- Electrical lengthening
.
Electrical lengthening is the modification of an aerial which is shorter than a whole-number multiple of a quarter of the radiated
wavelength , by means of a suitable electronic device, without changing the physical length of the aerial, in such a way that it corresponds electrically to the next whole-number multiple of a quarter of the used wavelength. A lengthening is only possible to the next whole-number multiple of a quarter of the radiated wavelength.Thus an aerial with a length corresponding to the eighth of the radiated wavelength can be extended only to a quarter-wave radiator, but not to ahalf wave radiator .Description
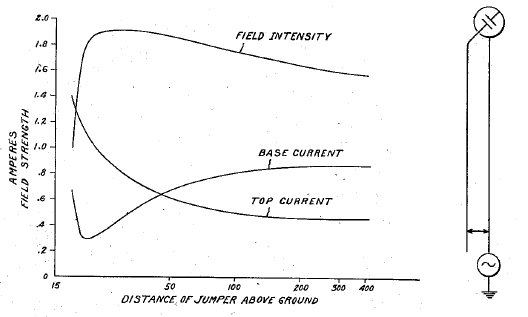
right|thumb|On the left, characteristics plotted from experimentally obtained data on coordinates with logarithmic abscissa. On the right, an antenna with increased effective inductance between the two points in accordance with the well known operation of shunt tuned circuits adjusted somewhat off resonance.Advantages
The electrical lengthening allows the construction of shorter aerials. It is applied in particular for aerials for
VLF ,longwave andmedium-wave transmitter s, because mast radiators of the necessary height cannot be realised economically.Disadvantages
The electrical lengthening reduces the bandwidth of the antenna if other phase control measures are not undertaken. An electrically extended aerial is less efficient than a non-extended antenna.
Technical realization
There are two possibilities for the realisation of the electric lengthening.
# switching in inductive coils in series with the aerial
# switching in metal surfaces, known as roof capacitance, at the aerial ends which formcapacitor s to earth.Often both measures are combined. The coils switched in series must be sometimes be placed in the middle of the aerial construction. The cabin installed at a height of 150-metres on theBlosenbergturm inBeromünster is such a construction, in which a lengthening coil is installed for the supply of the upper tower part (the Blosenbergturm has in addition a ring-shaped roof capacitor on its top)Application
Transmission aerials of transmitters working at frequencies below the longwave broadcasting band always apply electric lengthening. Broadcasting aerials of longwave broadcasting stations apply it often. However, for transmission aerials of NDBs electrical lengthening is extensively applied, because these use antennas which are considerably less tall then a quarter of the radiated wavelength.
ee also
*
Electrical shortening
*Loading coil
*Antenna tuner Further reading and references
*A. Nickle, US patent|2125804, "Antenna". (Filed
May 25 ,1934 ; Issued Aug 2, 1938)
*William W. Brown, US patent|2059186, "Antenna structure". (FiledMay 25 ,1934 ; Issued Oct 27, 1936).
* Robert B. Dome, US patent|2101674, "Antenna". (FiledMay 25 ,1934 ; Issued Dec 7, 1937)
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.