- Meridiani Planum
-
Meridiani Planum 
Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity looks southwest across Meridiani Planum; the Rover's discarded backshell and parachute are visible in the distance.Coordinates 0°12′N 357°30′E / 0.2°N 357.5°ECoordinates: 0°12′N 357°30′E / 0.2°N 357.5°E 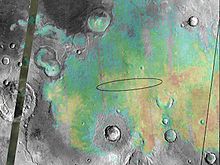 Hematite deposits in Meridiani Planum mapped from orbit, with Opportunity rover landing footprint ellipse.
Hematite deposits in Meridiani Planum mapped from orbit, with Opportunity rover landing footprint ellipse.
 Rock exposure near Beagle Crater.
Rock exposure near Beagle Crater.
Meridiani Planum is a plain located 2 degrees south of Mars' equator (centered at 0°12′N 357°30′E / 0.2°N 357.5°E), in the westernmost portion of Terra Meridiani. It hosts a rare occurrence of gray crystalline hematite. On Earth, hematite is often formed in hot springs or in standing pools of water; therefore, many scientists believe that the hematite at Meridiani Planum may be indicative of ancient hot springs or that the environment contained liquid water. The hematite is part of a layered sedimentary rock formation about 200 to 800 meters thick. Other features of Meridiani Planum include volcanic basalt and impact craters.
Contents
Mars rover Opportunity
In 2004, Meridiani Planum was the landing site for the second of NASA's two Mars Exploration Rovers, named Opportunity. It had also been the target landing site for Mars Surveyor 2001 Lander, which was cancelled after the failures of the Mars Climate Orbiter and Mars Polar Lander missions.
Results from Opportunity indicate that its landing site was once saturated for a long period of time with liquid water, possibly of high salinity and acidity. Features that suggest this include cross-bedded sediments, the presence of many small spherical pebbles that appear to be concretions, vugs inside rocks, and the presence of large amounts of magnesium sulfate and other sulfate-rich minerals such as jarosite.
Craters within Meridiani Planum
- Airy Crater – 40 kilometre (km) in diameter and about 375 km west-southwest of Opportunity
- Airy-0 – Lies within the Airy crater, and defines the Martian Prime Meridian
- Argo Crater – Visited by Opportunity
- Beagle Crater – Visited by Opportunity
- Beer Crater
- Eagle Crater – Landing site of Opportunity and 30 metre diameter
- Emma Dean Crater – Visited by Opportunity
- Endurance Crater – Visited by Opportunity
- Erebus Crater – Visited by Opportunity
- Mädler Crater
- Santa Maria Crater - Visited by Opportunity
- Victoria Crater – Visited by Opportunity and 750 metre diameter
- Vostok Crater – Visited by Opportunity
See also
External links
Categories:- Oxia Palus quadrangle
- Albedo features on Mars
- Plains on Mars
- Airy Crater – 40 kilometre (km) in diameter and about 375 km west-southwest of Opportunity
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

