- Champernowne constant
-
In mathematics, the Champernowne constant C10 is a transcendental real constant whose decimal expansion has important properties. It is named after mathematician D. G. Champernowne, who published it as an undergraduate in 1933.
In base 10, the number is defined by concatenating successive integers:
- C10 = 0.12345678910111213141516...
 can be expressed exactly as an infinite series:
can be expressed exactly as an infinite series:
Champernowne constants can also be constructed in other bases, similarly, for example:
- C2 = 0.11011100101110111... 2
- C3 = 0.12101112202122... 3.
Contents
Normality
A real number x is said to be normal if its digits in every base follow a uniform distribution: all digits being equally likely, all pairs of digits equally likely, all triplets of digits equally likely, etc. x is said to be normal in base b if its digits in base b follow a uniform distribution.
If we denote a digit string as [a0,a1,...], then, in base ten, we would expect strings [0],[1],[2],...,[9] to occur 1/10 of the time, strings [0,0],[0,1],...,[9,8],[9,9] to occur 1/100 of the time, and so on, in a normal number.
Champernowne proved that C10 is normal in base ten, although it is possible that it is not normal in other bases.[1]
Continued fraction expansion
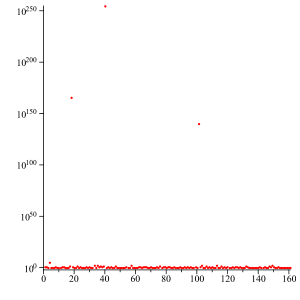 The first 161 quotients of the continued fraction of the Champernowne constant represented using the logarithmic scale.
The first 161 quotients of the continued fraction of the Champernowne constant represented using the logarithmic scale.
The simple continued fraction expansion of Champernowne's constant has been studied as well. Kurt Mahler showed that the constant is transcendental;[2] therefore its continued fraction does not terminate (because it is not rational) and is aperiodic (because it is not an irreducible quadratic).
The terms in the continued fraction expansion exhibit very erratic behaviour, with huge terms appearing between many small ones. For example, in base 10,
- C10 = [0; 8, 9, 1, 149083, 1, 1, 1, 4, 1, 1, 1, 3, 4, 1, 1, 1, 15,
-
- 4 57540 11139 10310 76483 64662 82429 56118 59960 39397 10457 55500 06620 04393 09026 26592 56314 93795 32077 47128 65631 38641 20937 55035 52094 60718 30899 84575 80146 98631 48833 59214 17830 10987,
- 6, 1, 1, 21, 1, 9, 1, 1, 2, 3, 1, 7, 2, 1, 83, 1, 156, 4, 58, 8, 54, ...].
-
The large number at position 19 has 166 digits. We get other extremely large numbers as part of the continued fraction if we continue. The next term of the continued fraction is huge, having 2504 digits. This can pose problems in computing the terms of the continued fraction, and may stress weak algorithms for computing the continued fraction. However, the fact that there are such large numbers as terms of the continued fraction expansion implies that the convergents obtained by stopping before these large number provide an exceptionally good approximation of the Champernowne constant. For example, truncating before the 4th partial quotient, we obtain the partial sum 10/81, which approximates Champernowne constant with an error of about 1 × 10-9, while truncating just before the 18th partial quotient, we get
that approximates Champernowne constant with an error of about 9 × 10-190.
Computation
Champernowne's constant for a given base b can be written as an infinite sum[3] by:
This sum may be used as a tool to analyze the constant.
The naïve method of adding the digits one by one may also be slower to perform on a computer than other more sophisticated algorithms.[4]
See also
- Copeland–Erdős constant, a similar normal number, defined using the prime numbers
- Liouville's constant, another constant defined by its decimal representation
References
- ^ D. G. Champernowne, The construction of decimals normal in the scale of ten, Journal of the London Mathematical Society, vol. 8 (1933), p. 254-260
- ^ K. Mahler, Arithmetische Eigenschaften einer Klasse von Dezimalbrüchen, Proc. Konin. Neder. Akad. Wet. Ser. A. 40 (1937), p. 421-428.
- ^ Parkin, S. T. "An Identity for Champernowne's Constant." From MathWorld"Champernowne's constant", References section.
- ^ Rytin, M. Champernowne Constant and Its Continued Fraction Expansion, (1999), http://library.wolfram.com/infocenter/MathSource/2876/
External links
- Weisstein, Eric W., "Champernowne constant" from MathWorld.
- Sequence
 A033307 in the On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences.
A033307 in the On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences.
Categories:- Mathematical constants
- Number theory
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.



![C_b = \sum_{n=1}^\infty\frac{\sum_{k=b^{n-1}}^{b^n-1}kb^{-n\left[k-(b^{n-1}-1)\right]}}{b^{\sum_{k=0}^{n-1}k(b-1)b^{k-1}}}.](6/83678e70048a15e479ae62bc4b0cb323.png)