- Tisza
:"Tisa" redirects here. For other uses, see
Tisa (disambiguation) andTisza (disambiguation) ."Geobox River
name =Tisza River
native_name =
other_name = _ro. Tisa
_ry. Тиса
_uk. Тиса
_sk. Tisa
_sr. Тиса/Tisa
other_name1 =

image_size = 300
image_caption = The Tisza inSzeged ,Hungary
country_type = Countries
state_type =
region_type =
district_type = Counties
city_type = Villages
country =Ukraine ,Romania ,Hungary ,Slovakia ,Serbia
country1 =
state =
state1 =
region =
region1 =
district =
district1 =
city =
city1 =
length = 1358
watershed = 157183
discharge_location =
discharge =
discharge_max =
discharge_min =
discharge1_location =
discharge1 =
source_name =
source_location =Eastern Carpathians
source_district =
source_region =
source_state =
source_country =Ukraine
source_lat_d =
source_lat_m =
source_lat_s =
source_lat_NS =
source_long_d =
source_long_m =
source_long_s =
source_long_EW =
source_elevation = 2020
source_length =
mouth_name =Danube
mouth_location = Downstream ofNovi Sad
mouth_district =
mouth_region =
mouth_state =
mouth_country =Serbia
mouth_lat_d =
mouth_lat_m =
mouth_lat_s =
mouth_lat_NS =
mouth_long_d =
mouth_long_m =
mouth_long_s =
mouth_long_EW =
mouth_elevation =
tributary_left =
tributary_left1 =
tributary_right =
tributary_right1 =
free =
free_type = Official River Code
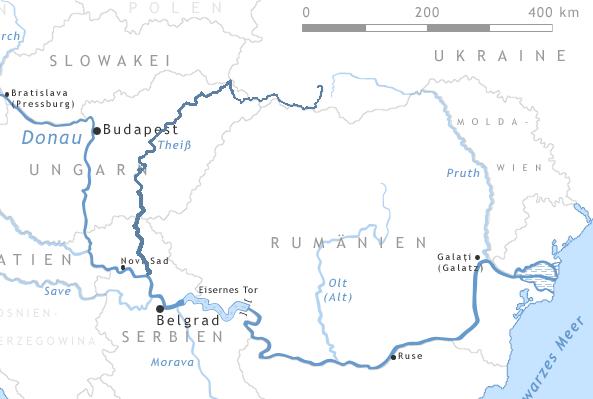
map_size = 300
map_caption =Map of the Tisza and southern part of theDanube The Tisza is one of the majorriver s ofCentral Europe . It originates inUkraine , with the White Tisza in theChornohora and Black Tisza in theGorgany range, flows partially along theRomania n border, entersHungary atTiszabecs , passes throughHungary , and falls into theDanube in centralVojvodina inSerbia . It forms the boundary between the regions ofBačka andBanat . The Tisza drains an area of about 157,186 km².Attila the Hun is said to have been buried under a diverted section of the river Tisza.Names for the river in the countries it flows through are:
* _ro. Tisa;
* _uk. Тиса ("Tysa");
* _sk. Tisa;
* _hu. Tisza (pronounced|'tisɒ);
* _sr. Тиса ("Tisa").The river was known as the "Tisia" in antiquity, and
Latin names for it included "Tissus", "Tisia", "Pathissus" (Pliny, "Naturalis historia", 4.25). InCroatian language , it is called "Tisa" (Tisa flows through areas with Croat minority in autonomic province Vojvodina in northern Serbia). It may be referred to as the "Theiss" ( _de. Theiß) in older English references, after the German name for that river.Regulation of the Tisza
The length of the Tisza in Hungary used to be 1419 km. It flowed through the
Great Hungarian Plain , which is one of the largest flat areas in central Europe. Sinceplains can cause a river to flow very slowly, the Tisza used to follow a path with many curves and turns, which led to many largefloods in the area.After several small-scale attempts,
István Széchenyi organised the "control of the Tisza" ( _hu. a Tisza szabályozása) which started onAugust 27 ,1846 and substantially ended in 1880. The new length of the river in Hungary was 966 km, with 589 km of "dead channels" and 136 km of new riverbed.The resultant length of the flood-protected river comprises 2,940 km (out of 4,220 km of all Hungarian protected rivers) which forms one of the largest flood protection systems in Europe; larger than the
Netherlands ' 1,500 km, thePo River 's 1,400 km, or theLoire Valley 's 480 km."Lake Tisza"
In the 1970s the building of the Kisköre Reservoir started with the purpose of helping to control floods as well as storing water for drought seasons. It turned out, however, that the resulting
Lake Tisza became one of the most popular tourist destinations in Hungary, since it had similar features toLake Balaton at drastically cheaper prices and it was not crowded.Navigation
The Tisza is navigable over much of its course. The river opened up for international navigation only recently; before, Hungary distinguished "national rivers" and "international rivers", indicating whether non-Hungarian vessels were allowed or not. After Hungary joined the
European Union , this distinction was lifted and vessels were allowed on the Tisza.Conditions of navigation differ with the circumstances: when the river is in flood, it is often unnavigable, just as it is at times of extreme drought. (Source: [http://www.noordersoft.com/indexen.html NoorderSoft Waterway Database)]
Tributaries and sub-tributaries
*
Čik (nearBačko Petrovo Selo )
*Jegrička (nearŽabalj )
*Begej (nearTitel )
*Maros (inSzeged )
**Arieş (near Gura Arieşului)
**Târnava (nearTeiuş )
***Târnava Mare (inBlaj )
***Târnava Mică (in Blaj)
*Körös (nearCsongrád )
**Sebes-Körös (nearGyoma )
***Berettyó (inSzeghalom )
**Fehér-Körös (near Gyula)
**Fekete-Körös (near Gyula)
*Zagyva (inSzolnok )
*Sajó (inTiszaújváros )
**Hernád (nearMiskolc )
*Bodrog (inTokaj )
**Ondava (nearCejkov )
**Latorca (near Cejkov)
***Laborec (nearOborin )
****Úzs (nearPavlovce nad Uhom )
****Cirocha (inHumenné )
***Stara
***Vicha
***Kerepets
*Kraszna (inVásárosnamény )
*Szamos (near Vásárosnamény)
**Someşul Mic (inDej )
***Someşul Cald (in Gilău)
***Someşul Rece (in Gilău)
**Someşul Mare (in Dej)
***Şieu (inBeclean )
****Bistriţa (nearBistriţa )
*Túr
*Batár
*Şugătag
*Baia
*Şaroş
*Săpânţa
*Valea Hotarului
*Bicu
*Sarasău
*Valea Iepei
*Iza
**Mara
*VisóReferences
* Administraţia Naţională Apelor Române - Cadastrul Apelor - Bucureşti
* Institutul de Meteorologie şi Hidrologie - Rîurile României - Bucureşti 1971External links
* [http://www.backabanat.com About Tisza]
* [http://www.historia.hu/archivum/2001/0102suli.htm The Living Tisza (Hungarian)]
* River Basin Report: Tisza River [http://www.ywat.org/knowledgebase/riverbasins/eu-tisza.html]
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
