- 1 gigametre
-
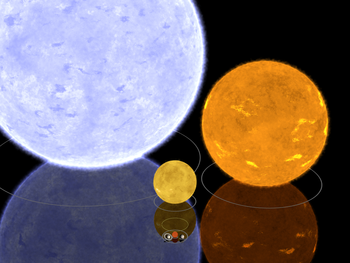 Upper part: Gamma Orionis, Algol B, the Sun (centre), underneath their darker mirror images (artist's interpretation), and other objects, to scale.
Upper part: Gamma Orionis, Algol B, the Sun (centre), underneath their darker mirror images (artist's interpretation), and other objects, to scale.
To help compare different distances this page lists lengths starting at 109 metres (1 gigametre (Gm) or 1 million kilometres).
Distances shorter than 109 metres
- 1.4 Gm — Diameter of Sun[1]
- 1.5 Gm — (proposed) Expected orbit from Earth of the James Webb Space Telescope
- 2.19 Gm — Closest approach of Comet Lexell to Earth, happened on 1 July 1770; closest comet approach on record
- 3 Gm — Total length of "wiring" in the human brain.[2]
- 4.2 Gm — Diameter of Algol B
- 5.0 Gm — Closest approach of Comet Halley to Earth, happened on 10 April 837
- 5.0 Gm — (proposed) Size of the arms of the giant triangle shaped Michelson interferometer of the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA) planned to start observations in or around 2015.
- 7.9 Gm — Diameter of Gamma Orionis
- 9.0 Gm — Estimated diameter of the event horizon of Sagittarius A*, the supermassive black hole in the center of the Milky Way galaxy
Distances longer than 1010 metres
See also
 Click on the thumbnail image to jump to the desired order of length magnitude: top-left is 1e6m, lower-right is 1e17m. (Image description)
Click on the thumbnail image to jump to the desired order of length magnitude: top-left is 1e6m, lower-right is 1e17m. (Image description)Orders of magnitude for length in E notation shorter than one metre: <−24 −24 −23 −22 −21 −20 −19 −18 −17 −16 −15 −14 −13 −12 −11 −10 −9 −8 −7 −6 −5 −4 −3 −2 −1 0 longer than 1 metre: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 References
- ^ Sun Fact Sheet
- ^ Neuroscience: The Science of the Brain [1] p.44
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
