- Macrovipera mauritanica
-
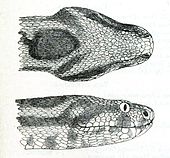
Macrovipera mauritanica 
Conservation status Scientific classification Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Subphylum: Vertebrata Class: Reptilia Order: Squamata Suborder: Serpentes Family: Viperidae Subfamily: Viperinae Genus: Macrovipera Species: M. mauritanica Binomial name Macrovipera mauritanica
(Duméril & Bibron, 1848)Synonyms - Echidna mauritanica - Duméril & Bibron, 1848
- Clotho ? mauritanica - Gray, 1849
- Vipera minuta - Eichwald, 1851
- Bitis mauritanica - Günther, 1858
- Vipera confluenta - Cope, 1863
- Vipera mauritanica - Strauch, 1869
- Vipera euphratica var. mauritanica - Boettger, 1883
- Vipera lebetina - Boulenger, 1896
- Vipera lebetina mauritanica - Schwartz, 1936
- Daboia (Daboia) lebetina mauritanica - Obst, 1983
- Macrovipera mauritanica - Herrmann, Joger & Nilson, 1992[1]
Macrovipera mauritanica is a venomous viper species found in northwestern Africa. No subspecies are currently recognized.[5]
Contents
Description
Reaches a maximum length of 180 cm.[2][6]
Common names
Moorish viper,[2] Sahara rock viper,[3] Atlas blunt-nosed viper,[4] Atlas adder,[7] mountain adder.[3]
Geographic range
Northwestern Africa: Morocco, Algeria and Tunisia. The type locality is "Algiers", according to Gray (1842), "Algeria" according to Schwarz (1936).[1] Limited to the coastal regions of Algeria. Coastal records from Tunisia may refer to M. deserti.[6]
Conservation status
This species is classified as Near Threatened (NT) according to the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species (v3.1, 2001).[8] Classified as such because this species is likely in significant decline (but at a rate of less than 30% over ten years) due to persecution, accidental mortality and over-harvested, therefore making it close to qualifying for Vulnerable. The population trend is down. Year assessed: 2005.[9]
See also
- List of viperine species and subspecies
- Viperinae by common name
- Viperinae by taxonomic synonyms
- Snakebite
References
- ^ a b McDiarmid RW, Campbell JA, Touré T. 1999. Snake Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference, vol. 1. Herpetologists' League. 511 pp. ISBN 1-893777-00-6 (series). ISBN 1-893777-01-4 (volume).
- ^ a b c Mallow D, Ludwig D, Nilson G. 2003. True Vipers: Natural History and Toxinology of Old World Vipers. Krieger Publishing Company, Malabar, Florida. 359 pp. ISBN 0-89464-877-2.
- ^ a b c U.S. Navy. 1991. Poisonous Snakes of the World. US Govt. New York: Dover Publications Inc. 203 pp. ISBN 0-486-26629-X.
- ^ a b Mehrtens JM. 1987. Living Snakes of the World in Color. New York: Sterling Publishers. 480 pp. ISBN 0-8069-6460-X.
- ^ "Macrovipera mauritanica". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. http://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=634978. Retrieved 9 August 2006.
- ^ a b Spawls S, Branch B. 1995. The Dangerous Snakes of Africa. Ralph Curtis Books. Dubai: Oriental Press. 192 pp. ISBN 0-88359-029-8.
- ^ Brown JH. 1973. Toxicology and Pharmacology of Venoms from Poisonous Snakes. Springfield, Illinois: Charles C. Thomas. 184 pp. LCCCN 73-229. ISBN 0-398-02808-7.
- ^ Daboia mauritanica at the IUCN Red List. Accessed 2 September 2007.
- ^ 2001 Categories & Criteria (version 3.1) at the IUCN Red List. Accessed 2 September 2007.
External links
- Macrovipera mauritanica at the Reptarium.cz Reptile Database. Accessed 9 August 2007.
- Video of Macrovipera mauritanica on YouTube. Accessed 9 September 2007.
Categories:- IUCN Red List near threatened species
- Viperinae
- Reptiles of Morocco
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.