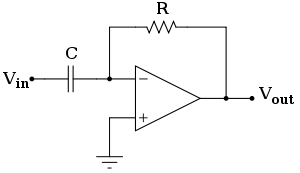
- Differentiator
-
A Differentiator is a circuit that is designed such that the output of the circuit is proportional to the time derivative of the input. There are two types of differentiator circuits, active and passive.
Contents
Theory
A differentiator circuit consists of an operational amplifier, resistors are used at feedback side and capacitors are used at the input side. The circuit is based on the capacitors current to voltage relationship:
where I is the current through the capacitor, C is the capacitance of the capacitor, and V is the voltage across the capacitor. The current flowing through the capacitor is then proportional to the derivative of the voltage across the capacitor. This current can then be connected to a resistor, which has the current to voltage relationship:
where R is the resistance of the resistor. If Vout is the voltage across the resistor and Vin is the voltage across the capacitor, we can rearrange these two equations to obtain the following equation:
From the above equation following conclusions can be made:
- Output is proportional to the time derivative of the input. Hence opamp acts as a differentiator.
- The minus sign indicates the phase difference of 180 degrees between the output and the input.
- Above equation is true for any frequency signal.
- If we select R and C in such a manner that R×C=1 then the above equation becomes
Here output is nothing but the time derivative of the input. Such differentiator is called as a perfect differentiator.
Thus, it can be shown that in an ideal situation the voltage across the resistor will be proportional to the derivative of the voltage across the capacitor with a gain of RC.
Operation
Input signal applied to the capacitor C. Capacitive reactance is the important in analysis of operation of differentiator.Capacitive reactance is Xc=1/2πfc.Capacitive reactance is directly proportional to the rate of change of input voltage applied to the capacitor. At low frequency reactance of capacitor is high and at high frequency reactance is low. Therefore, at low frequency gain(Rf/Xc) is low while at higher frequency gain is high with high output voltage.But at high frequencies differentiator circuit becomes unstable and start to oscillate.This high frequency gain of circuit is reduced by adding small value capacitor across feedback resistor Rf. If there is constant DC voltage applied as input then output voltage is 0 .If input voltage is changing from 0 to negative going voltage output voltage is positive DC.If input voltage applied is changing from 0 to positive going voltage then output is negative DC.[1]
Uses
The differentiator circuit is primarily used as a high pass filter.
See also
Reference
Categories:- Analog circuits
- Electronics stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.