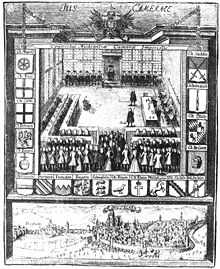
- Reichskammergericht
-
 Imperial Chamber Court building in Wetzlar, Germany
Imperial Chamber Court building in Wetzlar, Germany
The Reichskammergericht or Imperial Chamber Court was one of two highest judicial institutions in the Holy Roman Empire, the other one being the Aulic Council (German: Reichshofrat) in Vienna. It was founded in 1495 by the Imperial Diet in Worms. All legal proceedings in the Holy Roman Empire could be brought to the Imperial Chamber Court, except if the ruler of the territory had a so-called privilegium de non appellando, in which case the highest judicial institution was found by the ruler of that territory. Another exception was criminal law. The Imperial Chamber Court could only intervene in criminal cases if basic procedural rules had been violated.
The Imperial Chamber Court was infamous for the long time it took to reach a verdict. Some proceedings, especially in lawsuits between different states of the Empire, took several hundred years. Some of the lawsuits were not brought to an end by the time it was dissolved in 1806 following the downfall of the Holy Roman Empire. Yet, lately it has been discovered that this could often be attributed to a loss of interest on the part of the parties involved, and that the court could sometimes be much more efficient than previously thought. Sometimes the court even ordered injunctions within a few days.
Recent research also brought to light that, especially in the 18th century, the rulings of the court anticipated in many ways the constitutional establishment of civil liberties in Germany. For instance, the inviolability of one's housing or freedom of trade were legally introduced in the Empire by rulings of the court. At the end of the 18th century some contemporaries even compared the Imperial Chamber Court to the National Assembly in Revolutionary France.
Contents
History
At its foundation the court was seated in Frankfurt, but was later moved to Worms, Augsburg, Nürnberg, Regensburg, Speyer, Esslingen, again Speyer (1527 to 1689) and finally to Wetzlar until it was dissolved in 1806.
From the early Middle Ages there had been a Supreme Court of Justice for the Empire, the Hofgericht, in which the Emperor himself presided. This court was connected directly to the Emperor, so it ceased to act when he was abroad and disbanded when he died. In the 15th century, the Emperor ceased to command as much respect, so his court lost the confidence of his subjects. Its place was taken by the Kammergericht.
The Emperor or a deputy still presided in the court and it was still his personal court; but the members were now officials of the Empire. It was generally the legal members of the council who sat in the Kammergericht. The Kammergericht fell into disuse in the later years of the reign of Frederick III and the creation of a new and efficient court became a matter of pressing necessity, and was one of the most urgent of the reforms which were mooted in the reign of Maximilian I.
The "province of the Imperial Chamber", as it came to be gradually defined by statute and use, extended to breaches of the public peace, cases of arbitrary distrait or imprisonment, pleas which concerned the treasury, violations of the Emperor's decrees or the laws passed by the Imperial Diet, disputes about property between immediate tenants of the Empire or the subjects of different rulers, and finally suits against immediate tenants of the Empire, with the exception of criminal charges and matters relating to imperial fiefs, which went to the Aulic Council.
In all its business it suffered from the competition of the Aulic Council; and after the 16th century devoted itself exclusively to judicial work.
Composed of the personal advisers of the Emperor, the Aulic Council did justice on his behalf. The competition between the Aulic Council and the Imperial Chamber was finally regulated by the Treaty of Westphalia in 1648, which laid it down that the court which first dealt with a case should alone have competence to pursue it.
Membership
Membership of the court was determined by both the Holy Roman Emperor and the component states of the Empire. The Emperor named the chief justice, always a high aristocrat, several presidents of the court senates and some of the members of the court. The majority of the judges were selected by the Estates of the realm. Originally, half of the judges were Knights of the Empire, and the other half doctors of Roman law, but after 1548 all judges had to be doctors of law.
References
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.External links
Categories:- Legal history of the Holy Roman Empire
- 1495 establishments
- 1806 disestablishments
- Buildings and structures in Wetzlar
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.