Eng30.pdf. Retrieved 2011-01-20.
- ^ a b c d "Local Government Act of Bhutan 2009" (PDF). Government of Bhutan. 2009-09-11. http://www.nab.gov.bt/downloadsact/Dzo74.pdf. Retrieved 2011-01-20.
- ^ a b Law, Gwillim (2010-12-18). "Districts of Bhutan". Administrative Divisions of Countries ("Statoids"). http://www.statoids.com/ubt.html. Retrieved 2010-12-31.
- ^ a b Lahmeyer, Jan (2002). "BHUTAN – Historical Demographical Data of the Administrative Division". Population Statistics. http://www.populstat.info/Asia/bhutanp.htm. Retrieved 2010-12-31.
- ^ "Constitution of the Kingdom of Bhutan (English)" (PDF). Government of Bhutan. 2008-07-18. http://www.constitution.bt/TsaThrim%20Eng%20(A5).pdf. Retrieved 2010-11-13.
 Bhutan topics
Bhutan topicsHistory Geography PoliticalCities · Chiwogs · Dzongkhags (Districts) Dungkhags (Subdistricts) · Gewogs (village blocks) · VillagesNaturalClimate · Extreme points · Lakes · Glaciers · Mountains · Rivers · Protected areas · Valleys · WildlifePolitics King · Prime Minister · Political parties · Elections · Constitution · Foreign relations · Military · Law enforcement · Crime · Human rights (LGBT rights)Economy Demographics Culture Categories:- Types of country subdivisions
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.